pandas---文件读取与存储(csv、hdf、json、excel、sql)
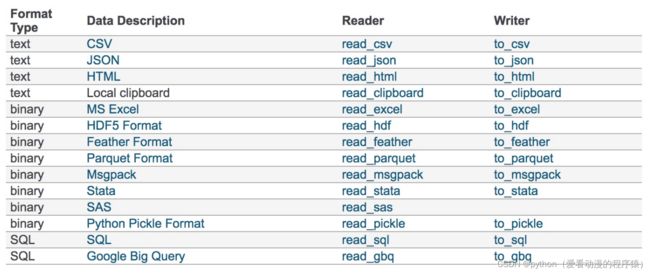
数据大部分存在于文件当中,所以pandas会支持复杂的IO操作,pandas的API支持众多的文件格
式,如CSV、SQL、EXCEL、JSON、 HDF5。
 1. csv文件
1. csv文件
pandas.read_csv(filepath_or_buffer, sep =',', usecols )
filepath_or_buffer:文件路径 sep :分隔符,默认用","隔开 usecols:指定读取的列名,列表形式
# 读取文件,并且指定只获取'open', 'close'指标
data = pd.read_csv("./data/stock_day.csv", usecols=['open', 'close'])
open close
02-27 23.53 24.16
02-26 22.80 23.53
02-11 22.88 22.82
02-22 22.25 22.28
02-14 21.49 21.92DataFrame.to_csv(path_or_buf=None, sep=', ’, columns=None, header=True, index=True,
mode='w', encoding=None)
path_or_buf:文件路径 sep:分隔符,默认用","隔开 columns:选择需要的列索引
header:boolean or list of string,default True,是否写进列索引值
index:是否写进行索引 mode:'w' 重写,'a' 追加
# 选取10行数据保存,便于观察数据
data[:10].to_csv("./data/test.csv", columns=['open'])
# 读取,查看结果
pd.read_csv("./data/test.csv")
Unnamed: 0 open
0 02-27 23.53
1 02-26 22.80
2 02-23 22.88
3 02-22 22.25
4 02-14 21.49
5 02-13 21.40
6 02-12 20.70
7 02-09 21.20
8 02-08 21.79
9 02-07 22.69
会发现将索引存入到文件当中,变成单独的一列数据。如果需要删除,可以指定index参数,删除
原来的文件,重新保存一次。
# index:存储不会讲索引值变成一列数据
data[:10].to_csv("./data/test.csv", columns=['open'], index=False)2. hdf文件
HDF5文件的读取和存储需要指定一个键,值为要存储的DataFrame。
pandas.read_hdf(path_or_buf,key =None,** kwargs)
从h5文件当中读取数据
path_or_buffer:文件路径 key:读取的键 return:Theselected object
DataFrame.to_hdf(path_or_buf, key, *\kwargs*)
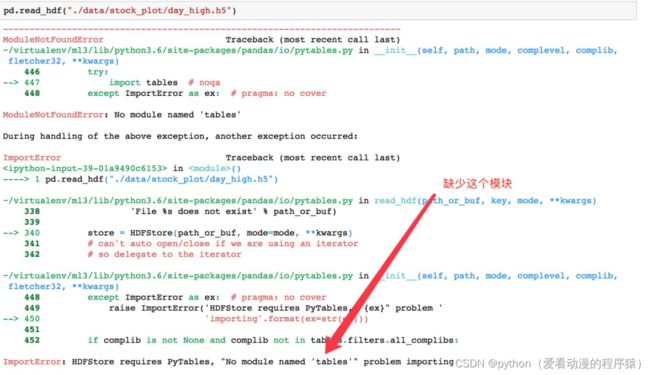
day_close = pd.read_hdf("./data/day_close.h5")如果读取的时候出现以下错误:
需要安装tables模块避免不能读取HDF5文件:
pip install tables存储文件:
day_close.to_hdf("./data/test.h5", key="day_close")再次读取的时候, 需要指定键的名字:
new_close = pd.read_hdf("./data/test.h5", key="day_close")注意:优先选择使用HDF5文件存储。
HDF5在存储的时候支持压缩,使用的方式是blosc,这个是速度最快的也是pandas默认支持的;
使用压缩可以提磁盘利用率,节省空间;
HDF5还是跨平台的,可以轻松迁移到hadoop 上面。
3. json文件
JSON是我们常用的一种数据交换格式,前面在前后端的交互经常用到,也会在存储的时候选择这
种格式。所以我们需要知道Pandas如何进行读取和存储JSON格式。
pandas.read_json(path_or_buf=None, orient=None, typ='frame', lines=False)
将JSON格式准换成默认的Pandas DataFrame格式。
orient : string,Indication of expected JSON string format。
'split':dict like {index -> [index], columns -> [columns], data -> [values]}
split 将索引总结到索引,列名到列名,数据到数据。将三部分都分开了。
'records':list like [{column -> value}, ... , {column -> value}]
records 以 columns:values 的形式输出
'index':dict like {index -> {column -> value}}
index 以 index:{columns:values}... 的形式输出
'columns':dict like {column -> {index -> value}},默认该格式
colums 以 columns:{index:values} 的形式输出
'values' : just the values array values,直接输出值。
lines:boolean,default False,按照每行读取json对象。
typ:default ‘frame’, 指定转换成的对象类型series或者dataframe。
读取:
json_read = pd.read_json("./data/Sarcasm_Headlines_Dataset.json", orient="records", lines=True)DataFrame.to_json(path_or_buf=None, orient=None, lines=False)
将Pandas对象存储为json格式,path_or_buf=None:文件地址
orient:存储的json形式,{‘split’,’records’,’index’,’columns’,’values’}
lines:一个对象存储为一行
# 存储文件
json_read.to_json("./data/test.json", orient='records')
# 修改lines参数为True
json_read.to_json("./data/test.json", orient='records', lines=True)
4. Excel文件
data = np.random.randint(0, 50, size=(10, 5))
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data, columns=['Python', 'Qianfeng', 'Java', 'NumPy', 'Pandas'])
dfdf1.to_excel:保存到excel文件
# sheet_name: 工作表名称
# header: 是否保存列索引
# index: 是否保存行索引
df.to_excel('data.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1', header=True, index=False)df1.read_excel:读取excel
pd.read_excel('data.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1', header=[0, 1])
# sheet_name=0: 读取第1个工作表
# names : 替换原来的列名
pd.read_excel('data.xlsx', sheet_name=0, header=0, names=list('ABCDE'))5. sql文件
需要安装pymysql:
pip install pymysql -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
需要安装sqlalchemy:
sqlalchemy是Python语言下的数据库引擎库
pip install sqlalchemy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simplefrom sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 创建数据
data = np.random.randint(0, 150, size=(150, 3))
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data, columns=['Python', 'Pandas', 'PyTorch'])
df.head()先连接MySQL:
# mysql+pymysql :数据库类型+驱动
# root:root :数据库用户名和密码
# localhost:3306 :数据库地址和MySQL端口
# db: 数据库名
conn = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost:3306/db')
df.to_sql保存到MySQL:
df.to_sql(
name='score', # 数据库中表名字
con=conn, # 数据库连接对象
index=False, # 是否保存行索引
if_exists='append' # 如果表存在,则追加数据
)pd.read_sql:从MySQL中加载数据
pd.read_sql(
sql='select * from score', # sql语句
con=conn, # 数据库连接对象
# index_col='Python' # 指定行索引的列名
)