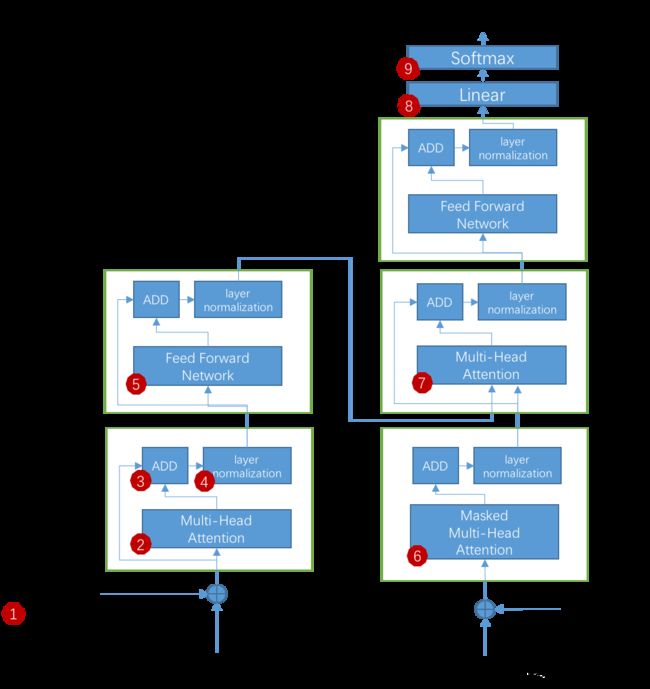
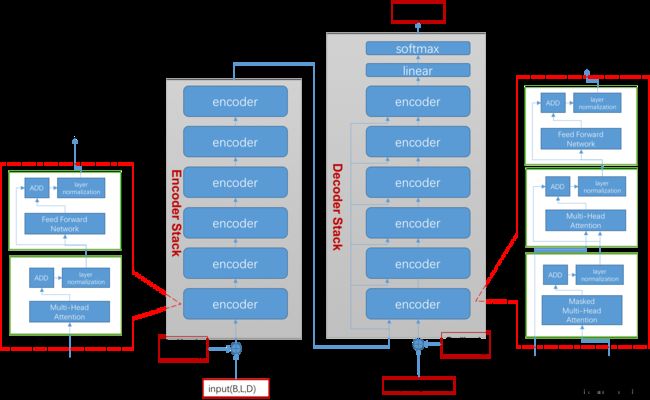
Transformer结构详解(有图,有细节)
文章目录
- 1. transformer的基本结构
- 2. 模块详解
-
- 2.1 模块1:Positional Embedding
- 2.2 模块2:Multi-Head Attention
-
- 2.2.1 Scaled Dot-Product Attention
- 2.2.2 Multi-Head
- 2.3 模块3:ADD
- 2.4 模块4:Layer Normalization
- 2.5 模块5:Feed Forward NetWork
- 2.6 模块6:Masked Multi-Head Attention
- 2.7 模块7: Multi-Head Attention
- 2.8 模块8:Linear
- 2.9 模块9:SoftMax
- 3. transformer在机器翻译任务中的使用
- 4 transformer 相关的其它问题
1. transformer的基本结构
2. 模块详解
2.1 模块1:Positional Embedding
P E PEPE模块的主要做用是把位置信息加入到输入向量中,使模型知道每个字的位置信息。对于每个位置的P E PEPE是固定的,不会因为输入的句子不同而不同,且每个位置的P E PEPE大小为1 ∗ n 1 *n1∗n(n为word embedding 的dim size),transformer中使用正余弦波来计算P E PEPE,具体如下:
P E ( p o s , 2 i ) = s i n ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) P E ( p o s , 2 i + 1 ) = c o s ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) PE_{(pos,2i)} = sin(pos/10000^{2i/d_{model}}) \\ PE_{(pos,2i+1)} = cos(pos/10000^{2i/d_{model}})PE(pos,2i)=sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)PE(pos,2i+1)=cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)
- p o s pospos代表的是一个字在句子中的位置,从0到名字长度减1,是下图中红色的序号。
- i ii代表的是dim 的序号,是下图中蓝色的序号:
- 当i ii为偶数时,此位置的值使用 s i n ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) sin(pos/10000^{2i/d_{model}})sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)来填充。
- 当i ii为奇数时,些位置的值使用 c o s ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) cos(pos/10000^{2i/d_{model}})cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)来填充

实现代码:
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
"Implement the PE function."
def __init__(self, d_model, dropout, max_len=5000):
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
# Compute the positional encodings once in log space.
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model).float()
position = torch.arange(0, max_len).unsqueeze(1).float()
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2).float() *
-(math.log(10000.0) / d_model)).float()
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0)
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + Variable(self.pe[:, :x.size(1)],
requires_grad=False)
return self.dropout(x)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
至于为什么选择这种方式,论文中给出的解释是:
- 我们之所以选择这个函数,是因为我们假设它可以让模型很容易地通过相对位置来学习,因为对任意确定的偏移k kk, P E p o s + k PE_{pos+k}PEpos+k可以表示为P E p o s PE_{pos}PEpos的线性函数。
理解:
由s i n ( α + β ) = s i n α c o s β + s i n β c o s α c o s ( α + β ) = c o s α c o s β − s i n β s i n α sin(\alpha+\beta)=sin\alpha cos\beta + sin\beta cos\alpha\\ cos(\alpha+\beta)=cos\alpha cos\beta - sin\beta sin\alphasin(α+β)=sinαcosβ+sinβcosαcos(α+β)=cosαcosβ−sinβsinα
推出:
P E ( p o s + k , 2 i ) = s i n ( ( p o s + k ) / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) = s i n ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) c o s ( k / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) + s i n ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) c o s ( k / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) = P E ( p o s , 2 i ) P E ( k , 2 i + 1 ) − P E ( p o s , 2 i + 1 ) P E ( k , 2 i )PE(pos+k,2i)=sin((pos+k)/100002i/dmodel)=sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)+sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)=PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i)PE(pos+k,2i)=sin((pos+k)/100002i/dmodel)=sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)+sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)=PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i)
PE(pos+k,2i)=sin((pos+k)/100002i/dmodel)=sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)+sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)=PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i)
P E ( p o s + k , 2 i + 1 ) = c o s ( ( p o s + k ) / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) = c o s ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) c o s ( k / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) − s i n ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) s i n ( k / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) = P E ( p o s , 2 i + 1 ) P E ( k , 2 i + 1 ) − P E ( p o s , 2 i ) P E ( k , 2 i )PE(pos+k,2i+1)=cos((pos+k)/100002i/dmodel)=cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)−sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)sin(k/100002i/dmodel)=PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i)PE(pos+k,2i+1)=cos((pos+k)/100002i/dmodel)=cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)−sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)sin(k/100002i/dmodel)=PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i)
PE(pos+k,2i+1)=cos((pos+k)/100002i/dmodel)=cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)cos(k/100002i/dmodel)−sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)sin(k/100002i/dmodel)=PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i)
以P E ( p o s + k , 2 i ) = P E ( p o s , 2 i ) P E ( k , 2 i + 1 ) − P E ( p o s , 2 i + 1 ) P E ( k , 2 i ) PE(pos+k,2i)=PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i+1)-PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i)PE(pos+k,2i)=PE(pos,2i)PE(k,2i+1)−PE(pos,2i+1)PE(k,2i)为例,当k kk确定时: P E ( k , 2 i + 1 ) PE(k,2i+1)PE(k,2i+1)、P E ( k , 2 i ) PE(k,2i)PE(k,2i)均为常数,P E ( p o s + k , 2 i ) = P E ( p o s , 2 i ) ∗ 常 数 2 i + 1 k − P E ( p o s , 2 i + 1 ) ∗ 常 数 i k PE(pos+k,2i)=PE(pos,2i) * 常数_{2i+1}^k - PE(pos,2i+1) * 常数_{i}^kPE(pos+k,2i)=PE(pos,2i)∗常数2i+1k−PE(pos,2i+1)∗常数ik
上式为即为1)中所说的线性函数。我们知道,每个位置(pos)的PE值均不同,因此我们可以根据PE的值区分位置,而由上面的线性函数,我们可以计量出两个位置的相对距离。 - 我们还尝试使用预先学习的positional embeddings 来代替正弦波,发现这两个版本产生了几乎相同的结果 。我们之所以选择正弦曲线,是因为它允许模型扩展到比训练中遇到的序列长度更长的序列。
理解:
第二点很好理解就是说了下正弦波的优点。这里我着重讲下正弦波存在的问题。在transformer架构里,我们计算两个特征的关系用的是点积的的方式(因为使用了Dot-Product Attention)。所以两个PE的关系(距离)实际是以它们的点积来表示的。举例如下[ 1 ] ^{[1]}[1]:
我们令c i = 1 / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l c_i=1/10000^{2i/d_{model}}ci=1/100002i/dmodel,则第t tt及t + 1 t+1t+1个位置的positional embedding 是:
P E t = [ s i n ( c 0 t ) c o s ( c 0 t ) s i n ( c 1 t ) c o s ( c 1 t ) ⋮ s i n ( c d 2 − 1 t ) c o s ( c d 2 − 1 t ) ] T PE_t={\left[ {sin(c0t)cos(c0t)sin(c1t)cos(c1t)⋮sin(cd2−1t)cos(cd2−1t)sin(c0t)cos(c0t)sin(c1t)cos(c1t)⋮sin(cd2−1t)cos(cd2−1t)
} \right]^T}PEt=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡sin(c0t)cos(c0t)sin(c1t)cos(c1t)⋮sin(c2d−1t)cos(c2d−1t)⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤T
P E t + k = [ s i n ( c 0 ( t + k ) ) c o s ( c 0 ( t + k ) ) s i n ( c 1 ( t + k ) ) c o s ( c 1 ( t + k ) ) ⋮ s i n ( c d 2 − 1 ( t + k ) ) c o s ( c d 2 − 1 ( t + k ) ) ] T PE_{t+k}={\left[ {sin(c0(t+k))cos(c0(t+k))sin(c1(t+k))cos(c1(t+k))⋮sin(cd2−1(t+k))cos(cd2−1(t+k))sin(c0(t+k))cos(c0(t+k))sin(c1(t+k))cos(c1(t+k))⋮sin(cd2−1(t+k))cos(cd2−1(t+k))
} \right]^T}PEt+k=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡sin(c0(t+k))cos(c0(t+k))sin(c1(t+k))cos(c1(t+k))⋮sin(c2d−1(t+k))cos(c2d−1(t+k))⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤T
则:P E t P E t + k = Σ j = 0 d 2 [ s i n ( c j t ) s i n ( c j ( t + k ) + c o s ( c j t ) c o s ( c j ( t + k ) ] = Σ j = 0 d 2 c o s ( c j ( t − ( t + k ) ) = Σ j = 0 d 2 c o s ( c j k )PEtPEt+k=Σd2j=0[sin(cjt)sin(cj(t+k)+cos(cjt)cos(cj(t+k)]=Σd2j=0cos(cj(t−(t+k))=Σd2j=0cos(cjk)PEtPEt+k=Σj=0d2[sin(cjt)sin(cj(t+k)+cos(cjt)cos(cj(t+k)]=Σj=0d2cos(cj(t−(t+k))=Σj=0d2cos(cjk)
PEtPEt+k=Σj=02d[sin(cjt)sin(cj(t+k)+cos(cjt)cos(cj(t+k)]=Σj=02dcos(cj(t−(t+k))=Σj=02dcos(cjk)
上式的第二行是使用了 c o s ( α − β ) = s i n α s i n β + c o s α c o s β cos(\alpha-\beta)=sin\alpha sin\beta + cos\alpha cos\betacos(α−β)=sinαsinβ+cosαcosβ 这个公式进行的变换。从最终的结果我们可以看出,两个embedding的距离度量只与间隔k kk有关,而c o s coscos函数关于y轴对称,即c o s x = c o s ( − x ) cosx=cos(-x)cosx=cos(−x),所以,P E t P E t + k PE_tPE_{t+k}PEtPEt+k的度量只与k kk的大小有关,与谁在前,谁在后无关。即,经过dot-attention机制后,我们把positional embedding中的顺序信息丢失了。所以,从这方面看,正弦波这种位置PE并不太适合在用在transformer结构中,这也可能是后面的bert,t5都采用的基于学习的positional embedding。(注:模块3会把顺序信息传递下去,但我们还是在算法的核心处理上丢失了信息。)
2.2 模块2:Multi-Head Attention
这个模块是transformer的核心,我们把这块拆成两部分来理解,先讲下其中的Scaled Dot-Product Attention(缩放的点积注意力机制),再讲Multi-Head。
2.2.1 Scaled Dot-Product Attention
我们先看下论文中的 Scaled Dot-Product Attention 步骤,如下图:![]()
下面我们对着上面的图讲一下,具体的看下每步做了什么。
- 首先说下Q,K,V,在transformer的encoder中,输入只有一个,即输入向量与位置向量的和,我们暂且叫做input_sum。Q,K,V就是这个input_sum通过三个linear层映射而来。如下图

由于linear的输入和输出均为d m o d e l d_{model}dmodel,所以Q,K,V的大小和input_sum的大小是一致的。
-
MatMul: 这步是实际是计算的 Q ∗ K T Q*K^TQ∗KT, 如下图:

从上图可以看出Q ∗ K T Q*K^TQ∗KT的结果s c o r e s scoresscores是一个L ∗ L L*LL∗L的矩阵(L为句字长度),其中scores中的[ i , j ] [i,j][i,j]位置表示的是Q QQ中的第i ii行的字和K T K^TKT中第j jj列的相似度(也可以说是重要度,我们可以这么理解,在机器翻译任务中,当我们翻译一句话的第i ii个字的的时候,我们要考虑原文中哪个位置的字对我们现在要翻译的这个位置的字的影响最大)。 -
Scale :这部分就是对上面的s c o r e s scoresscores进行了个类似正则化的操作。
s c o r e s = s c o r e s d q scores=\frac{scores}{\sqrt{d_q}}scores=dqscores (这里要说一下d q d_{q}dq,论文中给出的是d h d_{h}dh,即d m o d e l / h d_{model}/hdmodel/h, 因为论文中做了multi-head,所以 d q = d h d_q=d_{h}dq=dh),这里解释下除以d q \sqrt{d_q}dq的原因,原文是这样说的:“我们认为对于大的d k d_kdk,点积在数量级上增长的幅度大,将softmax函数推向具有极小梯度的区域4 ^44。为了抵消这种影响,我们对点积扩展1 d k \frac{1}{\sqrt{d_k}}dk1倍”。 -
Mask: 这步使用一个很小的值,对指定位置进行覆盖填充。这样,在之后计算softmax时,由于我们填充的值很小,所以计算出的概率也会很小,基本就忽略了。(如果不填个很小的值的话,后面我们计算softmax时,e x i ∑ i = 1 k e x i \frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_{i=1}^{k}{e^{x_i}}}∑i=1kexiexi ,当x = 0 x=0x=0时(padding的值),分子e 0 = 1 e^{0}=1e0=1这可不是一个很小的值。),mask操作在encoder和decoder过程中都存在,在encoder中我们是对padding的值进行mask,在decoder中我们主要是为了不让前面的词在翻译时看到未来的词,所以对当前词之后的词的信息进行mask。下面我们先看看encoder中关于padding的mask是怎么做的。

如上图,输入中有两个pad字符,s c o r e s scoresscores中的x都是pad参与计算产生的,我们为了排除pad产生的影响,我们提供了如图的mask,我们把scores与mask的位置一一对应,如果mask的值为0,则scores的对应位置填充一个非常小的负数(例如:− e 9 -e^9−e9)。最终得到的是上图最后一个表格。说了这么多,其实在pytorch中就一句话。
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
- 1
def attention(query, key, value, mask=None):
d_k = query.size(-1)
scores = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-2, -1)) \
/ math.sqrt(d_k)
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
p_attn = F.softmax(scores, dim = -1)
return torch.matmul(p_attn, value)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.2.2 Multi-Head
这里我们看看multi-head attention中的 multi-head是什么意思。我们假设d m o d e l = 512 d_{model}=512dmodel=512,h = 8 h=8h=8(8个头),说下transformer中是怎么处理的:
前面我们说过了,Q QQ、K KK、V VV三个矩阵是encoder的输入经过三个linear映射而成,它们的大小是[ B , L , D ] [B,L,D][B,L,D](batch size, max sentence length, embedding size), 这里为了说的清楚些,我们暂时不看[ B ] [B][B]这个维度。那么Q QQ、K KK、V VV的维度都为[ L , D ] [L,D][L,D],multi-head就是在[ D ] [D][D]维度上对数据进行切割,把数据切成等长的8段(h = 8 h=8h=8),这样Q QQ、K KK、V VV均被切成等长的8段,然后对应的Q QQ、K KK、V VV子段组成一组,每组通过 Scaled Dot-Product Attention 算法 计算出结果,这样的结果我们会得到8个,然后把这8个结果再拼成一个结果,就multi-head的结果。具体过程如下图:
![]()
2.3 模块3:ADD
此模块做了个类似残差的操作,不同的是不是用输入减去输出,而是用输入加上输出。(指Multi-Head Attention模块的输入和输出),具体操作就是把模块2的输入矩阵与模块2的输入矩阵的对应位置做加法运算。
2.4 模块4:Layer Normalization
不论是layer normalization还是batch normalization,其实做的都是一件事情,都是根据 x = a ∗ x − x ‾ s t d + e p s + b x = a * \frac{x - \overline{x}}{std + eps} + bx=a∗std+epsx−x+b对x xx的分布进行调整。不同的是x ‾ \overline{x}x和s t d stdstd的计算方式不同。如下图:![]()
batch normalization的x ‾ \overline{x}x和s t d stdstd是延粉色方向计算的,而layer normalization是延蓝色方向计算的。如果兄弟们去面试,可能面试官会问为什么这里没有使用BN,而使用了LN,我的理解是,BN对batch size的大小是有要求的,一般batch size越大,计算出的x ‾ \overline{x}x越好,而我用12G内存的GPU,跑transformer的模型时,batch size最多也就设置到32。batch size还是偏小的。所以使用与batch size无关的layer normlization。从另一个角度讲,batch size之所以小,是因为我们的embedding size 大,而layer normalization 正好是延这个方向做的,所以正好使得layer normalization计算的更稳定。
2.5 模块5:Feed Forward NetWork
Feed Forward NetWork 翻译成中文叫 前馈网络,其实就是MLP。我们这里不纠结于FFN的定义,我们直接看下transformer里是怎么实现的。如下图,我们先把输入向量从512维(d m o d e l d_{model}dmodel)映射到2048维,然后再映射到512维。实现时,就是使用两个linear层,第一个linear的输入是512维,输出是2048维,第二个linear的输入是2048,输出是512。![]()
2.6 模块6:Masked Multi-Head Attention
上文已讲了Multi-Head Attention,而且在讲 Scaled Dot-Product Attention 时也讲了mask机制,此模块的区别在于maked的策略不同,在encoder中我们是把padding给masked掉,这里我们除了要考虑padding,还要考虑预测时的未来变量问题,换句话说,我们是用一句话中的前N − 1 N-1N−1个字预测第N NN个字,那么我们在预测第N NN个字时,就不能让模型看到第N个字之后的信息,所以这里们把预测第N NN个字时,第N NN(包括)个字之后的字都masked掉。我们假设预测序列为’i like this apple’,则我们要做如下的mask。![]()
2.7 模块7: Multi-Head Attention
模块7 与上文 模块2(encoder 中 的 Multi-Head Attention) 代码实现上完全相同,区别再于模块2 只有一个输入,模块2把此输入经过三个linear映射成Q QQ、K KK、V VV , 而模块7的输入有两个,一个是decoder的输入经过第一个大模块传过来的值(为了方便,我们叫它input_x),一个是encoder最终结果(我们暂叫它input_memory), 模块7是把input_x通过一个linear映射成了Q QQ,然后通过两个linear把input_memory映射成K KK、V VV ,其它的与模块2完全一致。
2.8 模块8:Linear
此模块的目的是把模型的输transformer decoder的输出从d m o d e l d_{model}dmodel维度映射到词表大小的维度。linear本身也比较简单,这里不再细讲了。![]()
2.9 模块9:SoftMax
此模块会把上层linear的输出转化成概率,对应到某个字的概率。
3. transformer在机器翻译任务中的使用
在《Attention is All You Need》这篇文章中,是把transformer做为一个特征提取器放在一个Encoder-Decoder(下文用Encoder-Stack和Decoder-Stack,用以和transformer的encoder, decoder区分)架构中的,具体细节见下图:
上面的图片把整个结构基本都画出来了,这里再说下训练时的数据走向及流程:
1) 数据X XX 输入到Encoder-Stack中,得到输出变量e n c o d e r _ o u t p u t encoder\_outputencoder_output
2) e n c o d e r _ o u t p u t encoder\_outputencoder_output 做为K e y KeyKey和V a l u e ValueValue的原始输入 输入到Decoder-Stack中,Decoder-Stack的Query为上一轮Decoder-Stack的输出。
具体流程见下图:![]()
这里我提一下decoder stack的输入(上图中的Query),前面说过了,在transformer中,decoder的核心思想是用一个句子中的前N − 1 N-1N−1个字,预测第N NN个字,但在预测第一个字的时候,前面没有字,这时我们可以在每句话前面加上一个固定的开始标志(bos), 这样相当于把整个句子右移了一位。
4 transformer 相关的其它问题
这部分我是想写写transformer的并行等其它问题,但今天写的太累了,主要的也都写完了,就先发了。
References
[ 1 ] [1][1] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/166244505