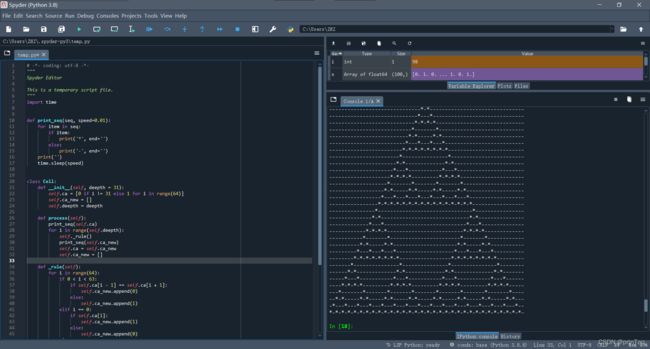
生命游戏 CA
1D形式
限制左边界
- 由于规则是计算出来的,实际上不需要用匹配的方式
- 长度可以是固定的,不必动态
- 人工append,没有完全按照游戏规则生成。在长度未知情况下,将更新过程分为append和refresh两部分。append拓展边界,refresh更新其他部分,但是要注意新增边界不能在一轮中更新两次
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#二种情况01
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def addone(x):
tmp = reverse(x[-1])
x=np.append(x,tmp)
return x
#
def refresh(x):
'''更新前面的
类似卷积,取三个匹配模板
'''
tmp = x.copy()
#补0
cal = np.insert(x,0,0)
cal = np.append(cal,0)
lenth = len(cal)
#这样x、cal对齐了
#卷积核
ConvKernal = np.array([[0,0,0],[0,0,1],[0,1,0],
[0,1,1],[1,0,0],[1,0,1],
[1,1,0],[1,1,1]])
thisValueTable = [1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0]#编码表
thisOnehot = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
#获取切片 thisSlice
if(lenth<3):
#需要特殊处理[1](不可能,来了就是错的)
#[1,1] 边界补0
pass
#滑动窗口
a = lenth-2#-3?
X_row=np.size(ConvKernal,0) #计算 X 的行数
for i in range(a):
thisSlice = cal[i:i+3]
#print(thisSlice)
#遍历卷积核
for j in range(X_row):
#模板匹配得onehot
#array([0, 0, 1])
if((ConvKernal[j,:] == thisSlice).all()):
#按照输出LUT
x[i]=thisValueTable[j]
#边界条件
print(thisSlice,x[i])
''' tmp = x.copy();
for i in (x.len-1) :
if(tmp[i]==tmp[i+1]):
x[i] = reverse(tmp[i])
'''
#完成更新
return x
def reverse(a):
'''类似激活函数
'''
if( a==0 ):
return 1
if( a==1 ):
return 0
def graph(arr):
#1D CA
rows = 5
cols = 11
array = np.zeros((rows, cols), dtype=np.uint8)
array[0, 5] = 1
array=arr
print(array)
def plot_ca(array):
cmap = plt.get_cmap('Blues')
plt.imshow(array, cmap=cmap, interpolation='none')
plot_ca(array)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
x=np.array([0])
finalLength=0#最后一行size
for i in range(10):
print(i)
print("轮数")
x=addone(x)
x=refresh(x)
print('本轮结果',x)
a = x.copy()
finalLength = len(x)
#a = a[:,np.newaxis];
if i==0:
final=a
#final = np.concatenate((final,a),axis=1)
#final = np.vstack((final,a))
#graph(final)
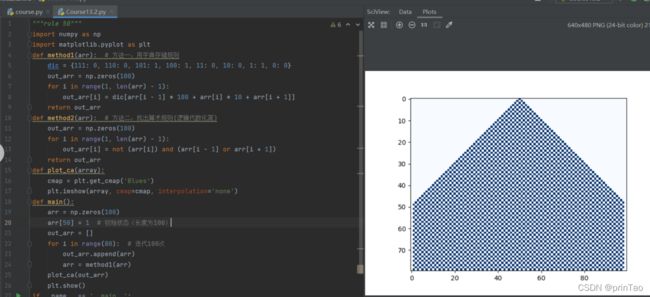
左右不限制
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Dec 1 15:15:54 2021
@author: 天房
"""
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
class Table:
def __init__(self,weight=15,height=31):
thistable = np.zeros((weight,height))
thistable[0][15] = 1
ruleTable = np.zeros(8)
ruleDic = {}
#def rule(self):
def refresh(x,thisValueTable):
'''更新前面的
类似卷积,取三个匹配模板
'''
tmp = x.copy()
x=x.copy()
#补0
cal = np.insert(x,0,0)
cal = np.append(cal,0)
lenth = len(cal)
#这样x、cal对齐了
ConvKernal = np.array([[0,0,0],[0,0,1],[0,1,0],
[0,1,1],[1,0,0],[1,0,1],
[1,1,0],[1,1,1]])
#thisValueTable = [0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1]#编码表
thisOnehot = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
#获取切片 thisSlice
if(lenth<3):
#需要特殊处理[1](不可能,来了就是错的)
#[1,1] 边界补0
pass
#滑动窗口
a = lenth-2#-3?
X_row=np.size(ConvKernal,0) #计算 X 的行数
for i in range(a):
thisSlice = cal[i:i+3]
#print(thisSlice)
#遍历卷积核
for j in range(X_row):
#模板匹配得onehot
#array([0, 0, 1])
if((ConvKernal[j,:] == thisSlice).all()):
#按照输出LUT
x[i]=thisValueTable[j]
#边界条件
#完成更新
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
#初始化rule
weight=12
height=31
thistable = np.zeros((weight,height))
thistable[0][15] = 1
thistable
thisValueTable=[0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1]
for typeNum in range(0,255):
for j in range(0,8):
thisValueTable[j] = (int)(typeNum/(2**(7-j)))
typeNum -= thisValueTable[j]*(2**(7-j))
print(thisValueTable)
#更新
for i in range(0,weight-1):
thistable[i+1]=refresh(thistable[i],thisValueTable)
#绘图
array=thistable
def plot_ca(array):
cmap = plt.get_cmap('Blues')
plt.imshow(array, cmap=cmap, interpolation='none')
plot_ca(array)
plt.show()
白嫖的各种算法:
写了类
计算规则种子,好
加速计算 利用Torch
class torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
in_channels(int) – 输入信号的通道。在文本分类中,即为词向量的维度
out_channels(int) – 卷积产生的通道。有多少个out_channels,就需要多少个1维卷积
kernel_size(int or tuple) - 卷积核的尺寸,卷积核的大小为(k,),第二个维度是由in_channels来决定的,所以实际上卷积大小为kernel_size*in_channels
stride(int or tuple, optional) - 卷积步长
padding (int or tuple, optional)- 输入的每一条边补充0的层数
dilation(int or tuple, `optional``) – 卷积核元素之间的间距
groups(int, optional) – 从输入通道到输出通道的阻塞连接数
bias(bool, optional) - 如果bias=True,添加偏置
torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels=weights, out_channels=8, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=false)
2D形式
加速计算 利用Torch
卷积滑动更新状态
减少内存消耗 利用状态机
压缩编码,在同一地址更新
https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4854466.html