搜索算法(五) DFS BFS 练习题
练习题
1.
力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/surrounded-regions/这题和417类似,都是从边界朝内部搜索,417用的是DFS,这里为了练习,就用BFS。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/surrounded-regions/这题和417类似,都是从边界朝内部搜索,417用的是DFS,这里为了练习,就用BFS。
首先从四条边界得到‘O’的坐标,加入队列。接着一层一层搜索,将所有相邻且为‘O'元素坐标加入队列,并且标记为已访问。
搜索结束后,遍历整个数组,将所有未访问的'O'标记为'X',因为所有边界可达的'O'都已被标记为访问过。
class Solution {
public:
void solve(vector>& board) {
int m = board.size();
int n = board[0].size();
queue> q;
vector> visit(m,vector(n,false));
for(int i=0;i path = {-1,0,1,0,-1};
while(!q.empty()){
int k = q.size();
for(int i=0;i=0 && x=0 && y 2.力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/这题是一道典型的DFS,题目不难,但注意不要写成引用传递了。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/这题是一道典型的DFS,题目不难,但注意不要写成引用传递了。
不然就会像我一开始那样,string插入弹出写了半天,老是不对。(因为确定不了一个数字到底是几位char)
仔细一看,写成值传递,这样函数结束时,path上新增的内容都会自然消除。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector res;
dfs(root,"",res);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, string path, vector& res){
if(root){
path += to_string(root->val);
if(!root->left && !root->right){
res.push_back(path);
}else{
path += "->";
dfs(root->left,path,res);
dfs(root->right,path,res);
}
}
}
}; 3.力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/
这题是典型的DFS,考虑到重复数字直接DFS,会产生重复的排列,有两种解决方法。
一是用set存储排列,自动去除了重复的排列。
二是跳过与前一个数字重复的数字(且前一个数字是未访问的)。
这里采用第二种方法:
class Solution {
public:
vector> permuteUnique(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector path;
vector> res;
vector visit(n,false);
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
dfs(nums,path,res,visit);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector& nums, vector path, vector>& res, vector visit){
if(path.size()==nums.size()){
res.push_back(path);
}else{
int n = nums.size();
for(int i=0;i 4.力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/sudoku-solver/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sudoku-solver/
解数独的关键在于记录每行每列每个3x3方块的数字,然后对空格处依次遍历可能的数字。
先预处理矩阵,然后DFS,需要注意的是DFS的递归方法中,最后找到目标解法后,要在每一层递归直接return,不然会继续遍历可能的数字。
class Solution {
public:
void solveSudoku(vector>& board) {
memset(row,false,sizeof(row));
memset(col,false,sizeof(col));
memset(cube,false,sizeof(cube));
for(int i=0;i<9;i++){
for(int j=0;j<9;j++){
if(board[i][j]=='.'){
path.push_back({i,j});
}else{
int m = board[i][j] - '0';
row[i][m] = col[j][m] = cube[i/3][j/3][m] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board,0);
}
bool dfs(vector>& board, int x){
if(x>=path.size()){
return true;
}
auto [a,b] = path[x];
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++){
if(!row[a][i] && !col[b][i] && !cube[a/3][b/3][i]){
row[a][i] = col[b][i] = cube[a/3][b/3][i] = true;
board[a][b] = '0' + i;
if(dfs(board,x+1))
return true;
row[a][i] = col[b][i] = cube[a/3][b/3][i] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
bool row[9][10];
bool col[9][10];
bool cube[3][3][10];
vector> path;
}; 5.力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees/这题挺绕的,记忆化DFS过不了所有的答案,必须要用拓朴排序。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees/这题挺绕的,记忆化DFS过不了所有的答案,必须要用拓朴排序。
虽然我不懂 这种解法为啥要叫拓扑排序,但看题解都这么说那就是了吧。
拓朴排序解这道题就绕开了搜索的问题。
要找高度最小的根节点,这个根节点应该出现在两个相距最远的叶子节点的中间位置。不然的话,其中一个子树的高度就会很高。
举个例子,两个叶子节点相距11,如果我选最中间的节点作为根节点,那么树高度为6.
如果随便选了叶子节点相邻的节点作为根节点,那么树高度为9。
有了这个思想之后,怎么实现代码呢?
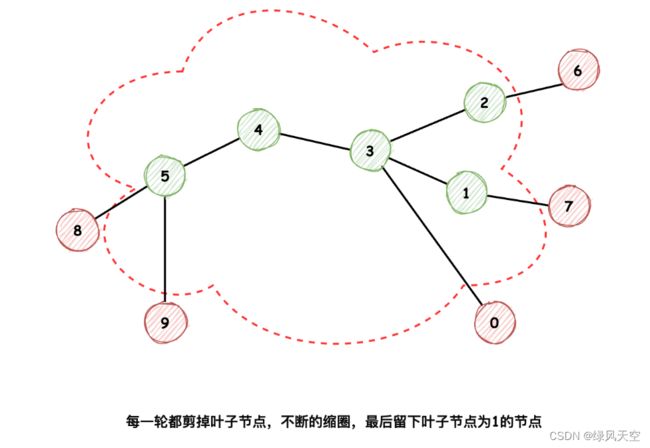
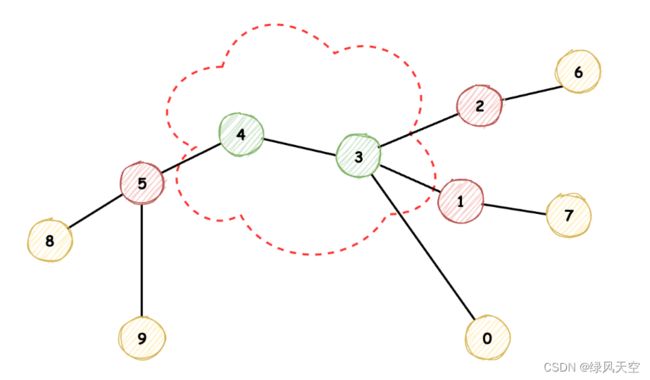
这个题解链接里的这两张图很好地说明了方法:
目标是寻找距离最远的两个叶子节点的中间节点,我们无法立刻知道哪两个叶子节点相距最远。
所以每次都删除掉最外围的叶子节点(也就是入度为1的节点),删掉叶子节点之后,与它们相连的入度为2的节点就会变成新的叶子节点,这样新一轮继续删除叶子节点,更新与它们相连的节点的度数。
这里有些类似层次遍历,每一次删除最外层节点,当删除到只剩下两个或一个节点时,可以认为它们是最中间的节点,作为答案返回。
看上图还是挺生动形象的,从相距最远的节点,一层一层剥开,最后找到中心节点。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector>& edges) {
if(n==1) return vector{0};
vector degree(n,0);
vector> connect(n);
for(auto e:edges){
connect[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1]);
connect[e[1]].emplace_back(e[0]);
degree[e[0]]++;
degree[e[1]]++;
}
queue q;
for(int i=0;i2){
int m = q.size();
n -= m;
for(int i=0;i res;
while(q.size()>0){
res.push_back(q.front());
q.pop();
}
return res;
}
}; Reference:
力扣