DirectSound播放PCM(可播放实时采集的音频数据)
前言
该篇整理的原始来源为http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/40540147。非常感谢该博主的无私奉献,写了不少关于不同多媒体库的博文。让我这个小白学习到不少。现在将其整理是为了收录,以备自己查看。
一、DirectSound简介
DirectSound是微软所开发DirectX的组件之一,可以在Windows 操作系统上录音,并且记录波形音效(waveform sound)。目前DirectSound 是一个成熟的API ,提供许多有用的功能,例如能够在较高的分辨率播放多声道声音。DirectSound3D(DS3D)最早是1993年与 DirectX 3 一起发表的。DirectX 8以后的DirectSound和DirectSound3D的(DS3D)被合称DirectX Audio。
DirectSound有以下几种对象:
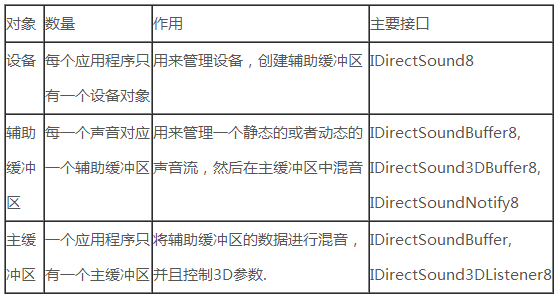
图1.DirectSound对象
二、DirectSound播放音频的流程
使用DirectSound播放音频一般情况下需要如下步骤:
1.初始化
- 创建一个IDirectSound8接口的对象
- 设置协作级
- 创建一个主缓冲对象
- 创建一个副缓冲对象
- 创建通知对象
- 设置通知位置
- 开始播放
2.循环播放声音
- 数据填充至副缓冲区
- 等待播放完成
三、结合接口详细分析
1.初始化
1)创建一个IDirectSound8接口的对象
通过DirectSoundCreate8()方法可以创建一个设备对象。这个对象通常代表缺省的播放设备。DirectSoundCreate8()函数原型如下。
1 HRESULT DirectSoundCreate8( 2 LPCGUID lpcGuidDevice, 3 LPDIRECTSOUND8 * ppDS8, 4 LPUNKNOWN pUnkOuter 5 )
参数的含义如下:
lpcGuidDevice:要创建的设备对象的GUID。可以指定为NULL,代表默认的播放设备。
ppDS8:返回的IDirectSound8对象的地址。
pUnkOuter:必须设为NULL。
例如如下代码即可创建一个IDirectSound8接口的对象
1 IDirectSound8 *m_pDS=NULL; 2 DirectSoundCreate8(NULL,&m_pDS,NULL);
2) 设置协作级
Windows 是一个多任务环境,同一时间有多个应用程序去访问设备。通过使用协作级别,DirectSound可以确保应用程序不会在别的设备使用时去访问,每个 DirectSound应用程序都有一个协作级别,这个级别决定着访问硬件的权限。
在创建一个设备对象以后,必须通过用IDirectSound8的SetCooperativeLevel()设置协作权限,否则将听不到声音。SetCooperativeLevel()的原型如下
1 HRESULT SetCooperativeLevel( 2 HWND hwnd, 3 DWORD dwLevel 4 )
参数的含义如下:
hwnd:应用程序窗口句柄。
dwLevel:支持以下几种级别:
DSSCL_EXCLUSIVE:与DSSCL_PRIORITY具有相同的作用。
DSSCL_NORMAL:正常的协调层级标志,其他程序可共享声卡设备进行播放。
DSSCL_PRIORITY:设置声卡设备为当前程序独占。
DSSCL_WRITEPRIMAR:可写主缓冲区,此时副缓冲区就不能进行播放处理,即不能将次缓冲区的数据送进混声器,再输出到主缓冲区上。这是最完全控制声音播放的方式。
3) 创建一个主缓冲对象
使用IDirectSound8的CreateSoundBuffer()可以创建一个IDirectSoundBuffer接口的主缓冲区对象。CreateSoundBuffer()的原型如下。
1 HRESULT CreateSoundBuffer( 2 LPCDSBUFFERDESC pcDSBufferDesc, 3 LPDIRECTSOUNDBUFFER * ppDSBuffer, 4 LPUNKNOWN pUnkOuter 5 )
参数的含义如下:
pcDSBufferDesc:描述声音缓冲的DSBUFFERDESC结构体的地址
ppDSBuffer:返回的IDirectSoundBuffer接口的对象的地址。
pUnkOuter:必须设置为NULL。
其中涉及到一个描述声音缓冲的结构体DSBUFFERDESC,该结构体的定义如下:
1 typedef struct _DSBUFFERDESC 2 { 3 DWORD dwSize; 4 DWORD dwFlags; 5 DWORD dwBufferBytes; 6 DWORD dwReserved; 7 LPWAVEFORMATEX lpwfxFormat; 8 } DSBUFFERDESC
简单解释一下其中的变量的含义:
dwSize:结构体的大小。必须初始化该值。
dwFlags:设置声音缓存的属性。有很多选项,可以组合使用,就不一一列出了。详细的参数可以查看文档。
dwBufferBytes:缓冲的大小。
dwReserved:保留参数,暂时没有用。
lpwfxFormat:指向一个WAVE格式文件头的指针。
设置DSBUFFERDESC完毕后,就可以使用CreateSoundBuffer()创建主缓冲了。示例代码如下:
1 DSBUFFERDESC dsbd; 2 memset(&dsbd,0,sizeof(dsbd)); 3 dsbd.dwSize=sizeof(dsbd); 4 dsbd.dwFlags=DSBCAPS_GLOBALFOCUS | DSBCAPS_CTRLPOSITIONNOTIFY |DSBCAPS_GETCURRENTPOSITION2; 5 dsbd.dwBufferBytes=MAX_AUDIO_BUF*BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE; 6 //WAVE Header 7 dsbd.lpwfxFormat=(WAVEFORMATEX*)malloc(sizeof(WAVEFORMATEX)); 8 dsbd.lpwfxFormat->wFormatTag=WAVE_FORMAT_PCM; 9 /* format type */ 10 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nChannels=channels; 11 /* number of channels (i.e. mono, stereo...) */ 12 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nSamplesPerSec=sample_rate; 13 /* sample rate */ 14 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nAvgBytesPerSec=sample_rate*(bits_per_sample/8)*channels; 15 /* for buffer estimation */ 16 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nBlockAlign=(bits_per_sample/8)*channels; 17 /* block size of data */ 18 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->wBitsPerSample=bits_per_sample; 19 /* number of bits per sample of mono data */ 20 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->cbSize=0; 21 22 23 //Creates a sound buffer object to manage audio samples. 24 HRESULT hr1; 25 if( FAILED(m_pDS->CreateSoundBuffer(&dsbd,&m_pDSBuffer,NULL))){ 26 return FALSE; 27 }
4) 创建一个副缓冲对象
使用IDirectSoundBuffer的QueryInterface()可以得到一个IDirectSoundBuffer8接口的对象。IDirectSoundBuffer8的GUID为IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8。示例代码如下。
1 IDirectSoundBuffer *m_pDSBuffer=NULL; 2 IDirectSoundBuffer8 *m_pDSBuffer8=NULL; 3 ... 4 if( FAILED(m_pDSBuffer->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8,(LPVOID*)&m_pDSBuffer8))){ 5 return FALSE ; 6 }
5) 创建通知对象
使用IDirectSoundBuffer8的QueryInterface()可以得到一个IDirectSoundNotify8接口的对象。IDirectSoundBuffer8的GUID为IID_IDirectSoundNotify。示例代码如下。
1 IDirectSoundBuffer8 *m_pDSBuffer8=NULL; 2 IDirectSoundNotify8 *m_pDSNotify=NULL; 3 … 4 if(FAILED(m_pDSBuffer8->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundNotify,(LPVOID*)&m_pDSNotify))){ 5 return FALSE ; 6 }
一句话概括一下通知对象的作用:当DirectSound缓冲区中的数据播放完毕后,告知系统应该填充新的数据。
6) 设置通知位置
使用IDirectSoundNotify8的SetNotificationPositions()可以设置通知的位置。SetNotificationPositions()的原型如下。
1 HRESULT SetNotificationPositions( 2 DWORD dwPositionNotifies, 3 LPCDSBPOSITIONNOTIFY pcPositionNotifies 4 )
参数含义如下。
dwPositionNotifies:DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY结构体的数量。既包含几个通知的位置。
pcPositionNotifies:指向DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY结构体数组的指针。
在这里涉及到一个结构体DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY,它描述了通知的位置。DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY的定义如下。
1 typedef struct DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY { 2 DWORD dwOffset; 3 HANDLE hEventNotify; 4 } DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY;
它的成员的含义如下。
dwOffset:通知事件触发的位置(距离缓冲开始位置的偏移量)。
hEventNotify:触发的事件的句柄。
7) 开始播放
使用IDirectSoundBuffer8的SetCurrentPosition ()可以设置播放的位置。SetCurrentPosition ()原型如下
1 HRESULT SetCurrentPosition( 2 DWORD dwNewPosition 3 )
其中dwNewPosition是播放点与缓冲区首个字节之间的偏移量。
使用IDirectSoundBuffer8的Play ()可以开始播放音频数据。Play ()原型如下。
1 HRESULT Play( 2 DWORD dwReserved1, 3 DWORD dwPriority, 4 DWORD dwFlags 5 )
参数含义:
dwReserved1:保留参数,必须取0。
dwPriority:优先级,一般情况下取0即可。
dwFlags:标志位。目前常见的是DSBPLAY_LOOPING。当播放至缓冲区结尾的时候,重新从缓冲区开始处开始播放。
2. 循环播放声音
1) 数据填充至副缓冲区
数据填充至副缓冲区之前,需要先使用Lock()锁定缓冲区。然后就可以使用fread(),memcpy()等方法将PCM音频采样数据填充至缓冲区。数据填充完毕后,使用Unlock()取消对缓冲区的锁定。如果是实时采集的音频数据,只要将音频数据复制到Lock()获取到的ppvAudioPtr1指向的地址,大小为pdwAudioBytes1,就可以播放了。(我使用的方式就是如此,实现了实时音频的播放,下文中的例子数据是读取自文件。)
Lock()函数的原型如下。
1 HRESULT Lock( 2 DWORD dwOffset, 3 DWORD dwBytes, 4 LPVOID * ppvAudioPtr1, 5 LPDWORD pdwAudioBytes1, 6 LPVOID * ppvAudioPtr2, 7 LPDWORD pdwAudioBytes2, 8 DWORD dwFlags 9 )
参数的含义如下。
dwOffset:锁定的内存与缓冲区首地址之间的偏移量。
dwBytes:锁定的缓存的大小。
ppvAudioPtr1:获取到的指向缓存数据的指针。
pdwAudioBytes1:获取到的缓存数据的大小。
ppvAudioPtr2:没有用到,设置为NULL。
pdwAudioBytes2:没有用到,设置为0。
dwFlags:暂时没有研究。
UnLock()函数的原型如下。
1 HRESULT Unlock( 2 LPVOID pvAudioPtr1, 3 DWORD dwAudioBytes1, 4 LPVOID pvAudioPtr2, 5 DWORD dwAudioBytes2 6 )
参数含义如下。
pvAudioPtr1:通过Lock()获取到的指向缓存数据的指针。
dwAudioBytes1:写入的数据量。
pvAudioPtr2:没有用到。
dwAudioBytes2:没有用到。
2) 等待播放完成
根据此前设置的通知机制,使用WaitForMultipleObjects()等待缓冲区中的数据播放完毕,然后进入下一个循环。
四、播放音频流程总结
DirectSound播放PCM音频数据的流程如下图所示。
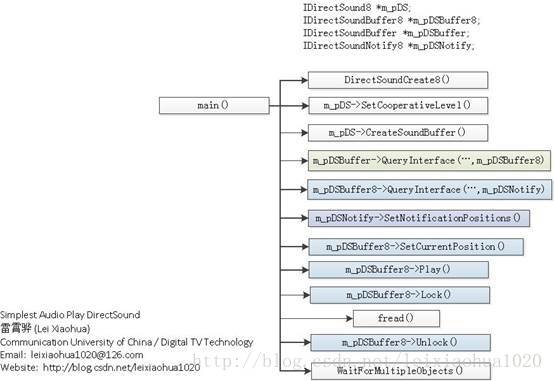
图2
其中涉及到的几个结构体之间的关系如下图所示。
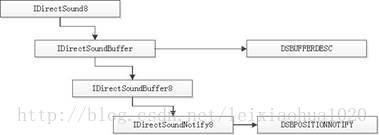
图3.结构体关系
五、使用示例代码
该代码也是直接使用的来自原博主的代码,如下
1 /** 2 * 最简单的DirectSound播放音频的例子(DirectSound播放PCM) 3 * Simplest Audio Play DirectSound (DirectSound play PCM) 4 * 5 * 雷霄骅 Lei Xiaohua 6 * [email protected] 7 * 中国传媒大学/数字电视技术 8 * Communication University of China / Digital TV Technology 9 * http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020 10 * 11 * 本程序使用DirectSound播放PCM音频采样数据。 12 * 是最简单的DirectSound播放音频的教程。 13 * 14 * 函数调用步骤如下: 15 * 16 * [初始化] 17 * DirectSoundCreate8():创建一个DirectSound对象。 18 * SetCooperativeLevel():设置协作权限,不然没有声音。 19 * IDirectSound8->CreateSoundBuffer():创建一个主缓冲区对象。 20 * IDirectSoundBuffer->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8..): 21 * 创建一个副缓冲区对象,用来存储要播放的声音数据文件。 22 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundNotify..): 23 * 创建通知对象,通知应用程序指定播放位置已经达到。 24 * IDirectSoundNotify8->SetNotificationPositions():设置通知位置。 25 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->SetCurrentPosition():设置播放的起始点。 26 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->Play():开始播放。 27 * 28 * [循环播放数据] 29 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->Lock():锁定副缓冲区,准备写入数据。 30 * fread():读取数据。 31 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->Unlock():解锁副缓冲区。 32 * WaitForMultipleObjects():等待“播放位置已经达到”的通知。 33 * 34 * This software plays PCM raw audio data using DirectSound. 35 * It's the simplest tutorial about DirectSound. 36 * 37 * The process is shown as follows: 38 * 39 * [Init] 40 * DirectSoundCreate8(): Init DirectSound object. 41 * SetCooperativeLevel(): Must set, or we won't hear sound. 42 * IDirectSound8->CreateSoundBuffer(): Create primary sound buffer. 43 * IDirectSoundBuffer->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8..): 44 * Create secondary sound buffer. 45 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundNotify..): 46 * Create Notification object. 47 * IDirectSoundNotify8->SetNotificationPositions(): 48 * Set Notification Positions. 49 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->SetCurrentPosition(): Set position to start. 50 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->Play(): Begin to play. 51 * 52 * [Loop to play data] 53 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->Lock(): Lock secondary buffer. 54 * fread(): get PCM data. 55 * IDirectSoundBuffer8->Unlock(): UnLock secondary buffer. 56 * WaitForMultipleObjects(): Wait for Notifications. 57 */ 58 #include <stdio.h> 59 #include <stdlib.h> 60 #include <windows.h> 61 #include <dsound.h> 62 63 64 #define MAX_AUDIO_BUF 4 65 #define BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE 192000 66 67 68 int sample_rate=8000; //PCM sample rate 69 int channels=1; //PCM channel number 70 int bits_per_sample=16; //bits per sample 71 72 BOOL main(int argc,char * argv[]) 73 { 74 int i; 75 FILE * fp; 76 if((fp=fopen("../out.pcm","rb"))==NULL){ 77 printf("cannot open this file\n"); 78 return -1; 79 } 80 81 IDirectSound8 *m_pDS=0; 82 IDirectSoundBuffer8 *m_pDSBuffer8=NULL; //used to manage sound buffers. 83 IDirectSoundBuffer *m_pDSBuffer=NULL; 84 IDirectSoundNotify8 *m_pDSNotify=0; 85 DSBPOSITIONNOTIFY m_pDSPosNotify[MAX_AUDIO_BUF]; 86 HANDLE m_event[MAX_AUDIO_BUF]; 87 88 SetConsoleTitle(TEXT("Simplest Audio Play DirectSound"));//Console Title 89 //Init DirectSound 90 if(FAILED(DirectSoundCreate8(NULL,&m_pDS,NULL))) 91 return FALSE; 92 if(FAILED(m_pDS->SetCooperativeLevel(FindWindow(NULL,TEXT("Simplest Audio Play DirectSound")),DSSCL_NORMAL))) 93 return FALSE; 94 95 96 DSBUFFERDESC dsbd; 97 memset(&dsbd,0,sizeof(dsbd)); 98 dsbd.dwSize=sizeof(dsbd); 99 dsbd.dwFlags=DSBCAPS_GLOBALFOCUS | DSBCAPS_CTRLPOSITIONNOTIFY |DSBCAPS_GETCURRENTPOSITION2; 100 dsbd.dwBufferBytes=MAX_AUDIO_BUF*BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE; 101 dsbd.lpwfxFormat=(WAVEFORMATEX*)malloc(sizeof(WAVEFORMATEX)); 102 dsbd.lpwfxFormat->wFormatTag=WAVE_FORMAT_PCM; 103 /* format type */ 104 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nChannels=channels; 105 /* number of channels (i.e. mono, stereo...) */ 106 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nSamplesPerSec=sample_rate; 107 /* sample rate */ 108 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nAvgBytesPerSec=sample_rate*(bits_per_sample/8)*channels; 109 /* for buffer estimation */ 110 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->nBlockAlign=(bits_per_sample/8)*channels; 111 /* block size of data */ 112 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->wBitsPerSample=bits_per_sample; 113 /* number of bits per sample of mono data */ 114 (dsbd.lpwfxFormat)->cbSize=0; 115 116 //Creates a sound buffer object to manage audio samples. 117 HRESULT hr1; 118 if( FAILED(m_pDS->CreateSoundBuffer(&dsbd,&m_pDSBuffer,NULL))){ 119 return FALSE; 120 } 121 if( FAILED(m_pDSBuffer->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundBuffer8,(LPVOID*)&m_pDSBuffer8))){ 122 return FALSE ; 123 } 124 //Get IDirectSoundNotify8 125 if(FAILED(m_pDSBuffer8->QueryInterface(IID_IDirectSoundNotify,(LPVOID*)&m_pDSNotify))){ 126 return FALSE ; 127 } 128 for(i =0;i<MAX_AUDIO_BUF;i++){ 129 m_pDSPosNotify[i].dwOffset =i*BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE; 130 m_event[i]=::CreateEvent(NULL,false,false,NULL); 131 m_pDSPosNotify[i].hEventNotify=m_event[i]; 132 } 133 m_pDSNotify->SetNotificationPositions(MAX_AUDIO_BUF,m_pDSPosNotify); 134 m_pDSNotify->Release(); 135 136 //Start Playing 137 BOOL isPlaying =TRUE; 138 LPVOID buf=NULL; 139 DWORD buf_len=0; 140 DWORD res=WAIT_OBJECT_0; 141 DWORD offset=BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE; 142 143 m_pDSBuffer8->SetCurrentPosition(0); 144 m_pDSBuffer8->Play(0,0,DSBPLAY_LOOPING); 145 //Loop 146 while(isPlaying){ 147 if((res >=WAIT_OBJECT_0)&&(res <=WAIT_OBJECT_0+3)){ 148 m_pDSBuffer8->Lock(offset,BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE,&buf,&buf_len,NULL,NULL,0); 149 150 // 如果是实时音频播放,那么下面的数据就可以把内存中buf_len大小的数据复制到buf指向的地址即可 151 if(fread(buf,1,buf_len,fp)!=buf_len){ 152 //File End 153 //Loop: 154 fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET); 155 fread(buf,1,buf_len,fp); 156 //Close: 157 //isPlaying=0; 158 } 159 160 offset+=buf_len; 161 offset %= (BUFFERNOTIFYSIZE * MAX_AUDIO_BUF); 162 printf("this is %7d of buffer\n",offset); 163 m_pDSBuffer8->Unlock(buf,buf_len,NULL,0); 164 } 165 res = WaitForMultipleObjects (MAX_AUDIO_BUF, m_event, FALSE, INFINITE); 166 } 167 168 return 0; 169 }
结语
最后,再次强调下,该博文是整理自http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/40540147。我只是改变了一点点格式,其实改变的地方非常少。只是加了点注释,即播放实时内存数据怎么使用(这是我在项目中的使用方式)。我一再强调,是为了尊重原博主的工作,毕竟直接把别人的东西拿来当作自己的,那就是小偷了。