(八)梯度下降法
一、 梯度下降法
1.1 梯度
本意是一个向量(矢量),表示某一函数在该点处的方向导数沿着该方向取得最大值,即函数在该点处沿着该方向变化最快,变化率最大
梯度下降:梯度下降法的计算过程就是沿梯度下降的方向求解极小值;对于一个损失函数,求在θ取某个值时J(损失)最小的一种思想;
不是一个机器学习算法;
基于搜索的最优化方法;
作用:最小化一个损失函数
1.2 示例
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plot_x = np.linspace(-1, 6, 140)
plot_y = (plot_x-2.5)**2-1
# 损失函数
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y)
plt.show()1.3 原理
J最小时该函数θ处导数为0;梯度下降时每一次取到的J都应比上一次小
plot_x = np.linspace(-1, 6, 200)
plot_y = (plot_x-2.5)**2-1# ------计算θ处的倒数
def dJ(theta):
return 2*(theta-2.5)
# ------θ处J的值
def J(theta):
try :
return (theta-2.5)**2 - 1.
except:
return float('inf')
# ------梯度下降
# init_theta:初始θ值
# eta:学习率,也就是步长
# n_iters:收敛速度和eta值相关,eta太小收敛慢
# epsilon:要求精度
def gradient_descent(init_theta, eta, n_iters=10000, epsilon=1e-8):
theta = init_theta
theta_history.append(init_theta)
i_iters = 0
while i_iters < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta)
last_theta = theta
# 下一个θ值
theta = theta - eta * gradient
# 把所有取过的θ放到theta_history中,为画图做准备
theta_history.append(theta)
# 当两次差值小于要求精度epsilon时,跳出函数,此时找到了θ
if(abs(J(theta)-J(last_theta)) < epsilon):
break
# 循环次数累积
i_iters+= 1
# ------绘制下降曲线
def plot_theta_history():
plt.plot(plot_x, J(plot_x))
plt.plot(np.array(theta_history), J(np.array(theta_history)),color = 'r', marker='+')
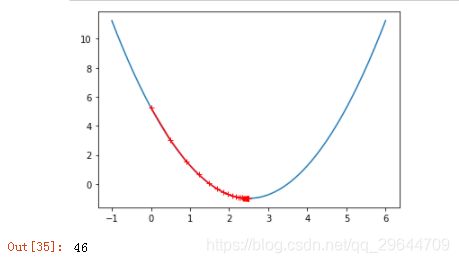
plt.show()1.4 不同eta对梯度下降结果的影响
① eta取0.01:学习率太小,收敛时间太长
eta = 0.01
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
len(theta_history)② eta取0.1
eta = 0.1
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
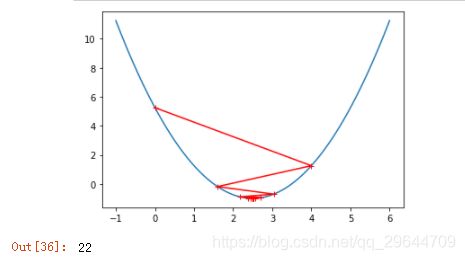
len(theta_history)③ eta取0.8
eta = 0.8
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta)
plot_theta_history()
len(theta_history)④ eta取1.1:学习率太大,离预期越来越远,最后抛出异常
eta = 1.1
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0.,eta,n_iters=10)
plot_theta_history()
len(theta_history)theta_history
'''
[0.0,
5.5,
-1.1000000000000005,
6.820000000000001,
-2.684000000000002,
8.720800000000004,
-4.964960000000007,
11.457952000000008,
-8.249542400000012,
15.399450880000016,
-12.979341056000022]
'''二、随机梯度下降法
批量梯度下降:对所有样本进行计算,搜索沿着损失函数减小最快的方向逐渐下降,当样本量很大时收敛速度会很慢;
随机梯度下降,只选出一个样本进行计算,不能保证搜索方向一定是损失函数减小的方向,也不能保证是减小最快的方向,但最后一定会找到或者靠近最小的损失函数,用少量的数据样本计算,大大缩短了收敛时间;
随机梯度下降法:很有可能跳出局部最优解,找到全局最优解。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
from sklearn import datasetsboston = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston.data
y = boston.target
# 数据清洗
X = x[y<50]
y = y[y<50]from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=666)# 数据归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(X_train)
X_train_scaler = scaler.transform(X_train)
X_test_scaler = scaler.transform(X_test)from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor
sgd = SGDRegressor()
sgd.fit(X_train_scaler,y_train)
sgd.score(X_test_scaler,y_test)
# 0.8129534790265714