一文详解Java自定义注解
目录
简介
JDK注解
@Target
@Retention
@Documented
@Inherited
第三方注解
自定义注解
举例
默认字符串注解
实现指定包名称扫描注解
简介
注解(Annotation)是Java SE 5.0 版本开始引入的概念,它是对 Java 源代码的说明,是一种元数据(描述数据的数据)。
Java中的注解主要分为以下三类:
- JDK的注解
- 第三方的注解
- 自定义注解
JDK注解
- Java内置注解
- @Override (标记重写方法)
- @Deprecated (标记过时)
- @SuppressWarnings (忽略警告)
- 元注解 (注解的注解)
- @Target (注解的作用目标)
- @Retention (注解的生命周期)
- @Document (注解是否被包含在JavaDoc中)
- @Inherited (是否允许子类集成该注解)
@Target
用于描述注解的使用范围,有一个枚举ElementType来指定,具体如下:
| Target类型 | 描述 |
| ElementType.TYPE | 应用于类、接口(包括注解类型)、枚举 |
| ElementType.FIELD | 应用于属性(包括枚举中的常量) |
| ElementType.METHOD | 应用于方法 |
| ElementType.PARAMETER | 应用于方法的形参 |
| ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR | 应用于构造函数 |
| ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE | 应用于局部变量 |
| ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE | 应用于注解类型 |
| ElementType.PACKAGE | 应用于包 |
| ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER | 应用于类型变量 |
| ElementType.TYPE_USE | 应用于任何使用类型的语句中(例如声明语句、泛型和强制转换语句中的类型) |
@Retention
表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息,用于描述注解的生命周期,也是一个枚举RetentionPoicy来决定的
| 取值 | 含义 |
| RetentionPolicy.SOURCE | 源码中保留,编译期可以处理 |
| RetentionPolicy.CLASS | Class文件中保留,Class加载时可以处理 |
| RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME | 运行时保留,运行中可以处理 |
一般填RetentionPoicy.RUNTIME即可
@Documented
如果用javadoc生成文档时,想把注解也生成文档,就带这个。
@Inherited
@Inherited 元注解是一个标记注解,@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一个使用了@Inherited修饰的annotation类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation将被用于该class的子类。注意,@Inherited annotation类型是被标注过的class的子类所继承。类并不从它所实现的接口继承annotation,方法并不从它所重载的方法继承annotation。
第三方注解
常见的有Spring,SpringBoot,Dubbo等等框架的注解
自定义注解
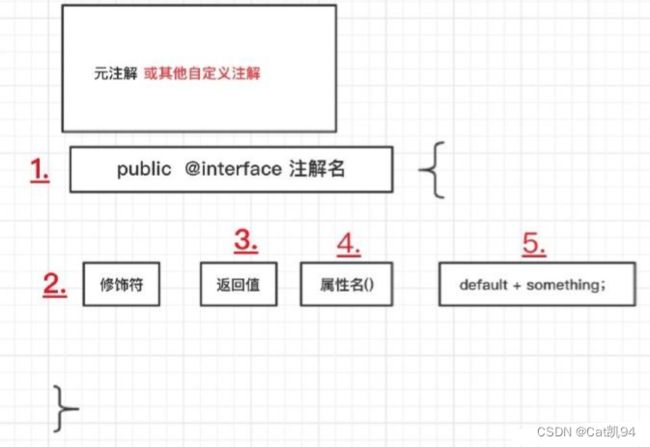
使用JDK中一些元注解,@Target,@Retention,@Document,@Inherited来修饰注解。具体格式如下:
/**
* 修饰符 @interface 注解名 {
* 注解元素的声明1
* 注解元素的声明2
* }
* 修饰符:访问修饰符必须为public,不写默认为pubic;
* 关键字:必须为@interface;
* 注解名: 注解名称为自定义注解的名称,使用时还会用到;
* 注解类型元素:注解类型元素是注解中内容,可以理解成自定义接口的实现部分;
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
/**
* 注解的元素声明的两种形式
* type elementName();
* type elementName() default value;
*/
String value() default "test";
}
- 修饰符: 访问修饰符必须为public,不写默认为pubic
- 关键字: 关键字为@interface
- 注解名称: 注解名称为自定义注解的名称,使用时还会用到
- 注解内容: 注解中内容,对注解的描述
举例
默认字符串注解
- 定义注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
String value() default "test";
}
- 配置注解
@Data
@Builder
@MyTestAnnotation
public class MyBean {
private String name;
private int age;
}- 利用反射解析注解
public class MyTest {
//isAnnotationPresent:判断当前元素是否被指定注解修饰
//getAnnotation:返回指定的注解
//getAnnotations:返回所有的注解
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//获取MyBean的Class对象
MyBean myBean = MyBean.builder().build();
Class clazz = myBean.getClass();
//判断myBean对象上是否有MyTestAnnotation注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyTestAnnotation.class)) {
System.out.println("MyBean类上配置了MyTestAnnotation注解!");
//获取该对象上MyTestAnnotation类型的注解
MyTestAnnotation myTestAnnotation = (MyTestAnnotation) clazz.getAnnotation(MyTestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myTestAnnotation.value());
} else {
System.out.println("MyBean类上没有配置MyTestAnnotation注解!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//结果
//Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:62125', transport: 'socket'
//MyBean类上配置了MyTestAnnotation注解!
//test
//Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:62125', transport: 'socket'
实现指定包名称扫描注解
结果示例:
@RpcComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.xlfc.consumer"})
可以扫描com.xlfc.consumer包下的所有类
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(CustomScannerRegistrar.class)//Spring框架下的注解
@Documented
public @interface RpcComponentScan {
String[] basePackages();
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
Class[] value();
}- 自定义扫描类的方法
public class CustomScannerRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware {
private static final String SPRING_BEAN_BASE_PACKAGE="com.xlfc";
private static final String BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME="basePackages";
private static final Class annotationClass = RpcComponentScan.class;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader=resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) {
CustomScanner rpcServiceScanner=new CustomScanner(beanDefinitionRegistry, Service.class);
CustomScanner springBeanScanner=new CustomScanner(beanDefinitionRegistry, Component.class);
if (resourceLoader!=null){
rpcServiceScanner.setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
springBeanScanner.setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
String[] packageToScan=getPackageToScan(annotationMetadata);
//其实就是扫描包下面有这些注解的类,将其加入到容器中后才可以使用。
springBeanScanner.scan(SPRING_BEAN_BASE_PACKAGE);
rpcServiceScanner.scan(packageToScan);
}
/**
* 获取到需要扫描的内容
* */
private String[] getPackageToScan(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
String[] packageToScan=new String[0];
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(
annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(annotationClass.getName()));//可见DubboComponentScanRegistrar的getPackagesToScan0方法
if (attributes!=null){
packageToScan=attributes.getStringArray(BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
}
//说明是没有扫描的
if (packageToScan.length==0){
packageToScan=new String[]{((StandardAnnotationMetadata)annotationMetadata).getIntrospectedClass().getPackage().getName()};
}
return packageToScan;
}
}