从零学 spring cloud第2-1课:基础 Web 开发
JSON返回
目前JSON 对象的使用在web开发中是最多的,我就不在这解释JSON是什么 了,下面直接上DEMO好了。我们创建一个项目,依然是使用 web方式,版本选择2.1.5。DEMO源码:https://github.com/heyu52/-spring-cloud。
在我的项目文件里创建一个包,命名为model,再创建一个包,命名为web。我们在model文件夹中创建一个类,类名为User
package com.cnblogs.demo.model;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return ("name=" + this.name + ",age=" + this.age + ",pass=" + this.sex);
}
}
我们在web包中新增一个Controller,命名为WebController
package com.cnblogs.demo.web;
import com.cnblogs.demo.model.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class WebController {
@RequestMapping(name="/getUser", method= RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser() {
User user=new User();
user.setName("csdn");
user.setAge(20);
user.setSex("男");
return user;
}
}
测试我们的方法
浏览器
运行程序,我们在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/getUser
如果你是用IE11,那么你会得到:

如果在谷歌浏览器中,那你会直接得到显示的结果:

如果你按F12,然后再按F5刷新页面,点开network,再点getuser

自己体会一下,这是多好友好的返回。
刚才我们代码中,使用了@RequestMapping(name="/getUser", method= RequestMethod.GET),
我们现在看看RequestMethod里面还有哪些
public enum RequestMethod {
GET,
HEAD,
POST,
PUT,
PATCH,
DELETE,
OPTIONS,
TRACE;
private RequestMethod() {
}
}
Post方式
我们最常用的,就是GET和POST这两种方式了。现在我们直接将GET改为POST,运行程序,刷新浏览器看一下
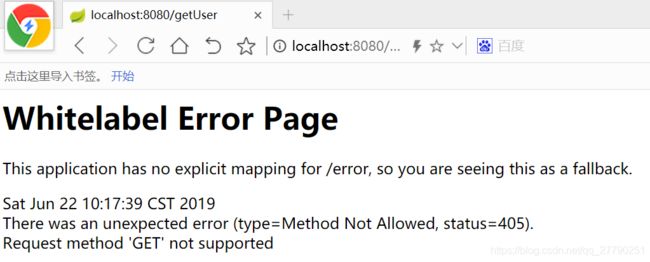
我们注意最后一行“Request method ‘GET’ not supported”,因为我们的方法设定只能使用POST方式访问了,现在我们使用上节安装的工具postman来调用它。
Postman
我们接下来使用Postman来调用它

我们就能看到我们的结果了。如果代码中是Get那我们上面也选用Get就好了。
测试类
我们在项目的test文件夹中,在项目文件包中再新建一个包web,新建一个测试类:WebControllerTest
代码如下:
package com.cnblogs.demo.web;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
@SpringBootTest
public class WebControllerTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new WebController()).build();
}
@Test
public void getUser() throws Exception {
String responseString = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/getUser"))
.andReturn().getResponse().getContentAsString();
System.out.println("result : "+responseString);
}
}
我们用鼠标在getUser中右键点一下,在弹出的菜单中,我们选择“运行’getUser’”
注意控制台输出
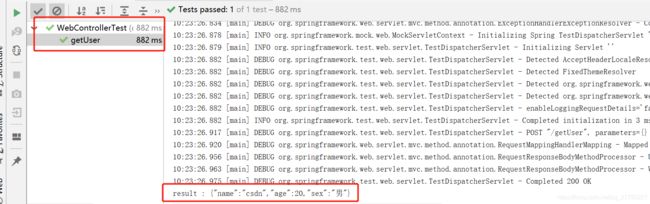
到底选择get还是post,还是说都支持,那要看具体的需求了没有固定死的。如果你把method= RequestMethod.POST删除,变成@RequestMapping(name="/getUser")那你是可以同时使用get和post方法调用的。
同时返回多个对象的集合
我们在webcontroler中新增一个getUsers的方法
@RequestMapping("/getUsers")
public List getUsers() {
List users=new ArrayList();
User user1=new User();
user1.setName("csdn001");
user1.setAge(10);
user1.setSex("男");
users.add(user1);
User user2=new User();
user2.setName("csdn002");
user2.setAge(20);
user2.setSex("男");
users.add(user2);
return users;
}
运行程序,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/getUsers
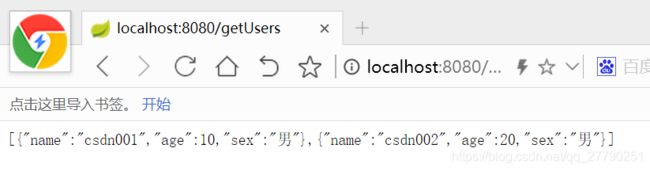
我们可以看到返回的是一个数组了。
优雅传参
一般传参数,一般用"? 参数=参数值"这种方式,现在也有一种"参数/参数值"的方式。
我们在webcontroller 中新增方法
@RequestMapping(name="/getUserName", method= RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUserName(String name) {
return "这是我传入的参数:"+name ;
}
运行程序,在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/getUserName?name=csdn
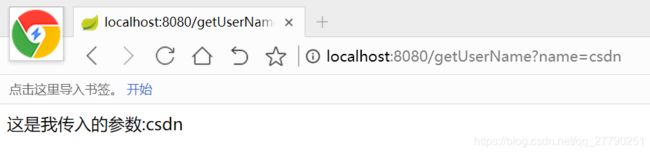
这就是第一种传参方式,接下来我们试第二种
@RequestMapping(value="getName/{name}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String get(@PathVariable String name) {
return "这是我传入的参数:"+name ;
}
运行程序,在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/getName/csdn

看个人喜欢好吧,我这里推荐第二种。