【高阶数据结构】——并查集
文章目录
- 并查集的原理
- 并查集的实现
- 并查集的应用
并查集的原理
在一些应用问题中,需要将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个单元素集合, 然后按一定的规律将归于同一组元素的集合合并。在此过程中要反复用到查询某一个元素归属于那个集合的运算。适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为
并查集(union-find set)。
并查集建立映射关系的一种方法:
template <class T>
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(const T* a, size_t n)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// 建立映射关系
_a.push_back(a[i]);
_indexMap[a[i]] = i;
}
}
private:
vector<T> _a; //编号找人
map<T, int> _indexMap; //人找编号
};
举个栗子:
比如:某公司今年校招全国总共招生10人,西安招4人,成都招3人,武汉招3人,10个人来自不同的学校,起先互不相识,每个学生都是一个独立的小团体,现给这些学生进行编号:{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 给以下数组用来存储该小集体,数组中的数字代表:该小集体中具有成员的个数。(负号下文解释)
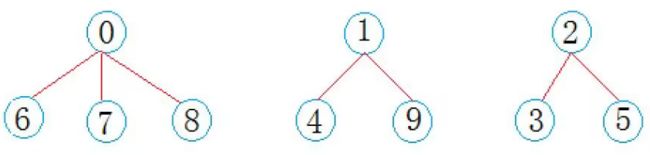
毕业后,学生们要去公司上班,每个地方的学生自发组织成小分队一起上路,于是:西安学生小分队 s1={0,6,7,8},成都学生小分队 s2={1,4,9},武汉学生小分队 s3={2,3,5} 就相互认识了,10个人形成了三个小团体。假设右三个群主0,1,2担任队长,负责大家的出行。
一趟火车之旅后,每个小分队成员就互相熟悉,称为了一个朋友圈。
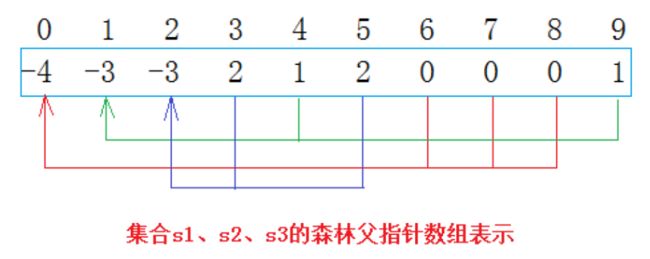
从上图可以看出:编号6,7,8同学属于0号小分队,该小分队中有4人(包含队长0);编号为4和9的同学属于1号小分队,该小分队有3人(包含队长1),编号为3和5的同学属于2号小分队,该小分队有3个人(包含队长1)。仔细观察数组中内融化,可以得出以下结论:
- 数组的下标对应集合中元素的编号
- 数组中如果为负数,负号代表根,数字代表该集合中元素个数
- 数组中如果为非负数,代表该元素双亲在数组中的下标
现在0集合有7个人,2集合有3个人,总共两个朋友圈。
通过以上例子可知,并查集一般可以解决一下问题:
- 查找元素属于哪个集合
沿着数组表示树形关系以上一直找到根(即:树中中元素为负数的位置) - 查看两个元素是否属于同一个集合
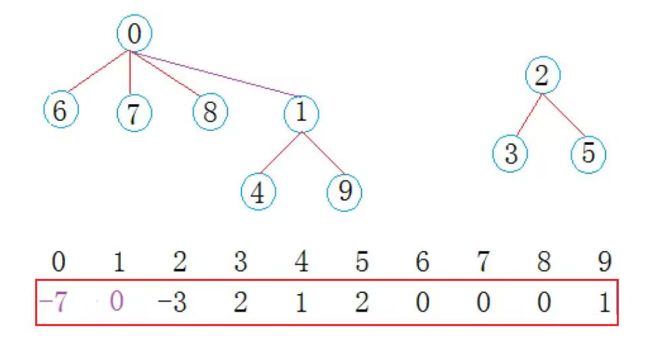
沿着数组表示的树形关系往上一直找到树的根,如果根相同表明在同一个集合,否则不在 - 将两个集合归并成一个集合
将两个集合中的元素合并
将一个集合名称改成另一个集合的名称 - 集合的个数
遍历数组,数组中元素为负数的个数即为集合的个数。
并查集的实现
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(int size)
:_set(size, -1)
{}
//查询
size_t FindRoot(int x)
{
int root = x;
while (_set[root] >= 0)
{
root = _set[root];
}
//压缩路径(优化)
while (_set[x] >= 0)
{
int parent = _set[x];
_set[x] = root;
x = parent;
}
return root;
}
//合并两个集合
void Union(int x1, int x2)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
if (root1 != root2) //不属于一个集合,将二者合并
{
//将节点少的集合合并到节点多的集合当中(优化)
if (abs(_set[root1]) < abs(_set[root2]))
swap(root1, root2);
_set[root1] += _set[root2];
_set[root2] = root1;
}
}
// 判断x1和x2是否在同一个集合中
bool Insert(int x1, int x2)
{
return FindRoot(x1) == FindRoot(x2);
}
//查看set中有多少对集合
size_t SetCount()
{
size_t cnt = 0;
for (auto e : _set)
if (e < 0) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
private:
vector<int> _set;
};
并查集的应用
省份数量
//并查集代码
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
UnionFindSet ufs(isConnected.size());
for(size_t i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); i++)
{
for(size_t j = 0; j < isConnected[i].size(); j++)
{
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1)
ufs.Union(i,j);
}
}
return ufs.SetCount();
}
};
当我们没有实现并查集时,其实也是可以直接使用数组模拟的。
class Solution {
public:
size_t FindRoot(int x)
{
while(ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = ufs[x];
}
return x;
}
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
ufs.resize(isConnected.size(), -1);
for(int i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < isConnected[i].size(); j++)
{
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(i);
int root2 = FindRoot(j);
if(root1 != root2)
{
if(abs(ufs[root1]) < abs(ufs[root2]))
swap(root1, root2);
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
}
int cnt = 0;
for(auto& e : ufs)
if(e < 0) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
private:
vector<int> ufs;
};
等式方程的可满足性
class Solution {
public:
int Find(int x)
{
while(ufs[x] >= 0)
x = ufs[x];
return x;
}
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations) {
ufs.resize(26, -1);
for(auto& str : equations)
{
if(str[1] == '=')
{
int root1 = Find(str[0]-'a');
int root2 = Find(str[3]-'a');
if(root1 != root2)
{
if(abs(ufs[root1]) < abs(ufs[root2]))
swap(root1, root2);
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
for(auto& str : equations)
{
if(str[1] == '!')
{
int root1 = Find(str[0]-'a');
int root2 = Find(str[3]-'a');
if(root1 == root2)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private:
vector<int> ufs;
};