Flink AggregateFunction窗口函数,merge何时执行
1.前言
在我们使用Flink DataStream API编写业务代码时,aggregate()算子和AggregateFunction无疑是非常常用的。编写一个AggregateFunction需要实现4个方法:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.flink.api.common.functions;
import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* The {@code AggregateFunction} is a flexible aggregation function, characterized by the following
* features:
*
*
* - The aggregates may use different types for input values, intermediate aggregates, and
* result type, to support a wide range of aggregation types.
*
- Support for distributive aggregations: Different intermediate aggregates can be merged
* together, to allow for pre-aggregation/final-aggregation optimizations.
*
*
* The {@code AggregateFunction}'s intermediate aggregate (in-progress aggregation state) is
* called the accumulator. Values are added to the accumulator, and final aggregates are
* obtained by finalizing the accumulator state. This supports aggregation functions where the
* intermediate state needs to be different than the aggregated values and the final result type,
* such as for example average (which typically keeps a count and sum). Merging intermediate
* aggregates (partial aggregates) means merging the accumulators.
*
*
The AggregationFunction itself is stateless. To allow a single AggregationFunction instance to
* maintain multiple aggregates (such as one aggregate per key), the AggregationFunction creates a
* new accumulator whenever a new aggregation is started.
*
*
Aggregation functions must be {@link Serializable} because they are sent around between
* distributed processes during distributed execution.
*
*
Example: Average and Weighted Average
*
* {@code
* // the accumulator, which holds the state of the in-flight aggregate
* public class AverageAccumulator {
* long count;
* long sum;
* }
*
* // implementation of an aggregation function for an 'average'
* public class Average implements AggregateFunction {
*
* public AverageAccumulator createAccumulator() {
* return new AverageAccumulator();
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator merge(AverageAccumulator a, AverageAccumulator b) {
* a.count += b.count;
* a.sum += b.sum;
* return a;
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator add(Integer value, AverageAccumulator acc) {
* acc.sum += value;
* acc.count++;
* return acc;
* }
*
* public Double getResult(AverageAccumulator acc) {
* return acc.sum / (double) acc.count;
* }
* }
*
* // implementation of a weighted average
* // this reuses the same accumulator type as the aggregate function for 'average'
* public class WeightedAverage implements AggregateFunction {
*
* public AverageAccumulator createAccumulator() {
* return new AverageAccumulator();
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator merge(AverageAccumulator a, AverageAccumulator b) {
* a.count += b.count;
* a.sum += b.sum;
* return a;
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator add(Datum value, AverageAccumulator acc) {
* acc.count += value.getWeight();
* acc.sum += value.getValue();
* return acc;
* }
*
* public Double getResult(AverageAccumulator acc) {
* return acc.sum / (double) acc.count;
* }
* }
* }
*
* @param The type of the values that are aggregated (input values)
* @param The type of the accumulator (intermediate aggregate state).
* @param The type of the aggregated result
*/
@PublicEvolving
public interface AggregateFunction extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* Creates a new accumulator, starting a new aggregate.
*
* The new accumulator is typically meaningless unless a value is added via {@link
* #add(Object, Object)}.
*
*
The accumulator is the state of a running aggregation. When a program has multiple
* aggregates in progress (such as per key and window), the state (per key and window) is the
* size of the accumulator.
*
* @return A new accumulator, corresponding to an empty aggregate.
*/
ACC createAccumulator();
/**
* Adds the given input value to the given accumulator, returning the new accumulator value.
*
*
For efficiency, the input accumulator may be modified and returned.
*
* @param value The value to add
* @param accumulator The accumulator to add the value to
* @return The accumulator with the updated state
*/
ACC add(IN value, ACC accumulator);
/**
* Gets the result of the aggregation from the accumulator.
*
* @param accumulator The accumulator of the aggregation
* @return The final aggregation result.
*/
OUT getResult(ACC accumulator);
/**
* Merges two accumulators, returning an accumulator with the merged state.
*
*
This function may reuse any of the given accumulators as the target for the merge and
* return that. The assumption is that the given accumulators will not be used any more after
* having been passed to this function.
*
* @param a An accumulator to merge
* @param b Another accumulator to merge
* @return The accumulator with the merged state
*/
ACC merge(ACC a, ACC b);
}
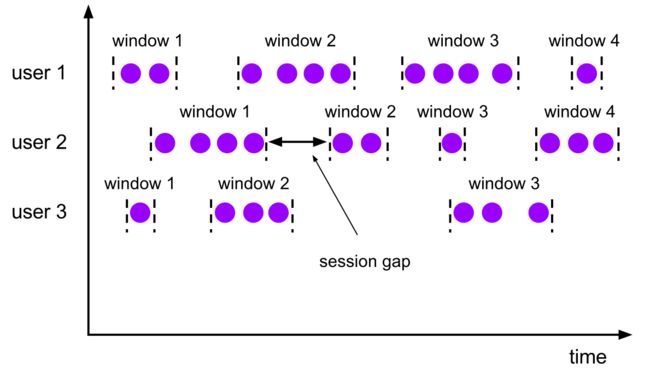
前三个方法都很容易理解,但第四个merge()方法就有些令人费解了:到底什么时候需要合并两个累加器的数据呢?最近也有童鞋问到了这个问题。实际上,这个方法是专门为会话窗口(session window)服务的。下面来解析一下会话窗口。
Session Window & MergingWindowAssigner
stream.keyBy("userId").window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(gap)))
在普通的翻滚窗口和滑动窗口中,窗口的范围是按时间区间固定的,虽然范围有可能重合,但是处理起来是各自独立的,并不会相互影响。但是会话窗口则不同,其范围是根据事件之间的时间差是否超过gap来确定的(超过gap就形成一个新窗口),也就是说并非固定。所以,我们需要在每个事件进入会话窗口算子时就为它分配一个初始窗口,起点是它本身所携带的时间戳(这里按event time处理),终点则是时间戳加上gap的偏移量。这样的话,如果两个事件所在的初始窗口没有相交,说明它们属于不同的会话;如果相交,则说明它们属于同一个会话,并且要把这两个初始窗口合并在一起,作为新的会话窗口。多个事件则依次类推,最终形成上面图示的情况。
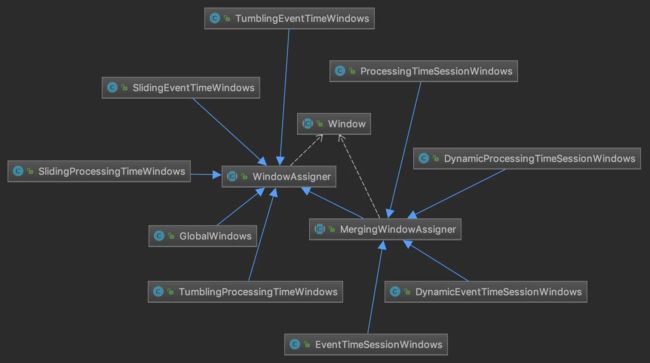
为了支持会话窗口的合并,它们的WindowAssigner也有所不同,称为MergingWindowAssigner,如下类图所示。
MergingWindowAssigner是一个抽象类,代码很简单,定义了用于合并窗口的mergeWindows()方法以及合并窗口时的回调MergeCallback。
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners;
import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.windows.Window;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* A {@code WindowAssigner} that can merge windows.
*
* @param The type of elements that this WindowAssigner can assign windows to.
* @param The type of {@code Window} that this assigner assigns.
*/
@PublicEvolving
public abstract class MergingWindowAssigner extends WindowAssigner {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* Determines which windows (if any) should be merged.
*
* @param windows The window candidates.
* @param callback A callback that can be invoked to signal which windows should be merged.
*/
public abstract void mergeWindows(Collection windows, MergeCallback callback);
/**
* Callback to be used in {@link #mergeWindows(Collection, MergeCallback)} for specifying which
* windows should be merged.
*/
public interface MergeCallback {
/**
* Specifies that the given windows should be merged into the result window.
*
* @param toBeMerged The list of windows that should be merged into one window.
* @param mergeResult The resulting merged window.
*/
void merge(Collection toBeMerged, W mergeResult);
}
}
所有MergingWindowAssigner实现类的mergeWindows()方法都是相同的,即直接调用TimeWindow.mergeWindows()方法。