SPP、SPPF 、 SimSPPF 、 ASPP、 SPPCSPC详解
分享自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43694096/article/details/126354660
1. 原理
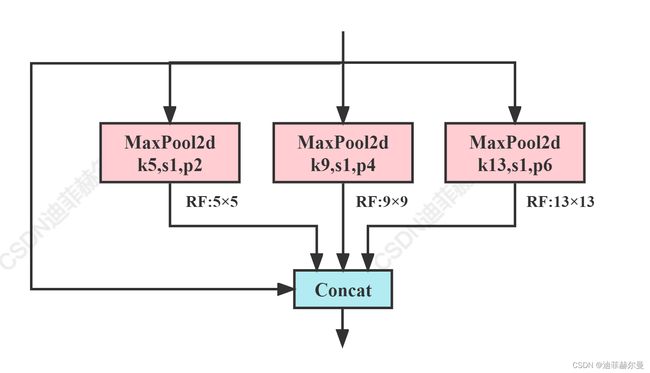
1.1 SPP(Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
SPP 模块是何凯大神在2015年的论文《Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolution Networks for Visual Recognition》中提出来的.
SPP全称为空间金字塔池化结构,主要是为了解决两个问题
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) layer https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))
1.2 SPPF (Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast)
这个是Yolov5作者基于SPP提出的,速度较SPP快很多(2.5倍),所以叫做SPP-Fast
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))
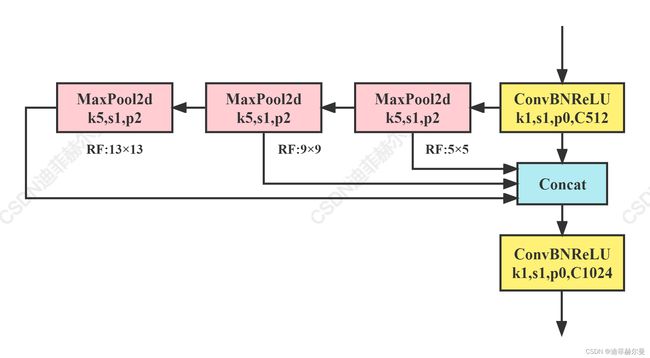
1.3 SimSPPF(Simplified SPPF)
美团YOLOv6提出的模块,感觉和SPPF只差了一个激活函数,简单测试了一下,单个ConvBNReLU速度比ConvBNSiLU快18%
class SimConv(nn.Module):
'''Normal Conv with ReLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, groups=1, bias=False):
super().__init__()
padding = kernel_size // 2
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
bias=bias,
)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.act = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class SimSPPF(nn.Module):
'''Simplified SPPF with ReLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5):
super().__init__()
c_ = in_channels // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = SimConv(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = SimConv(c_ * 4, out_channels, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))
1.4 ASPP (Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
受到SPP的启发,语义分割模型DeepLabv2中提出了ASPP模块(空洞空间金字塔池化),该模块使用具有不同采样率的多个并行空洞卷积·。为每个采样率提取的特征在单独的分支中进一步处理,并融合以生成最终的结果。该模块通过不同的空洞率构建不同的感受野的卷积核,用来获取多尺度物体信息,具体结构比较简单如下图所示:

ASPP 是在DeepLab中提出来的,在后续的DeepLab版本中对其做了改进,如加入BN层,加入深度可分离卷积等,但基本的思路还是没变。
# without BN version
class ASPP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel=512, out_channel=256):
super(ASPP, self).__init__()
self.mean = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # (1,1)means ouput_dim
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,out_channel, 1, 1)
self.atrous_block1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 1, 1)
self.atrous_block6 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, padding=6, dilation=6)
self.atrous_block12 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, padding=12, dilation=12)
self.atrous_block18 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, padding=18, dilation=18)
self.conv_1x1_output = nn.Conv2d(out_channel * 5, out_channel, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
size = x.shape[2:]
image_features = self.mean(x)
image_features = self.conv(image_features)
image_features = F.upsample(image_features, size=size, mode='bilinear')
atrous_block1 = self.atrous_block1(x)
atrous_block6 = self.atrous_block6(x)
atrous_block12 = self.atrous_block12(x)
atrous_block18 = self.atrous_block18(x)
net = self.conv_1x1_output(torch.cat([image_features, atrous_block1, atrous_block6,
atrous_block12, atrous_block18], dim=1))
return net
1.5 RFB(Receptive Field Block)
RFB模块是在《ECCV2018:Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection》一文中提出的,该文的出发点是模拟人类视觉的感受野从而加强网络的特征提取能力,在结构RFV借鉴了Inception的思想,主要是在Inception的基础上加入了空洞卷积,从而有效增大了感受野。
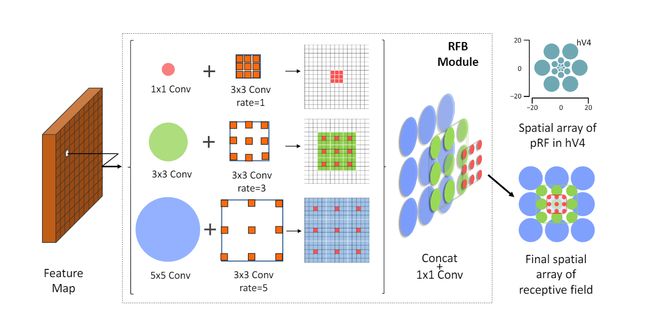

RFB和RFB-s的架构,RFB-s用于浅层人类视网膜主题图中模拟较小的pRF,使用具有较小内核的更多分支。
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, relu=True, bn=True):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.out_channels = out_planes
if bn:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.01, affine=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else None
else:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True)
self.bn = None
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else None
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
if self.bn is not None:
x = self.bn(x)
if self.relu is not None:
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class BasicRFB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, scale=0.1, map_reduce=8, vision=1, groups=1):
super(BasicRFB, self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
self.out_channels = out_planes
inter_planes = in_planes // map_reduce
self.branch0 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=groups, relu=False),
BasicConv(inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=stride, padding=(1, 1), groups=groups),
BasicConv(2 * inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=vision + 1, dilation=vision, relu=False, groups=groups)
)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=groups, relu=False),
BasicConv(inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=stride, padding=(1, 1), groups=groups),
BasicConv(2 * inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=vision + 2, dilation=vision + 2, relu=False, groups=groups)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=groups, relu=False),
BasicConv(inter_planes, (inter_planes // 2) * 3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, groups=groups),
BasicConv((inter_planes // 2) * 3, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=groups),
BasicConv(2 * inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=vision + 4, dilation=vision + 4, relu=False, groups=groups)
)
self.ConvLinear = BasicConv(6 * inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, relu=False)
self.shortcut = BasicConv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, relu=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
def forward(self, x):
x0 = self.branch0(x)
x1 = self.branch1(x)
x2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((x0, x1, x2), 1)
out = self.ConvLinear(out)
short = self.shortcut(x)
out = out * self.scale + short
out = self.relu(out)
return out
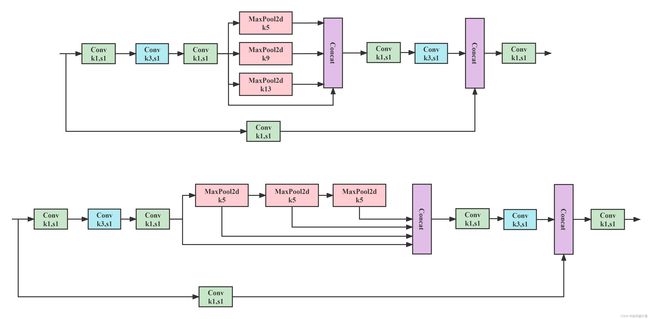
1.6 SPPCSPC
该模块是YOLOv7中使用的SPP结构,表现优于SPPF,但参数量和计算量提升了很多。
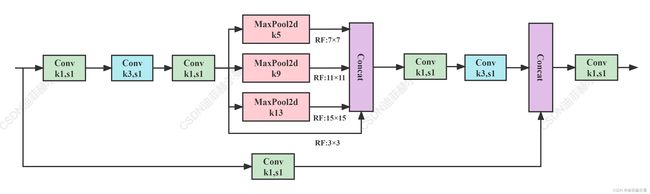
class SPPCSPC(nn.Module):
# CSP https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPPCSPC, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1] + [m(x1) for m in self.m], 1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))
#分组SPPCSPC 分组后参数量和计算量与原本差距不大,不知道效果怎么样
class SPPCSPC_group(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPPCSPC_group, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g=4)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g=4)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1, g=4)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1] + [m(x1) for m in self.m], 1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))
1.7 SPPFCSPC
借鉴了SPPF的思想将SPPCSPC优化了一下,得到了SPPFCSPC,在保持感受野不变的情况下获得速度提升;
目前这个结构被YOLOv6 3.0版本使用了,效果很不错,大家可以看YOLOv6 3.0的论文,里面有详细的实验结果。
class SPPFCSPC(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=5):
super(SPPFCSPC, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
x2 = self.m(x1)
x3 = self.m(x2)
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat((x1,x2,x3, self.m(x3)),1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))
2. 参数量对比
这里以yolov5s.yaml中使用各个模型替换SPP模块
3. 改进方式
- (1) : 各个代码放入
common.py中 - (2):
yolo.py中加入类名 - (3): 修改
配置文件
yolov5配置文件如下:
# YOLOv5 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
# [-1, 1, ASPP, [512]], # 9
# [-1, 1, SPP, [1024]],
# [-1, 1, SimSPPF, [1024, 5]],
# [-1, 1, BasicRFB, [1024]],
# [-1, 1, SPPCSPC, [1024]],
# [-1, 1, SPPFCSPC, [1024, 5]], #
]
4 Issue
Q Why use SPPCPC instead of SPPFCSPC
yolov5’s SPPF is much faster than SPP
why not try to replace SPPCSPC with SPPFCSPC:
A: Max pooling uses very few compution,if you programing well, above one could run three max pool layers in parallel, while below one must process thress max pool layers sequentially
By the way,you could replace SPPCSPC by SPPFCSPC at inference time if your hardware is fridndly to SPPFCSPC