Java中Stream的 flatMap 与 map 实际使用场景与区别对比
基本概念
Stream 流式操作,一般用于操作集合即 List 一类的数据结构,JDK 1.8 后的新特性
Stream 中的 map
一般用于对List 中的每一个元素执行指定方法使得最终结果为最终的集合为每一个记录的某一属性的集合(get 方法)或者通过自定义的转换方法等通过方法的加工将每一个元素处理为另一种元素最终返回成为一种全新元素的集合,即 简单来说 Stream 的 map 使得其中的元素转为另一种元素的映射(map)方法。
Stream 中的 flatMap
flat (扁平化)
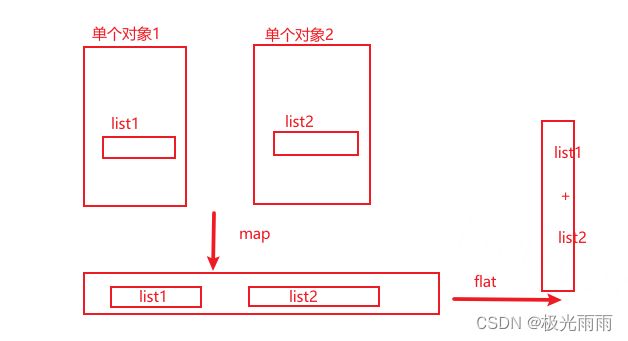
当我们处理某一个集合时,这个集合中的某一个属性依旧是一个集合即 类似于二维数组可以如下理解:
我们定义一个人的类,每个人又有很多衣服,衣服也定义一个类,所以可以如下定义:

如果我们处理一个人的List 集合,并想把所有人的 服装List 合并到一起时就可以使用 flatMap
案例如下:
List<Clothes> clothesList1 = new ArrayList<>();
clothesList1.add(new Clothes("大衣"));
clothesList1.add(new Clothes("外套"));
List<Clothes> clothesList2 = new ArrayList<>();
clothesList2.add(new Clothes("衬衣"));
clothesList2.add(new Clothes("短袖"));
// 第一个人
HumanBeing humanBeing = new HumanBeing();
humanBeing.setClothesList(clothesList1);
// 第二个人
HumanBeing humanBeing2 = new HumanBeing();
humanBeing2.setClothesList(clothesList2);
List<HumanBeing> humanBeingList = new ArrayList<>();
humanBeingList.add(humanBeing);
humanBeingList.add(humanBeing2);
// flatMap 执行
List<Clothes> collect = humanBeingList.stream()
.flatMap(aPerson -> aPerson.getClothesList().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// map 执行
List<List<Clothes>> collect1 = humanBeingList.stream()
.map(item -> item.getClothesList())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("collect = " + collect);
结果如下:
collect1 = [[Clothes(name=大衣, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null), Clothes(name=外套, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null)], [Clothes(name=衬衣, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null), Clothes(name=短袖, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null)]]
collect = [Clothes(name=大衣, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null), Clothes(name=外套, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null), Clothes(name=衬衣, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null), Clothes(name=短袖, type=null, price=0.0, weight=0.0, size=null)]
可以看的出我们最终的结果中 flatMap 将每一个人的衣服集合合并到了一个集合中。而 普通的map 只是将多个List 加入到了一个 List 相当于一个二维数组。
flatMap 可以看做两个流程,先执行 普通的map,然后执行 flat 扁平化过程,可以如图理解如下: