ROS1代码向ROS2移植
ROS1代码向ROS2移植
- 前言
- 安装ros2 foxy
- 配置vscode
- ros2基本操作
-
- 创建工作空间
- 添加工作空间环境变量
- 创建ros2功能包
- 安装第三方功能包
- 节点相关指令
- 功能包内相关文件注解
-
- cmakelist.txt文件注解
- package.xml文件注解
- ros1代码向ros2移植技巧
前言
由于ros2的种种优点,特别是通信和节点去中心化的优点,我们团队决定将我们的代码从ros1移植到ros2,我们选择的ros2版本为foxy,ubuntu环境为20.04,现在记录以下移植大概过程。本博客内容将不定期更新。
这里列举一些ros2的学习教程:
鱼香ros B站教学视频.
ros2官方文档.
ros2功能包
创客制造ros2教程
古月居ros2代码移植
安装ros2 foxy
可以使用鱼香ros一键配置ros环境,配置前记得将系统的源设置为国内源(清华源、中科大、阿里云等),鱼香ros一键安装ros2.
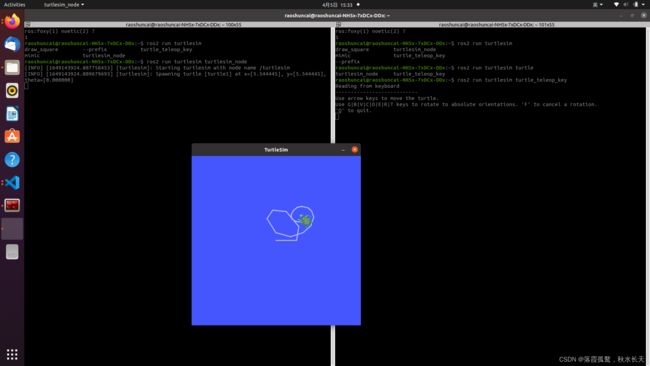
安装完后可以用小乌龟测试一下安装效果:
ros2 run turtlesim turtlesim_node
ros2 run turtlesim turtle_teleop_key
配置vscode
这里就不将怎么安装vscode了,正常下载安装即可。使用vscode的目的只是为了写代码时可以有提示,更方便,不使用vscode也可以。
配置vscode主要包括安装插件,主要安装以下插件:
python;c/c++:对应编程语言解释器
Chinese (Simplified) (简体中文) Language Pack for Visual Studio Code:汉化插件
ros:ros1插件
这里不推荐安装ros2插件,不太好用。
ros2基本操作
创建工作空间
mkdir -p ~/my_workspace/src
cd ~/my_workspace
colcon build
用上面的三句话就可以初始化一个工作空间,在ros2中,没有了catkin功能包。ros2的编译工具是colcon,但安装ros2时默认是不安装colcon的,因此要安装colcon:
sudo apt-get install python3-colcon-common-extensions
只编译一个功能包:
colcon build --packages-select easy_planner
添加工作空间环境变量
和ros1不同,ros2添加环境变量是用下面的命令:
cd ~/my_workspace
source install/setup.bash
创建ros2功能包
创建功能包用以下命令:
ros2 pkg create <功能包名> --build-type {cmake,ament_cmake,ament_python} --dependencies <依赖名>
安装第三方功能包
sudo apt install ros-[版本]-[功能包名]
这里的版本用系统当前环境变量ros版本代替,功能包名就是要安装的功能包的名字,比如我想安装ros2版本foxy的gazebo-ros功能包,则用下面的语句:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros
节点相关指令
ros2 node list //查看节点列表
功能包内相关文件注解
cmakelist.txt文件注解
先通过注释的方式解释一下功能包cmakelist.txt文件里的代码功能。
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5) //指定cmake版本
project(easy_planner) //指定功能包名称
# Default to C99
if(NOT CMAKE_C_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 99)
endif()
# Default to C++14
if(NOT CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
endif()
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(std_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(geometry_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(nav_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(tf2 REQUIRED)
find_package(tf2_ros REQUIRED) //这些都是当前功能包依赖的其他外部功能包,
//编译时,如果A功能包依赖了B功能包,
//那就会先编译B功能包
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# uncomment the line when a copyright and license is not present in all source files
#set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# uncomment the line when this package is not in a git repo
#set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
include_directories( //指定头文件目录,当前头文件目录为功能包下的include目录
include
)
add_executable(easy_planner1 src/easy_planner.cpp src/DStarPlanner.cpp) //重点是下面这几个语句,这个语句是将cpp文件编译成为一个可执行文件,第一个参数即为可执行文件名,第二三个参数是互相关联的两个cpp文件,编译时,它们将编译成一个文件。
ament_target_dependencies(easy_planner1 rclcpp std_msgs geometry_msgs nav_msgs tf2 tf2_ros) //指定可执行文件的依赖,比如说这里说的是easy_planner1依赖rclcpp、std_msgs等文件
add_executable(easy_planner2 src/easy_planner1.cpp src/DStarPlanner.cpp) //同上
ament_target_dependencies(easy_planner2 rclcpp std_msgs geometry_msgs nav_msgs tf2 tf2_ros)
install(TARGETS
easy_planner1
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}) //这里是将编译完的可执行文件放到工作空间install目录下
//如果没放到这个目录下,导入工作空间环境变量之后就可能找不到这个可执行文件。
install(TARGETS
easy_planner2
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
ament_package()
package.xml文件注解
再通过注释的方式讲一下package.xml文件的代码功能:
<?xml version="1.0"?> //xml版本
<package format="2">
<name>ugvc_planner</name> //功能包名
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>The ugvc_planner package</description> //功能包描述
<!-- One maintainer tag required, multiple allowed, one person per tag -->
<!-- Example: -->
<!-- <maintainer email="[email protected]">Jane Doe</maintainer> -->
<maintainer email="[email protected]">u5</maintainer>
//记录作者等信息
<!-- One license tag required, multiple allowed, one license per tag -->
<!-- Commonly used license strings: -->
<!-- BSD, MIT, Boost Software License, GPLv2, GPLv3, LGPLv2.1, LGPLv3 -->
<license>TODO</license>
<!-- Url tags are optional, but multiple are allowed, one per tag -->
<!-- Optional attribute type can be: website, bugtracker, or repository -->
<!-- Example: -->
<!-- <url type="website">http://wiki.ros.org/ugvc_localplanner</url> -->
<!-- Author tags are optional, multiple are allowed, one per tag -->
<!-- Authors do not have to be maintainers, but could be -->
<!-- Example: -->
<!-- <author email="[email protected]">Jane Doe</author> -->
<!-- The *depend tags are used to specify dependencies -->
<!-- Dependencies can be catkin packages or system dependencies -->
<!-- Examples: -->
<!-- Use depend as a shortcut for packages that are both build and exec dependencies -->
<!-- <depend>roscpp</depend> -->
<!-- Note that this is equivalent to the following: -->
<!-- <build_depend>roscpp</build_depend> -->
<!-- <exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend> -->
<!-- Use build_depend for packages you need at compile time: -->
<!-- <build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> -->
<!-- Use build_export_depend for packages you need in order to build against this package: -->
<!-- <build_export_depend>message_generation</build_export_depend> -->
<!-- Use buildtool_depend for build tool packages: -->
<!-- <buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> -->
<!-- Use exec_depend for packages you need at runtime: -->
<!-- <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend> -->
<!-- Use test_depend for packages you need only for testing: -->
<!-- <test_depend>gtest</test_depend> -->
<!-- Use doc_depend for packages you need only for building documentation: -->
<!-- <doc_depend>doxygen</doc_depend> -->
<buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> //对于这个文件,这些才是重点,当前功能包依赖了哪些其他功能包,都应该在这里列出来
<depend>roscpp</depend>
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
<depend>geometry_msgs</depend>
<depend>nav_msgs</depend>
<depend>tf</depend>
<!-- The export tag contains other, unspecified, tags -->
<export>
<!-- Other tools can request additional information be placed here -->
</export>
</package>
ros1代码向ros2移植技巧
下面我将通过我的移植经验向大家展示移植过程中的经验。
1、首先是现在ros2中文教程比较少,英文论坛里的内容也没有很多。很多ros2的中文教程都是英文直译而来,如果能看懂英文教程还是尽量区看英文教程: ros2官方文档.
2、有些功能我们如果没有找到对应教程,可以采用以下方法解决,这里举TF的例子。
在ros2中,TF的有些函数用法和ros1不太一样,比如下面的语句:
tf::StampedTransform transformB2O;
try
{
plistener.waitForTransform("/odom", "/base_link",
ros::Time::now(), ros::Duration(10.0));
plistener.lookupTransform("/odom", "/base_link",
ros::Time(0), transformB2O); // Global image
}
catch(tf::TransformException &ex)
{
ROS_ERROR("%s",ex.what());
ros::Duration(1.0).sleep();
continue;
}
这个语句就是用来订阅odom坐标系和base_link坐标系的TF的,但参考ros2官方教程,例程中只用了下面的语句:
geometry_msgs::msg::TransformStamped transformStamped;
// Look up for the transformation between target_frame and turtle2 frames
// and send velocity commands for turtle2 to reach target_frame
try {
transformStamped = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform(
toFrameRel, fromFrameRel,
tf2::TimePointZero);
} catch (tf2::TransformException & ex) {
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(), "Could not transform %s to %s: %s",
toFrameRel.c_str(), fromFrameRel.c_str(), ex.what());
return;
}
没有了waitForTransform函数。我试了一下,将这段代码替换原来的ros1的代码,发现终端总是会报下面的错误:
[turtle_tf2_listener_debug-4] [INFO] [1630223454.942322623] [listener_debug]: Could not transform odom to base_link: "odom" passed to lookupTransform argument target_frame does not exist
意思就是没收到odom到base_link的坐标转换,这就让我很迷惑,后面我又用了官方教程给的tf debug的教程:tf_debug,用
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo odom base_link
终端显示可以有数据输出,即odom到base_link的转换是存在的。
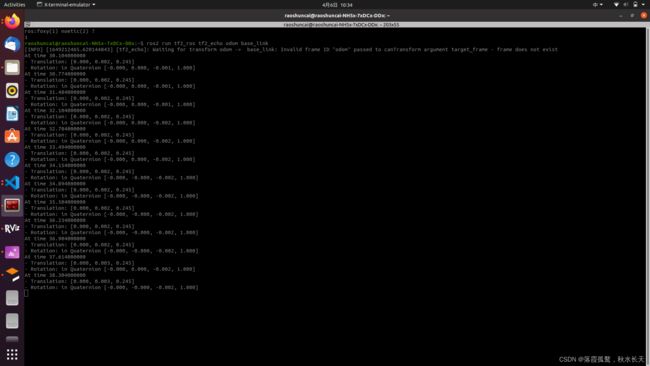
我找了好久,终于在一个论坛里找到了答案,原来是因为接受时间序不对。但找到了问题怎么解决呢。我想到了一个办法,既然tf2_ros功能包的tf2_echo工具可以接收TF,那就看一下tf2_echo的源码是怎么写的,学习一下就行了。
于是我就去找到了它的源码,寻找过程如下:
先进入ros wiki中,找到packages并进入:
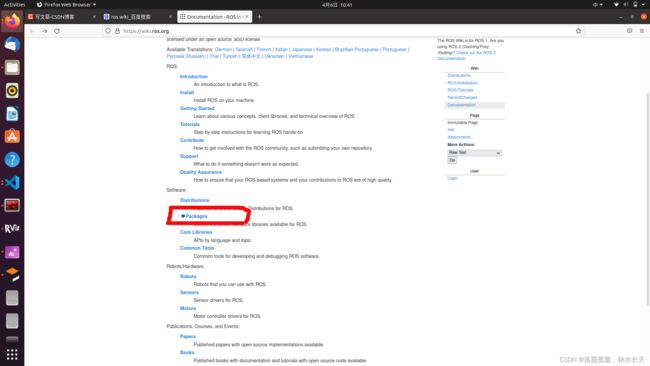
再在红线上的区域选择foxy,就可以找到foxy版本下的所有功能包,
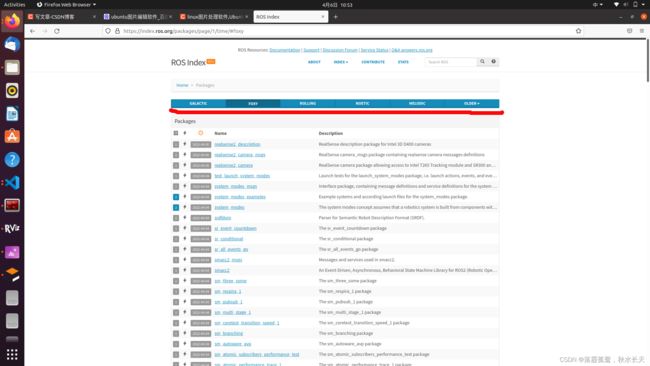 再在右上角的搜索栏输入tf2_ros就可以找到各个版本对应的tf2_ros功能包,选择foxy版本的进入:
再在右上角的搜索栏输入tf2_ros就可以找到各个版本对应的tf2_ros功能包,选择foxy版本的进入:
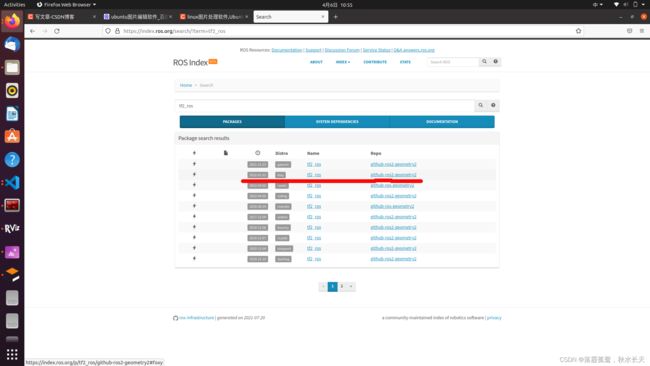 进入后在右边栏可以看到一个browse code,这个就是元源码入口,双击进入就可以看到tf2_ros功能包源码,我们找到tf2_echo实现代码,发现源码多了这部分,加入之后移植代码就可以接受TF数据了:
进入后在右边栏可以看到一个browse code,这个就是元源码入口,双击进入就可以看到tf2_ros功能包源码,我们找到tf2_echo实现代码,发现源码多了这部分,加入之后移植代码就可以接受TF数据了:
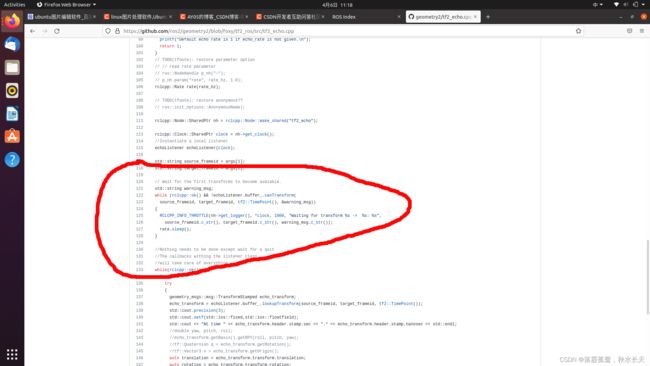
上面是第二个经验。