基于LDA主题模型文本分类
一、LDA整体思想
LDA主题模型主要用于推测文档的主题分布,可以将文档集中每篇文档的主题以概率分布的形式给出根据主题进行主题聚类或文本分类。LDA主题模型不关心文档中单词的顺序,通常使用词袋特征(bag-of-word feature)来代表文档。
LDA模型认为主题可以由一个词汇分布来表示,而文章可以由主题分布来表示。
比如有两个主题,美食和美妆。LDA说两个主题可以由词汇分布表示,他们分别是:
{面包:0.4,火锅:0.5,眉笔:0.03,腮红:0.07}
{眉笔:0.4,腮红:0.5,面包:0.03,火锅:0.07}
同样,对于两篇文章,LDA认为文章可以由主题分布这么表示:
《美妆日记》{美妆:0.8,美食:0.1,其他:0.1}
《美食探索》{美食:0.8,美妆:0.1,其他:0.1}
所以想要生成一篇文章,可以先以一定的概率选取上述某个主题,再以一定的概率选取那个主题下的某个单词,不断重复这两步就可以生成最终文章。
将文档集中每篇文档的主题以概率分布的形式给出,通过分析一些文档抽取出它们的主题(分布)出来后,便可以根据主题(分布)进行主题聚类或文本分类。
它是一种典型的词袋模型,即一篇文档是由一组词构成,词与词之间没有先后顺序的关系。此外,一篇文档可以包含多个主题,文档中每一个词都由其中的一个主题生成。
二、如何生成文档
在LDA模型中,一篇文档生成的方式如下:
- 从狄利克雷分布alpha中取样生成文档 i 的主题分布θi
- 从主题的多项式分布θi中取样生成文档i第 j 个词的主题zij
- 从狄利克雷分布beta中取样生成主题zij对应的词语分布φzij
- 从词语的多项式分布φzij中采样最终生成词语wij
其中,类似Beta分布是二项式分布的共轭先验概率分布,而狄利克雷分布(Dirichlet分布)是多项式分布的共轭先验概率分布。
![]()
具体公式逻辑参考:
一文详解LDA主题模型 - 知乎
通俗理解LDA主题模型_lda模型_v_JULY_v的博客-CSDN博客
二、Python实现
import gensim
from gensim import corpora
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # To ignore all warnings that arise here to enhance clarity
from gensim.models.coherencemodel import CoherenceModel
from gensim.models.ldamodel import LdaModel
# 准备数据
PATH = "E:/data/output.csv"
file_object2=open(PATH,encoding = 'utf-8',errors = 'ignore').read().split('\n') #一行行的读取内容
data_set=[] #建立存储分词的列表
for i in range(len(file_object2)):
result=[]
seg_list = file_object2[i].split()
for w in seg_list :#读取每一行分词
result.append(w)
data_set.append(result)
print(data_set)
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(data_set) # 构建 document-term matrix
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in data_set]
#Lda = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel # 创建LDA对象
#计算困惑度
def perplexity(num_topics):
ldamodel = LdaModel(corpus, num_topics=num_topics, id2word = dictionary, passes=30)
print(ldamodel.print_topics(num_topics=num_topics, num_words=15))
print(ldamodel.log_perplexity(corpus))
return ldamodel.log_perplexity(corpus)
#计算coherence
def coherence(num_topics):
ldamodel = LdaModel(corpus, num_topics=num_topics, id2word = dictionary, passes=30,random_state = 1)
print(ldamodel.print_topics(num_topics=num_topics, num_words=10))
ldacm = CoherenceModel(model=ldamodel, texts=data_set, dictionary=dictionary, coherence='c_v')
print(ldacm.get_coherence())
return ldacm.get_coherence()
# 绘制困惑度折线图
x = range(1,15)
# z = [perplexity(i) for i in x]
y = [coherence(i) for i in x]
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('主题数目')
plt.ylabel('coherence大小')
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
plt.title('主题-coherence变化情况')
plt.show()from gensim.models import LdaModel
import pandas as pd
from gensim.corpora import Dictionary
from gensim import corpora, models
import csv
# 准备数据
PATH = "E:/data/output1.csv"
file_object2=open(PATH,encoding = 'utf-8',errors = 'ignore').read().split('\n') #一行行的读取内容
data_set=[] #建立存储分词的列表
for i in range(len(file_object2)):
result=[]
seg_list = file_object2[i].split()
for w in seg_list :#读取每一行分词
result.append(w)
data_set.append(result)
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(data_set) # 构建 document-term matrix
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in data_set]
lda = LdaModel(corpus=corpus, id2word=dictionary, num_topics=5, passes = 30,random_state=1)
topic_list=lda.print_topics()
print(topic_list)
result_list =[]
for i in lda.get_document_topics(corpus)[:]:
listj=[]
for j in i:
listj.append(j[1])
bz=listj.index(max(listj))
result_list.append(i[bz][0])
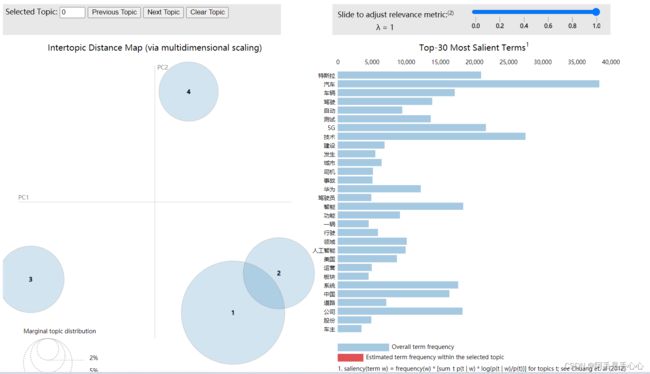
print(result_list)import pyLDAvis.gensim
pyLDAvis.enable_notebook()
data = pyLDAvis.gensim.prepare(lda, corpus, dictionary)
pyLDAvis.save_html(data, 'E:/data/topic.html')
LDA主题模型简介及Python实现_阿丢是丢心心的博客-CSDN博客