深度学习基础之回归问题与正则化——慕课学习笔记
回归和分类的区别和联系:
●区别:
- 分类:使用训练集推断输入x所对应的离散类别(如: +1, -1)。
- 回归:使用训练集推断输入x所对应的输出值,为连续实数。
●联系:
- 利用回归模型进行分类:可将回归模型的输出离散化以进行分类,即y = sign(f(x))。
- 利用分类模型进行回归:也可利用分类模型的特点,输出其连续化
的数值。
线性模型:
●狭义线性(linear)模型:
- 通常指自变量与因变量之间按比例、成直线的关系,在数学上可理解为-阶导数为常数的函数,如y= θ"x;
- 线性通常表现为一次曲线。
●广义线性(generalized linear model, GLM ) 模型:
是线性模型的扩展,主要通过联结函数g(link function),使预测
值落在响应变量的变幅内。例如逻辑回归:
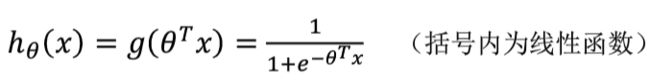
线性回归:
●线性回归模型中,假设自变量和因变量满足如下形式:y= he(x)= θ"x
●问题:已知一些数据,如何求里面的未知参数,给出一个最优解。
●因此通常将参数求解问题转化为求最小误差问题。一般采用模型预测结果与真实结果的差的平方和作为损失函数:


求解使得损失函数最小的参数θ:
■矩阵解法。scikit-learn中的LinearRegression类使用的是矩阵解法(有时也称为最小二乘法)。可以解出线性回归系数θ。

■梯度下降法。梯度下降(Gradient descent )是利用一阶的梯度信息找到函数局部最优解的一种方法。

线性回归的正则化:
●应对过拟合(Overfitting)。因为在某些情况下,学习得到的模型在
训练集_上也许误差较小。但是对于测试集中之前未见样本的预测却未
必有效。为此可以在损失函数中加入正则化项。以线性回归为例:

其中a是正则化参数(regularization parameter),用于控制两个不同的
目标的平衡。
1.第一个目标是使假设更好地拟合训练数据。
2.第二个目标是要正则化处理,使得模型不要太复杂。
逻辑回归:
●线性回归的输出值的范围通常是无法限定的。
●逻辑回归通过使用logistic函数(或称为sigmoid函数)将其转化为(0,1)区间的数值。

通过一个实例比较线性回归(一次回归)与多项式回归(二次回归):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 线性回归模块
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures # 生成多项式特征模块
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties # 字体属性模块
# 设置字体为宋体,用于坐标轴上数字显示
font_set = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=20)
# 绘图
def runplt():
plt.figure()# 定义figure
plt.title(u'披萨的价格和直径',fontproperties=font_set)
plt.xlabel(u'直径(inch)',fontproperties=font_set)
plt.ylabel(u'价格(美元)',fontproperties=font_set)
plt.axis([0, 25, 0, 25]) # 横纵坐标范围
plt.grid(True) # 显示网格
return plt
#训练集和测试集数据
X_train = [[6], [8], [10], [14], [18]]
y_train = [[7], [9], [13], [17.5], [18]]
X_test = [[7], [9], [11], [15]]
y_test = [[8], [12], [15], [18]]
#画出横纵坐标和训练集散点图
plt1 = runplt()
plt1.scatter(X_train, y_train,s=40)
#给出一些点用于画出线性回归的曲线
xx = np.linspace(0, 26, 100)
# 线性回归拟合
regressor = LinearRegression()
regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
yy = regressor.predict(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0], 1))
# 显示中文
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.plot(xx, yy, label="线性回归")
#二次回归
#首先生成多项式特征
quadratic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
X_train_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
regressor_quadratic = LinearRegression()
regressor_quadratic.fit(X_train_quadratic, y_train)
#numpy.reshape(重塑)给数组一个新的形状而不改变其数据。在指定的间隔内返回均匀间隔的数字
#给出一些点用于画出线性回归的曲线
xx = np.linspace(0, 26, 100)
# print (xx.shape)
# print (xx.shape[0])
xx_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0], 1))
# print (xx.reshape(xx.shape[0], 1).shape)
plt.plot(xx, regressor_quadratic.predict(xx_quadratic), 'r-',label="二次回归")
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
X_test_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(X_test)
print('线性回归 r-squared:', regressor.score(X_test, y_test))
print('二次回归 r-squared:', regressor_quadratic.score(X_test_quadratic, y_test))
