Windows10+Python+Yolov8+ONNX图片缺陷识别,并在原图中标记缺陷,有onnx模型则无需配置,无需训练。
目录
一、训练自己数据集的YOLOv8模型
1.博主电脑配置
2.深度学习GPU环境配置
3.yolov8深度学习环境准备
4.准备数据集
二、Python+Onnx模型进行图像缺陷检测,并在原图中标注
1、模型转换
2、查看模型结构
3、修改输入图片的尺寸
4、 图像数据归一化
5、模型推理
6、推理结果筛选
7、像素还原
8、筛选重叠面积
9、标记缺陷
一、训练自己数据集的YOLOv8模型
如果已经有了自己数据集的onnx模型或pt模型,则可以直接跳到二。
1.博主电脑配置
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 12G
Intel(R) Xeon(R) E5-2670 v2 2.50GHz
DDR3 16G
2.深度学习GPU环境配置
python3.9.16+cuda11.1+pytorch1.9.0+torchvision0.10.0+Anaconda3
打开Anaconda Prompt
conda create --name 环境名字(字母组成) python=3.9.16activate 你环境的名字pip install ultralytics
conda install pytorch==1.9.0 torchvision==0.10.03.yolov8深度学习环境准备
到这个网站下载yolov8模型,并解压,尽量放在不含中文路径的文件夹内,解压后是ultralytics-main文件夹。然后我们再Anaconda内cd进这个文件夹
cd C:\Users\SlowS\Desktop\ultralytics-main(你电脑上ultralytics-main的路径)
pip install -r requirements.txt4.准备数据集
在主目录ultralytics-main下创建my_data文件夹,在my_data文件夹内创建Annotations、images、ImageSets、labels这几个文件夹。这几个文件夹名字不能更改!!!
| Annotations | 放xml标注文件,如果没有也不用管 |
| images | 放数据集文件 |
| ImageSets | 放txt文件,暂时不用管 |
| labels | 放txt标注文件,暂时不用管 |
通过python下载labelimg,并开始标注数据集
然后参考博客来划分数据集,并进行训练。(2条消息) YOLOv8教程系列:一、使用自定义数据集训练YOLOv8模型(详细版教程,你只看一篇->调参攻略),包含环境搭建/数据准备/模型训练/预测/验证/导出等_Zhijun.li@Studio的博客-CSDN博客
二、Python+Onnx模型进行图像缺陷检测,并在原图中标注
1、模型转换
通过训练得到的模型是pt文件,我们需要转换为onnx文件
from ultralytics import YOLO
# 加载模型
model = YOLO("models\\best.pt")
# 转换模型
model.export(format="onnx")
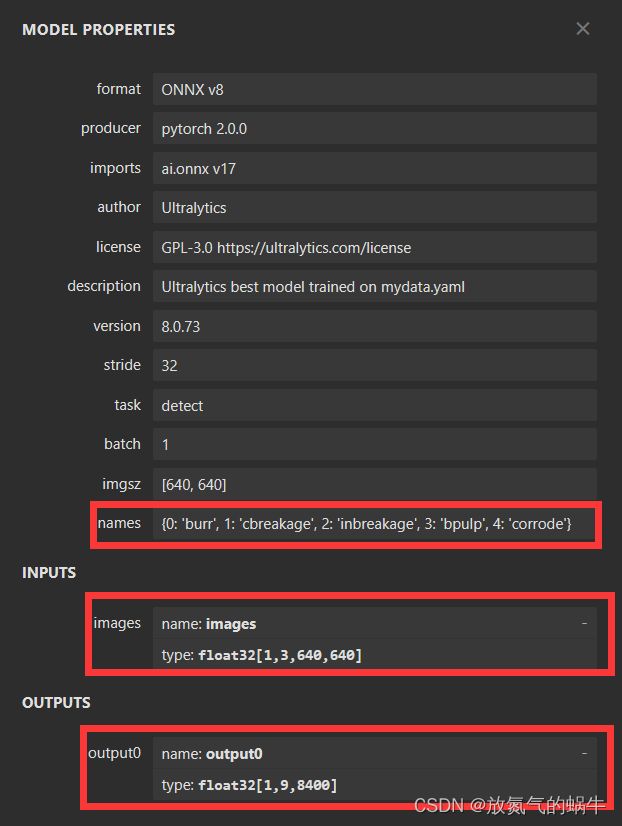
2、查看模型结构
通过以下网站来查看onnx模型结构
best.onnx (netron.app)
可以得到,输入图片的尺寸要求为3*640*640,输出结果为float32的n*8400二维数组,n为数据集缺陷种类的数量
3、修改输入图片的尺寸
为防止图片畸变,所以需要将图片修改为如下形状
import onnxruntime
import numpy as np
import tkinter
from tkinter import filedialog
import random
import cv2
# 弹出文件选择框,让用户选择要打开的图片
filepath = tkinter.filedialog.askopenfilename()
# 如果用户选择了一个文件,则加载该文件并显示
if filepath != '':
# 读取图片
image = cv2.imread(filepath)
# 获取图像尺寸
h, w = image.shape[:2]
# 将BGR图像转换为RGB图像
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 尺寸变换
if h > w:
img = cv2.resize(image, (int(w / h * 640) , 640))
else:
img = cv2.resize(image, (640 , int(h / w * 640)))
# 创建单色背景图像
background = np.zeros((640, 640, 3), np.uint8)
background[:] = (255, 0, 0)
# 将图像居中放置
x_offset = (640 - img.shape[1]) // 2
y_offset = (640 - img.shape[0]) // 2
background[y_offset:y_offset+img.shape[0], x_offset:x_offset+img.shape[1]] = img
# 显示图片
cv2.imshow('Result', background)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()4、 图像数据归一化
为了方便深度学习模型对图片数据进行推理,需要对读入图片进行归一化处理
# 将像素值转换为浮点数,并将其归一化到0~1之间
img = image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# 将图像从HWC格式转换为CHW格式
img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
# 将图像从CHW格式转换为NCHW格式,批次大小为1
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)5、模型推理
将修改好的图像数据,用onnx模型推理工具进行推理,得到n*8400二维数组的推理结果,n为数据集缺陷种类的数量
# onnx测试
session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnx_model_path)
inputs = {session.get_inputs()[0].name: image}
logits = session.run(None, inputs)[0]
# 将输出转换为二维数组
# 将(1, 9, 8400)的形状转换为(9, 8400)的形状
output = logits.reshape((9, -1))
# 将二维数组转置为(8400, 9)的形状
output = output.transpose((1, 0))6、推理结果筛选
9*8400二维数组转成8400*9方便处理,9列数据分别表示了检测框的中心x坐标、y坐标、宽度、高度、每个缺陷的置信系数
需要筛选出缺陷置信系数大于阈值的检测框
# 缺陷位置和缺陷置信系数
selected = np.zeros((0, 9))
# 缺陷置信系数
Thresh = np.zeros((0, 1))
# 缺陷类型
typ = np.zeros((0, 1), dtype=int)
i = 0
# 循环遍历每一行,筛选大于阈值的缺陷
for n in range(num.shape[0]):
# 如果第4~8列中有大于阈值的元素
if np.any(num[n, 4:] > threshold):
# 将这一行添加到selected数组中
selected = np.vstack((selected, num[n]))
# 如果第4列大于阈值
if selected[i, 4] == max(selected[i, 4:]):
# 将type数组第i个元素赋值为缺陷类型0
typ = np.vstack((typ, 0))
# 将Thresh数组第i个元素赋值为缺陷类型0的阈值
Thresh = np.vstack((Thresh, selected[i, 4]))
elif selected[i, 5] == max(selected[i, 4:]):
typ = np.vstack((typ, 1))
Thresh = np.vstack((Thresh, selected[i, 5]))
elif selected[i, 6] == max(selected[i, 4:]):
typ = np.vstack((typ, 2))
Thresh = np.vstack((Thresh, selected[i, 6]))
elif selected[i, 7] == max(selected[i, 4:]):
typ = np.vstack((typ, 3))
Thresh = np.vstack((Thresh, selected[i, 7]))
elif selected[i, 8] == max(selected[i, 4:]):
typ = np.vstack((typ, 4))
Thresh = np.vstack((Thresh, selected[i, 8]))
i = i + 17、像素还原
将筛选结果还原成原图像素点坐标
# 获取selected数组的第0、1、2和3列,分别对应缺陷中心x,y坐标,宽度,高度
x_center = select[:, 0]
y_center = select[:, 1]
width = select[:, 2]
height = select[:, 3]
# 计算左上角坐标
x_min = x_center - width / 2
y_min = y_center - height / 2
# 创建bbox数组,将左上角坐标和宽度、高度存储进去
bbox = np.zeros((select.shape[0], 6))
bbox[:, 0] = x_min
bbox[:, 1] = y_min
bbox[:, 2] = width
bbox[:, 3] = height
# 将type数组和Thresh数组分别添加到bbox数组的第4列和第5列
bbox[:, 4] = typ
bbox[:, 5] = thresh
# 图像比例恢复
if h > w:
bbox[:, :4] *= (h/640)
bbox[:, 0] -= (h/2-w/2)
else:
bbox[:, :4] *= (w/640)
bbox[:, 1] -= (w/2-h/2)
# 将二维数组转换为二维列表
my_list = [list(row) for row in bbox]
# 将 0~4 列转换为 int 型,5 列转换为 float 型
for i in range(len(my_list)):
for j in range(len(my_list[i])):
if j < 5:
my_list[i][j] = int(my_list[i][j])
else:
my_list[i][j] = float(my_list[i][j])8、筛选重叠面积
根据阈值去除同一缺陷种类的重复检测框
i = 0
bbox = sorted(bbox, key=lambda x: x[3])
while i < (len(bbox) - 1):
if bbox[i][4] == bbox[i + 1][4]:
# 计算两个框之间的重叠面积
x1 = max(bbox[i][0], bbox[i + 1][0])
y1 = max(bbox[i][1], bbox[i + 1][1])
x2 = min(bbox[i][0] + bbox[i][2], bbox[i + 1][0] + bbox[i + 1][2])
y2 = min(bbox[i][1] + bbox[i][3], bbox[i + 1][1] + bbox[i + 1][3])
intersection = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
area1 = bbox[i][2] * bbox[i][3]
area2 = bbox[i + 1][2] * bbox[i + 1][3]
nms = 1 - intersection / (area1 + area2 - intersection)
# print(nms)
# 去除多余框
if nms < threshold and bbox[i][5] >= bbox[i + 1][5]:
del bbox[i + 1]
elif nms < threshold and bbox[i][5] < bbox[i + 1][5]:
del bbox[i]
elif nms > threshold:
i = i + 1
else:
i = i + 19、标记缺陷
根据处理完的缺陷位置信息,使用方框将缺陷标记出来
# 循环遍历 bbox 列表中的每一行
for bbox in bbox_list:
# 获取方框的左上角坐标和宽度、高度
x, y, w, h = bbox[:4]
# 随机生成颜色值
color = (random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255))
# 绘制方框
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
# 在方框左上角上加上缺陷类型和置信系数
defect_type = bbox[4]
confidence = bbox[5]
with open(typ_txt, 'r') as f:
labels = f.read().splitlines()
str_confidence = "{:.3f}".format(confidence)
cv2.putText(img, labels[defect_type] + ' ' + str_confidence, (x, y - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, color, 3)
# 保存绘制好方框的图像
cv2.imwrite('5.jpg', img)
# 创建窗口并显示完整图像
cv2.namedWindow("Image", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
# 循环等待按键输入
while True:
if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27:
break
# 关闭窗口并释放资源
cv2.destroyAllWindows()关注私信发源码。
目前在完成Python+onnx实时检测程序,敬请期待!