【Python】多线程编程 ② ( 进程与线程 | 进程的内存空间 | 并行执行概念 | 线程的创建和执行 | threading.Thread() 函数解析 )
文章目录
- 一、进程与线程
-
- 1、进程的内存空间
- 2、线程之间的共享内存
- 3、并行执行概念
- 二、Python 多线程编程
-
- 1、线程的创建和执行
- 2、threading.Thread() 函数解析
- 3、代码示例 - 线程创建运行
- 4、代码示例 - 线程并行运行
一、进程与线程
1、进程的内存空间
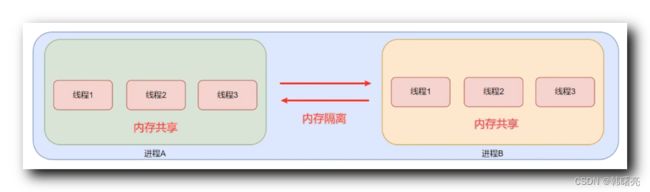
在 操作系统 中 , 进程 之间 的 内存空间 是 隔离的 , 不同的进程 拥有各自的 内存空间 ,
这些内存空间 都从 0 开始计数 , 但是 这些 内存空间 只占总内存 的一小部分 ;
一个 进程 中 可以有若干 线程 , 这些 线程 共享 进程的 内存空间 ;
进程 只能 访问 操作系统 分配给自己的 内存空间 , 不能访问其它 进程 的 内存空间 ;
- 下图中 , 进程 A 只能访问自己的内存 , 不能访问 进程 B 的内存 ;
2、线程之间的共享内存
一个 进程 中的 若干 线程 , 可以共享 进程 的 内存空间 ;
线程 只能 访问 本进程 的内存空间 , 不能访问 其它 进程的 内存空间 ;
3、并行执行概念
进程 之间 可以 并行执行 , 操作系统 中的 多个 进程 , 可以在 同一时间 做 不同的 工作 ;
线程 之间 可以 并行执行 , 进程 中的 多个线程 , 可以在 同一时间 做 不同的 工作 ;
二、Python 多线程编程
1、线程的创建和执行
所有的编程语言 都允许 多线程编程 , Python 也支持 多线程编程 ;
Python 多线程编程 功能 是由 threading 模块提供的 ;
在 Python 中 , 进行 多线程编程 ,
首先 , 需要导入 threading 模块 ;
import threading
然后 , 执行 threading.Thread() 方法 , 创建 线程实例对象 ;
thread_obj = threading.Thread()
最后 , 调用 线程对象#start() 函数 , 启动线程 ;
thread_obj.start()
2、threading.Thread() 函数解析
threading.Thread() 函数 用于创建一个新的线程对象 , 并可以通过指定线程函数和参数来配置线程的行为 ;
threading.Thread 函数原型如下 :
threading.Thread(target=None, args=(), kwargs={})
- target 参数 : 线程中要执行的函数 , 指定线程在启动后要执行的操作 , 默认值为 None ;
- args 参数 : 类型为元组 , 包含传递给线程函数的参数 , 默认为 () 空元组 , 元素不可更改 ;
- kwargs 参数 : 类型为字典 , 包含传递给线程函数的关键字参数,默认为 {} 空字典 ;
创建线程对象后会返回 线程 实例对象 , 可以调用 线程 实例对象 的 start() 方法 启动线程 ;
线程启动后 , 将在后台独立执行 , 并且可以 在进程中 与 进程中的其他线程 并行运行 ;
3、代码示例 - 线程创建运行
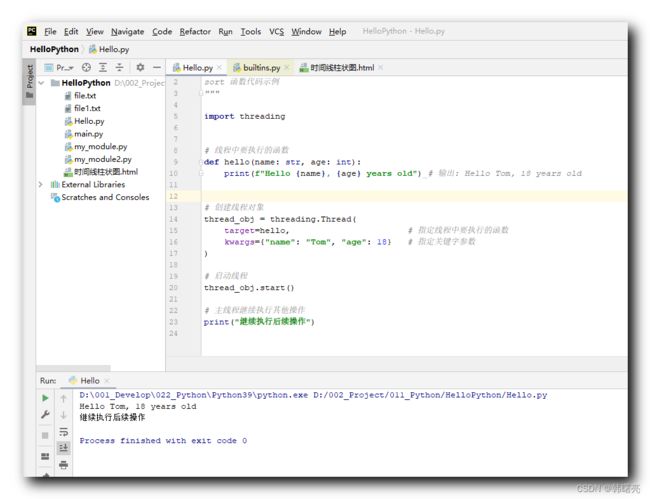
在下面的代码中 ,
首先 , 定义了一个名为 hello 的函数作为线程函数,
然后 , 调用 threading.Thread() 函数创建了一个新的线程实例对象 ,
通过 target=hello 关键字指定线程执行的是 hello 函数 ,
通过 kwargs 关键字指定 hello 函数的参数 , name 参数值为 " Tom " 字符串 , age 参数值为 18 数字类型 ,
kwargs={"name": "Tom", "age": 18} # 指定关键字参数
再后 , 调用 函数实例对象 的 start() 方法启动线程 ;
最后,主线程继续执行其他操作 ;
代码示例 :
"""
多线程 代码示例
"""
import threading
# 线程中要执行的函数
def hello(name: str, age: int):
print(f"Hello {name}, {age} years old") # 输出: Hello Tom, 18 years old
# 创建线程对象
thread_obj = threading.Thread(
target=hello, # 指定线程中要执行的函数
kwargs={"name": "Tom", "age": 18} # 指定关键字参数
)
# 启动线程
thread_obj.start()
# 主线程继续执行其他操作
print("继续执行后续操作")
执行结果 :
D:\001_Develop\022_Python\Python39\python.exe D:/002_Project/011_Python/HelloPython/Hello.py
Hello Tom, 18 years old
继续执行后续操作
Process finished with exit code 0
4、代码示例 - 线程并行运行
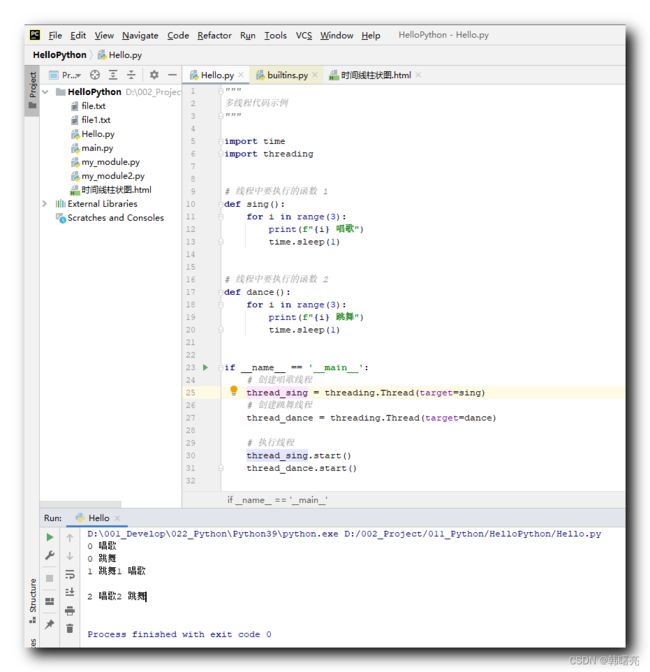
在下面的代码中 ,
首先 , 定义了两个函数 , 这两个函数都需要长时间才能执行完毕 ;
# 线程中要执行的函数 1
def sing():
for i in range(3):
print(f"{i} 唱歌")
time.sleep(1)
# 线程中要执行的函数 2
def dance():
for i in range(3):
print(f"{i} 跳舞")
time.sleep(1)
然后 , 创建两个线程 , 分别执行上述两个函数 ;
# 创建唱歌线程
thread_sing = threading.Thread(target=sing)
# 创建跳舞线程
thread_dance = threading.Thread(target=dance)
最后 , 启动两个线程 , 两个线程的命令行输出内容交替打印出来 ;
# 执行线程
thread_sing.start()
thread_dance.start()
代码示例 :
"""
多线程代码示例
"""
import time
import threading
# 线程中要执行的函数 1
def sing():
for i in range(3):
print(f"{i} 唱歌")
time.sleep(1)
# 线程中要执行的函数 2
def dance():
for i in range(3):
print(f"{i} 跳舞")
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建唱歌线程
thread_sing = threading.Thread(target=sing)
# 创建跳舞线程
thread_dance = threading.Thread(target=dance)
# 执行线程
thread_sing.start()
thread_dance.start()
执行结果 :
D:\001_Develop\022_Python\Python39\python.exe D:/002_Project/011_Python/HelloPython/Hello.py
0 唱歌
0 跳舞
1 跳舞1 唱歌
2 唱歌2 跳舞
Process finished with exit code 0