C语言qsort函数用法---使用冒泡排序实现qsort函数
void qsort(void* base, size_t num, size_t width, int (cmp)(const void e1, const void* e2));
参数含义:
- void* base–比较对象
- size_t num–比较对象的大小
- size_t width–比较对象中一个元素的大小
- int (cmp)(const void e1, const void* e2)–是一个函数指针,设计比较原则。 (const void* e1, const void* e2)两个参数是待排序的两个元素的地址
1、int数组排序:
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2) //比较规则
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;//强制转换成int*,然后解引用成整形数据,返回其差值。
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,1,2 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, size, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}printf("\r\n");
return 0;
}
// 因为函数要求返回整型,所以直接返回会有警告或者错误
// return *(float*)e1 - *(float*)e2;
int cmp_float(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
if (*(float*)e1 == *(float*)e2)
{
return 0;
}
else if (*(float*)e1 > *(float*)e2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
int main()
{
float farr[] = { 9.0,8.0,8.9,7.2,7.0,6.0,5.0,4.0 };
int sizef = sizeof(farr) / sizeof(farr[0]);
qsort(farr, sizef, sizeof(farr[0]), cmp_float);
for (int i = 0; i < sizef; i++)
{
printf("%.1f ", farr[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
return 0;
}
3、结构体数组排序:
struct Stu {
char name[15];
int age;
};
int cmp_stu_age(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
if (((struct Stu*)e1)->age == ((struct Stu*)e2)->age)
{
return 0;
}
else if (((struct Stu*)e1)->age > ((struct Stu*)e2)->age)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
int cmp_stu_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
// 比较字符串不能用<>=来比较,应该用strcmp函数
// strcmp函数返回值也是大于返回大于0的一个数,等于返回0,小于返回一个小与0的数
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
int main()
{
struct Stu s[3] = { {"zhangsan",20}, {"lisi",30} ,{"wangwu",10} };
int sizes = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
// age比较
qsort(s, sizes, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_age);
for (int i = 0; i < sizes; i++)
{
printf("%s,%d ",s[i].ch,s[i].age);
}printf("\r\n");
// name比较
qsort(s, sizes, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_name);
for (int i = 0; i < sizes; i++)
{
printf("%s,%d ", s[i].ch, s[i].age);
}printf("\r\n");
return 0;
}
4、使用冒泡排序实现qsort函数
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2,int width)
{
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
void bubble_sort(void* base, int size, int width, int (*cmp)(void* e1, void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++)
{
//找元素时,每次都加宽度width,
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{
//交换
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr1[10] = { 10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,1,2 };
int size1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
bubble_sort(arr1, size1, sizeof(arr1[0]), cmp_int);
for (int i = 0; i < size1; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr1[i]);
}printf("\r\n");
return 0;
}
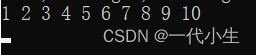
输出结果:
在bublle_sort函数中,为什么是这么判断:if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)??
因为传入的base是无类型的,所以不确定是什么数组,因此把base强制转换成char*,方便一个字节一个字节的读取数据,那么每次要读取几个字节呢?这是根据width来判断的,在main函数中传入的就是整型数据的大小,所以这里每次读取width个字节作为一个数据变量,进行cmp比较。如果比较返回值大于0则交换这两个值。