视觉SLAM十四讲笔记-9-3
视觉SLAM十四讲笔记-9-3
文章目录
- 视觉SLAM十四讲笔记-9-3
-
- 9.3 实践:Ceres BA
- 9.4 实践:g2o求解BA
9.3 实践:Ceres BA
BAL 数据集提供了若干个场景,每一个场景里的相机和路标点信息由一个文本文件给定。在本例中,使用 problem-16-22106-pre.txt文件作为例子。数据格式参考官网:link
Data Format
Each problem is provided as a bzip2 compressed text file in the following format.
<num_cameras> <num_points> <num_observations>
<camera_index_1> <point_index_1> <x_1> <y_1>
...
<camera_index_num_observations> <point_index_num_observations> <x_num_observations> <y_num_observations>
<camera_1>
...
<camera_num_cameras>
<point_1>
...
<point_num_points>
首先,通过定义的 common.h 中定义的 BALProblem 类读入该文件的内容,然后分别用 Ceres 和 g2o 进行求解。
需要注意的是, BAL 数据集有其自身的特殊之处:
- BAL 的相机内参模型由焦距 f f f 和畸变参数 k 1 , k 2 k_1,k_2 k1,k2 给出。 f f f 类似于我们提到的 f x f_x fx 和 f y f_y fy 。由于照片像素基本上是正方形,所以在很多实际场合中 f x f_x fx] 非常接近于 f y f_y fy ,用同一个值也未尝不可。此外,这个模型没有 c x c_x cx 和 c y c_y cy,因为存储的数据已经去掉了这两个值。
- 因为BAL数据在投射时假设投影平面在相机光心之后,所以按照之前用的模型计算,需要在投影之后乘以系数 -1。不过,大部分数据集仍使用光心前面的投影平面,在使用数据集之前应该仔细阅读格式说明。
用 BALProblem 类读取数据之后,可以调用 Noemalize 函数对原始数据进行归一化,或者通过 Perturb 函数给数据加上噪声。归一化是指将所有路标点的中心置为零,然后做一个合适尺度的缩放。这会使得优化过程中数值更加稳定,防止在极端情况下处理很大或者有很大偏移的 BA 问题。
mkdir BundleAdjustmentCeres
cd BundleAdjustmentCeres/
code .

在 bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp 文件中,实现了 Ceres 求解 BA 的过程。用 Ceres 的关键是定义出投影误差模型,该模型在 SnavelyReprojectionError.h 中给出。
//launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "g++ - 生成和调试活动文件",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request":"launch",
"program":"${workspaceFolder}/build/bundle_adjustment_ceres",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "为 gdb 启动整齐打印",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "Build",
"miDebuggerPath": "/usr/bin/gdb"
}
]
}
//tasks.json
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"options":{
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build" //指明在哪个文件夹下做下面这些指令
},
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "cmake", //label就是这个task的名字,这个task的名字叫cmake
"command": "cmake", //command就是要执行什么命令,这个task要执行的任务是cmake
"args":[
".."
]
},
{
"label": "make", //这个task的名字叫make
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"command": "make", //这个task要执行的任务是make
"args": [
]
},
{
"label": "Build",
"dependsOrder": "sequence", //按列出的顺序执行任务依赖项
"dependsOn":[ //这个label依赖于上面两个label
"cmake",
"make"
]
}
]
}
#CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project(BUNDLEADJUSTMENTCERES)
#在g++编译时,添加编译参数,比如-Wall可以输出一些警告信息
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -Wall -std=c++14")
LIST(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
#一定要加上这句话,加上这个生成的可执行文件才是可以Debug的,不然不加或者是Release的话生成的可执行文件是无法进行调试的
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
#添加头文件
include_directories(include)
#此工程要调用opencv库,因此需要添加opancv头文件和链接库
#寻找OpenCV库
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
#添加头文件
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
find_package(CSparse REQUIRED)
include_directories(${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR})
#find Ceres
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED)
include_directories(${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_library(bal_common src/common.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_ceres bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp)
#链接OpenCV库
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_ceres ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${CERES_LIBRARIES} bal_common)
//SnavelyReprojectionError.h
/*
该文件给出了投影误差模型
*/
#ifndef SnavelyReprojection_H
#define SnavelyReprojection_H
#include 在类的括号中实现了 Ceres 计算误差的接口,估计数据通过 CamProjectionWithDistortion 函数中得到。注意在 Ceres 中,必须以 double 数组形式存储优化变量。该类的静态函数 Create 作为外部调用接口,直接返回一个可自动求导的 Ceres 代价函数。
只需要调用 Create 函数,把代价函数放入 ceres::Problem 中即可。
然后,在 bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp 中实现了 BA 搭建和求解的部分:
//bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp
#include 在 ceres::Solver::Options 中,可以设定求解的方法。使用 SPARSE_SCHUR 会让 Ceres 实际求解的过程和前面描述的一样,即先对路标部分进行 Schur 边缘化,以加速的方式求解此问题。不过,在 Ceres 中不能控制哪部分变量被边缘化,这是由 Ceres 求解器自动寻找并计算。
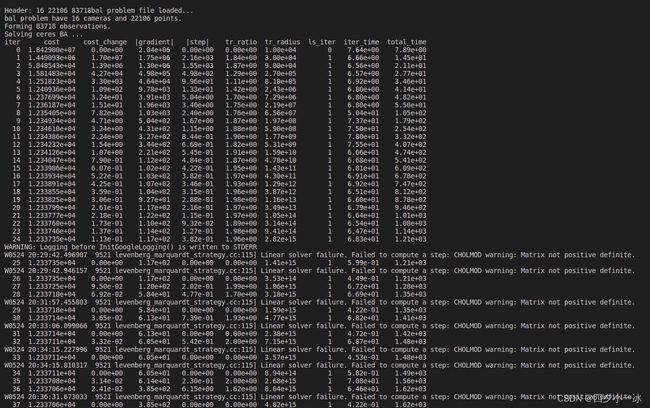
BA 优化的求解输出如下:
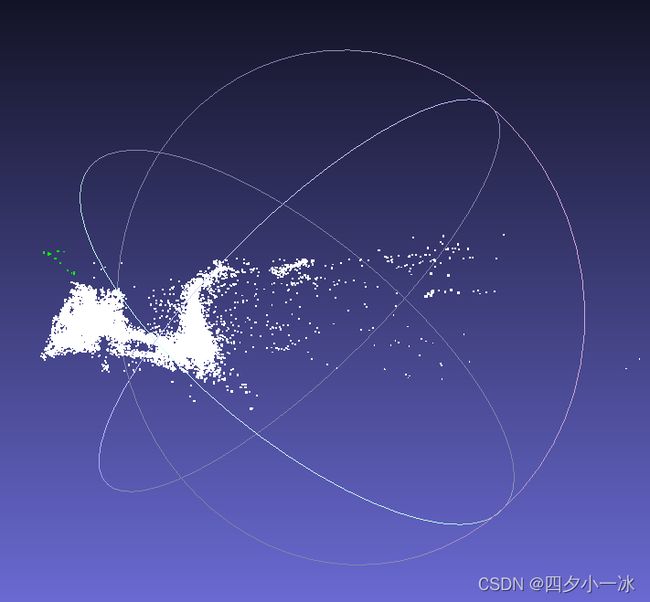
用 Meshlab 打开两个点云:


9.4 实践:g2o求解BA
g2o 求解 BA 问题时,使用图模型来描述问题的结构,所以需要用节点来表示相机和路标,然后用边表示它们之间的观测。仍然使用自定义的点和边,只需要覆盖一些关键函数即可。针对相机和路标,定义如下结构体,并使用 override 关键字对基类虚函数进行覆盖:
mkdir BundleAdjustmentG2o
cd BundleAdjustmentG2o
code .
//launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "g++ - 生成和调试活动文件",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request":"launch",
"program":"${workspaceFolder}/build/bundle_adjustment_g2o",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "为 gdb 启动整齐打印",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "Build",
"miDebuggerPath": "/usr/bin/gdb"
}
]
}
//tasks.json
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"options":{
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build" //指明在哪个文件夹下做下面这些指令
},
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "cmake", //label就是这个task的名字,这个task的名字叫cmake
"command": "cmake", //command就是要执行什么命令,这个task要执行的任务是cmake
"args":[
".."
]
},
{
"label": "make", //这个task的名字叫make
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"command": "make", //这个task要执行的任务是make
"args": [
]
},
{
"label": "Build",
"dependsOrder": "sequence", //按列出的顺序执行任务依赖项
"dependsOn":[ //这个label依赖于上面两个label
"cmake",
"make"
]
}
]
}
#CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project(BUNDLEADJUSTMENTG2O)
#在g++编译时,添加编译参数,比如-Wall可以输出一些警告信息
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -Wall -std=c++14")
LIST(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
#一定要加上这句话,加上这个生成的可执行文件才是可以Debug的,不然不加或者是Release的话生成的可执行文件是无法进行调试的
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories( ${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
#添加头文件
include_directories(include)
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
find_package(CSparse REQUIRED)
include_directories(${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR})
find_package (glog 0.6.0 REQUIRED)
#find g2o
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
include_directories(${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS})
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_csparse_extension g2o_stuff g2o_core cxsparse)
add_library(bal_common src/common.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_g2o bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp)
#链接OpenCV库
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_g2o Sophus::Sophus ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${G2O_LIBS} bal_common glog::glog)
#include 运行结果如下:

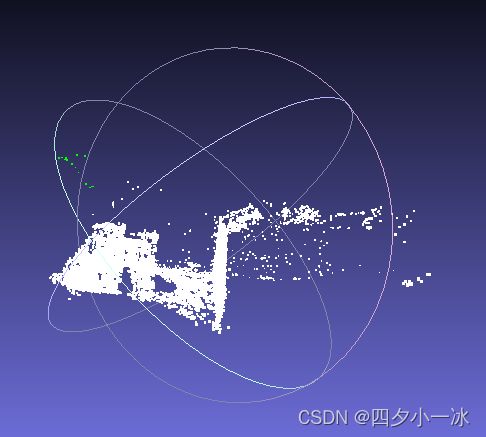
用 Meshlab 打开两个点云:


g2o 和 Ceres 的一大不同之处在于,在使用系数优化时, g2o 必须手动设置哪些顶点为边缘顶点,否则就会报运行错误。其余地方和 Ceres 实验大同小异。
在只有观测方程的情况下,构建最小二乘问题,对位姿和路标同时做调整,即所谓的 BA。