iOS--runtime
什么是Runtime
- runtime是由C和C++、汇编实现的一套API,为OC语言加入了面向对象、运行时的功能
- 运行时(runtime)将数据类型的确定由编译时推迟到了运行时
- 平时编写的OC代码,在程序运行过程中,最终会转换成runtime的C语言代码——runtime是Objective-C 的幕后⼯作者
如类结构中的ro和rw属性
- ro(read-only)在编译时已经确定
- rw(read-write)在运行时才确定,因此可以使用runtime进行修改
方法的本质是什么
方法的本质是发送消息objc_msgSend,即寻找IMP的过程
发送消息会有以下⼏个流程:
- 快速查找流程——通过汇编
objc_msgSend查找缓存cache_t是否有imp实现 - 慢速查找流程——通过C++中
lookUpImpOrForward递归查找当前类和父类的rw中methodlist的方法 - 动态方法解析——通过调用
resolveInstanceMethod和resolveClassMethod来动态方法决议——实现消息动态处理 - 快速转发流程——通过
CoreFoundation来触发消息转发流程,forwardingTargetForSelector实现快速转发,由其他对象来实现处理方法 - 慢速转发流程——先调用
methodSignatureForSelector获取到方法的签名,生成对应的invocation;再通过forwardInvocation来进行处理 - 以上流程均无法挽救就崩溃并报错
SEL和IMP的关系
遇到这种问题先要解释两者分别是什么?再解释两者的关系
SEL是方法编号,也是方法名,在dyld加载镜像到内存时,通过_read_image方法加载到内存的表中了
IMP是函数实现指针,找IMP就是找函数实现的过程
SEL和IMP的关系就可以解释为:
SEL就相当于书本的⽬录标题IMP就是书本的⻚码函数就是具体页码对应的内容
比如我们想在《程序员的自我修养——链接、装载与库》一书中找到“动态链接”(SEL),肯定会翻到179页(IMP),179页会开始讲述具体内容(函数实现)
能否向运⾏时创建的类中添加实例变量
具体情况具体分析:
- 编译好的类不能添加实例变量
- 运行时创建的类可以添加实例变量,但若已注册到内存中就不行了
原因:
- 编译好的实例变量存储的位置在
ro,而ro是在编译时就已经确定了的 - ⼀旦编译完成,内存结构就完全确定就⽆法修改
- 只能修改
rw中的方法或者可以通过关联对象的方式来添加属性
利用runtime-API创建对象
这题对runtime-API要求程度比较高
API介绍
动态创建类
/**
*创建类
*
*superClass: 父类,传Nil会创建一个新的根类
*name: 类名
*extraBytes: 额外的内存空间,一般传0
*return:返回新类,创建失败返回Nil,如果类名已经存在,则创建失败
*/
Class FXPerson = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "LGPerson", 0);
添加成员变量
/**
*添加成员变量
*这个函数只能在objc_allocateClassPair和objc_registerClassPair之间调用。不支持向现有类添加一个实例变量
*这个类不能是元类,不支持在元类中添加一个实例变量
*实例变量的最小对齐为1 << align,实例变量的最小对齐依赖于ivar的类型和机器架构。对于任何指针类型的变量,请通过log2(sizeof(pointer_type))
*
*cls 往哪个类添加
*name 添加的名字
*size 大小
*alignment 对齐处理方式
*types 签名
*/
class_addIvar(FXPerson, "fxName", sizeof(NSString *), log2(sizeof(NSString *)), "@");
注册到内存
/**
*往内存注册类
*
* cls 要注册的类
*/
objc_registerClassPair(FXPerson);
添加属性变量
/**
*往类里面添加属性
*
*cls 要添加属性的类
*name 属性名字
*attributes 属性的属性数组。
*attriCount 属性中属性的数量。
*/
class_addProperty(targetClass, propertyName, attrs, 4);
添加方法
/**
*往类里面添加方法
*
*cls 要添加方法的类
*sel 方法编号
*imp 函数实现指针
*types 签名
*/
class_addMethod(FXPerson, @selector(setHobby), (IMP)fxSetter, "v@:@");
整体使用
// hobby的setter-IMP
void fxSetter(NSString *value) {
printf("%s/n",__func__);
}
// hobby的getter-IMP
NSString *fxHobby() {
return @"iOS";
}
// 添加属性变量的封装方法
void fx_class_addProperty(Class targetClass, const char *propertyName) {
objc_property_attribute_t type = { "T", [[NSString stringWithFormat:@"@\"%@\"",NSStringFromClass([NSString class])] UTF8String] }; //type
objc_property_attribute_t ownership0 = { "C", "" }; // C = copy
objc_property_attribute_t ownership = { "N", "" }; //N = nonatomic
objc_property_attribute_t backingivar = { "V", [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_%@",[NSString stringWithCString:propertyName encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]].UTF8String }; //variable name
objc_property_attribute_t attrs[] = {type, ownership0, ownership, backingivar};
class_addProperty(targetClass, propertyName, attrs, 4);
}
// 打印属性变量的封装方法
void fx_printerProperty(Class targetClass){
unsigned int outCount, i;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(targetClass, &outCount);
for (i = 0; i < outCount; i++) {
objc_property_t property = properties[i];
fprintf(stdout, "%s %s\n", property_getName(property), property_getAttributes(property));
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// 动态创建类
Class FXPerson = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "FXPerson", 0);
// 添加成员变量
class_addIvar(FXPerson, "name", sizeof(NSString *), log2(sizeof(NSString *)), "@");
// 注册到内存
objc_registerClassPair(FXPerson);
// 添加属性变量
fx_class_addProperty(FXPerson, "hobby");
fx_printerProperty(FXPerson);
// 添加方法(为属性方法添加setter、getter方法)
class_addMethod(FXPerson, @selector(setHobby:), (IMP)fxSetter, "v@:@");
class_addMethod(FXPerson, @selector(hobby), (IMP)fxHobby, "@@:");
// 开始使用
id person = [FXPerson alloc];
[person setValue:@"Felix" forKey:@"name"];
NSLog(@"FXPerson的名字是:%@ 爱好是:%@", [person valueForKey:@"name"], [person valueForKey:@"hobby"]);
}
return 0;
}
注意事项
- 记得导入
- 添加成员变量
class_addIvar必须在objc_registerClassPair前,因为注册到内存时ro已经确定了,不能再往ivars添加(同第四个面试题) - 添加属性变量
class_addProperty可以在注册内存前后,因为是往rw中添加的 class_addProperty中“属性的属性”——nonatomic/copy是根据属性的类型变化而变化的class_addProperty不会自动生成setter和getter方法,因此直接调用KVC会崩溃
不只可以通过KVC打印来检验,也可以下断点查看ro、rw的结构来检验
关联对象分析
实则是为了解决分类创建属性的问题
分类直接添加属性的后果
- 编译会出现警告:没有setter方法和getter方法
- 运行会报错:-[FXPerson setName:]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x100f61180’
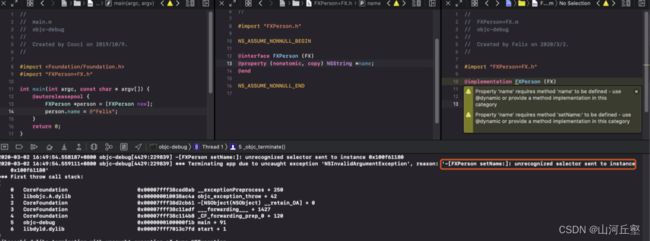
为什么不能直接添加属性
Category在runtime中是用一个结构体表示的:
struct category_t {
const char *name;
classref_t cls;
struct method_list_t *instanceMethods;
struct method_list_t *classMethods;
struct protocol_list_t *protocols;
struct property_list_t *instanceProperties;
// Fields below this point are not always present on disk.
struct property_list_t *_classProperties;
...
};
里面虽然可以添加属性变量,但是这些properties并不会自动生成Ivar,也就是不会有 @synthesize的作用,dyld加载期间,这些分类会被加载并patch到相应的类中。这是一个动态过程,Ivar不能动态添加
解决方案
手动实现setter、getter方法,关联对象
- (void)setName:(NSString *)name {
/**
参数一:id object : 给哪个对象添加属性,这里要给自己添加属性,用self。
参数二:void * == id key : 属性名,根据key获取关联对象的属性的值,在objc_getAssociatedObject中通过次key获得属性的值并返回。
参数三:id value : 关联的值,也就是set方法传入的值给属性去保存。
参数四:objc_AssociationPolicy policy : 策略,属性以什么形式保存。
*/
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"name", name, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)name {
/**
参数一:id object : 获取哪个对象里面的关联的属性。
参数二:void * == id key : 什么属性,与objc_setAssociatedObject中的key相对应,即通过key值取出value。
*/
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"name");
}
关联对象原理
setter方法——objc_setAssociatedObject分析
苹果设计接口时往往会加个中间层——即使底层实现逻辑发生变化也不会影响到对外接口
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy) {
_object_set_associative_reference(object, (void *)key, value, policy);
}
跟进去看看_object_set_associative_reference实现
void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) {
// This code used to work when nil was passed for object and key. Some code
// probably relies on that to not crash. Check and handle it explicitly.
// rdar://problem/44094390
if (!object && !value) return;
assert(object);
if (object->getIsa()->forbidsAssociatedObjects())
_objc_fatal("objc_setAssociatedObject called on instance (%p) of class %s which does not allow associated objects", object, object_getClassName(object));
// retain the new value (if any) outside the lock.
// 在锁之外保留新值(如果有)。
ObjcAssociation old_association(0, nil);
// acquireValue会对retain和copy进行操作,
id new_value = value ? acquireValue(value, policy) : nil;
{
// 关联对象的管理类
AssociationsManager manager;
// 获取关联的 HashMap -> 存储当前关联对象
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
// 对当前的对象的地址做按位去反操作 - 就是 HashMap 的key (哈希函数)
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
if (new_value) {
// break any existing association.
// 获取 AssociationsHashMap 的迭代器 - (对象的) 进行遍历
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
// secondary table exists
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
// 根据key去获取关联属性的迭代器
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
// 替换设置新值
j->second = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
} else {
// 到最后了 - 直接设置新值
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
}
} else {
// create the new association (first time).
// 如果AssociationsHashMap从没有对象的关联信息表,
// 那么就创建一个map并通过传入的key把value存进去
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap;
associations[disguised_object] = refs;
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
object->setHasAssociatedObjects();
}
} else {
// setting the association to nil breaks the association.
// 如果传入的value是nil,并且之前使用相同的key存储过关联对象,
// 那么就把这个关联的value移除(这也是为什么传入nil对象能够把对象的关联value移除)
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
refs->erase(j);
}
}
}
}
// release the old value (outside of the lock).
// 最后把之前使用传入的这个key存储的关联的value释放(OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN策略存储的)
if (old_association.hasValue()) ReleaseValue()(old_association);
}
ObjcAssociation old_association(0, nil)处理传进来的值得到new_value- 获取到管理所有关联对象的
hashmap总表的管理者AssociationsManager,然后拿到hashmap总表AssociationsHashMap DISGUISE(object)对关联对象的地址进行取反操作得到哈希表对应的下标index- 如果
new_value为空(即对属性赋值为nil)就直接找到相应的表进行删除 - 如果
new_value不为空,就拿到总表的迭代器通过拿到的下标index进行遍历查找;如果找到管理对象的关联属性哈希map表,然后再通过key去遍历取值 -
- 如果取到了,就先把新值设置到key上,再将旧值释放掉
-
- 如果没取到,就直接将新值设置在key上
getter方法——objc_getAssociatedObject分析
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key) {
return _object_get_associative_reference(object, (void *)key);
}
id _object_get_associative_reference(id object, void *key) {
id value = nil;
uintptr_t policy = OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN;
{
// 关联对象的管理类
AssociationsManager manager;
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
// 生成伪装地址。处理参数 object 地址
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
// 所有对象的额迭代器
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
// 内部对象的迭代器
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
// 找到 - 把值和策略读取出来
ObjcAssociation &entry = j->second;
value = entry.value();
policy = entry.policy();
// OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN - 就会持有一下
if (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN) {
objc_retain(value);
}
}
}
}
if (value && (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_AUTORELEASE)) {
objc_autorelease(value);
}
return value;
}
objc_getAssociatedObject是objc_setAssociatedObject的逆过程

weak置空原理
当面试官问你weak置空原理是什么,你可能只知道weak怎么用却不知道怎么答吧
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
FXPerson *person = [[FXPerson alloc] init];
id __weak person = object;
}
return 0;
}
Xcode菜单栏Debug->Debug Workflow->Always show Disassembly打上勾查看汇编——汇编代码会来到libobjc库的objc_initWeak
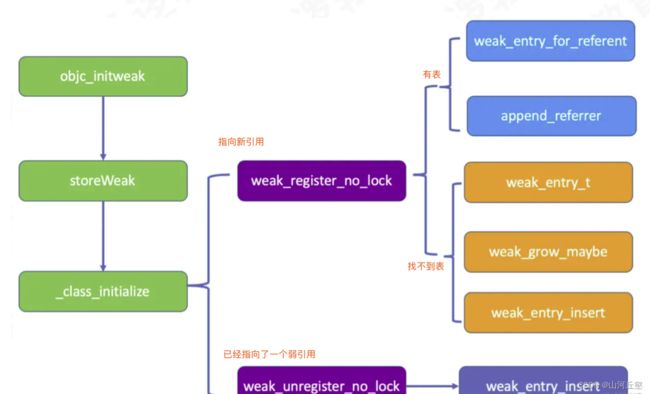
weak创建过程
objc_initWeak
- location:表示__weak指针的地址(我们研究的就是__weak指针指向的内容怎么置为nil)
- newObj:所引用的对象,即例子中的person
id
objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj)
{
if (!newObj) {
*location = nil;
return nil;
}
return storeWeak<DontHaveOld, DoHaveNew, DoCrashIfDeallocating>
(location, (objc_object*)newObj);
}
storeWeak
HaveOld:weak指针之前是否已经指向了一个弱引用HaveNew:weak指针是否需要指向一个新引用CrashIfDeallocating:如果被弱引用的对象正在析构,此时再弱引用该对象,是否应该crash
storeWeak最主要的两个逻辑点(源码太长,这里不贴了)
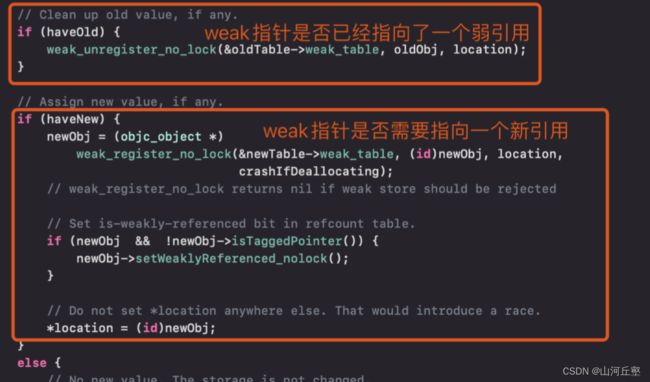
由于是第一次调用,所以走
haveNew分支——获取到的是新的散列表SideTable,主要执行了weak_register_no_lock方法来进行插入
weak_register_no_lock
- 主要进行了
isTaggedPointer和deallocating条件判断 - 将被弱引用对象所在的
weak_table中的weak_entry_t哈希数组中取出对应的weak_entry_t - 如果
weak_entry_t不存在,则会新建一个并插入 - 如果存在就将指向被弱引用对象地址的指针
referrer通过函数append_referrer插入到对应的weak_entry_t引用数组

append_referrer
找到弱引用对象的对应的weak_entry哈希数组中插入
weak创建流程
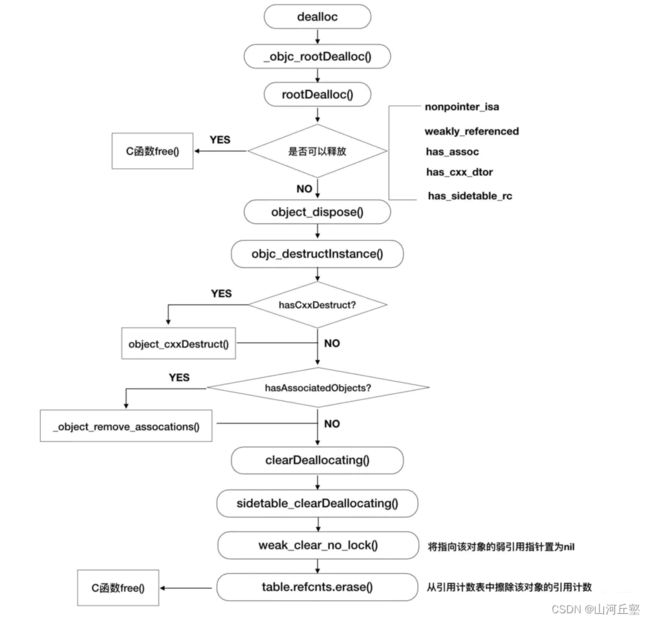
weak销毁过程
由于弱引用在析构dealloc时自动置空,所以查看dealloc的底层实现并LLVM调试
_objc_rootDealloc->rootDeallocrootDealloc->object_disposeobject_dispose->objc_destructInstanceobjc_destructInstance->clearDeallocatingclearDeallocating->sidetable_clearDeallocatingsidetable_clearDeallocating3->table.refcnts.erase(it)
weak销毁流程
Method Swizzing坑点
黑魔法应用
在日常开发中,再好的程序员都会犯错,比如数组越界
NSArray *array = @[@"F", @"e", @"l", @"i", @"x"];
NSLog(@"%@", array[5]);
NSLog(@"%@", [array objectAtIndex:5]);
因此为了避免数组越界这种问题,大神们开始玩起了黑魔法——method swizzing
- 新建
NSArray分类 - 导入
runtime头文件—— - 写下新的方法
- 在
+load利用黑魔法交换方法
#import "NSArray+FX.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation NSArray (FX)
+ (void)load {
// 交换objectAtIndex方法
Method oriMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(objectAtIndex:));
Method swiMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(fx_objectAtIndex:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod1, swiMethod1);
// 交换取下标方法
Method oriMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
Method swiMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(fx_objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod2, swiMethod2);
}
- (void)fx_objectAtIndex:(NSInteger)index {
if (index > self.count - 1) {
NSLog(@"objectAtIndex————————数组越界");
return;
}
return [self fx_objectAtIndex:index];
}
- (void)fx_objectAtIndexedSubscript:(NSInteger)index {
if (index > self.count - 1) {
NSLog(@"取下标————————数组越界");
return;
}
return [self fx_objectAtIndexedSubscript:index];
}
@end
然而程序还是无情的崩了…

其实在iOS中NSNumber、NSArray、NSDictionary等这些类都是类簇(Class Clusters),一个NSArray的实现可能由多个类组成。所以如果想对NSArray进行方法交换,必须获取到其真身进行方法交换,直接对NSArray进行操作是无效的
以下是NSArray和NSDictionary本类的类名

这样就好办了,可以使用runtime取出本类
坑点一
黑魔法最好写成单例,避免多次交换
比如说添加了[NSArray load]代码,方法实现又交换回去了导致了崩溃
将+load方法改写成单例(虽然不常见,但也要避免)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
// 交换objectAtIndex方法
Method oriMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(objectAtIndex:));
Method swiMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(fx_objectAtIndex:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod1, swiMethod1);
// 交换取下标方法
Method oriMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
Method swiMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(fx_objectAtIndexedSubscript:));
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod2, swiMethod2);
});
}
坑点二
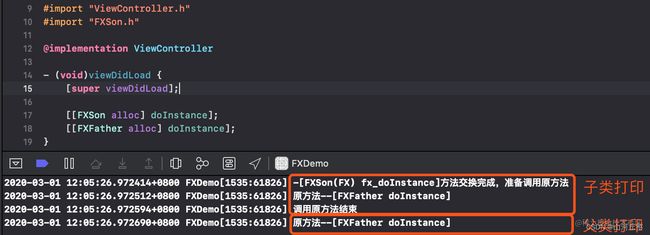
①子类交换父类实现的方法
- 父类
FXPerson类中有-doInstance方法,子类FXSon类没有重写 FXSon类新建分类做了方法交换,新方法中调用旧方法FXPerson类、FXSon类调用-doInstance
子类打印出结果,而父类调用却崩溃了,为什么会这样呢?
因为FXSon类交换方法时取得doInstance先在本类搜索方法,再往父类里查找,在FXFather中找到了方法实现就把它跟新方法进行交换了。可是新方法是在FXSon分类中的,FXFather找不到imp就unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x600002334250
所以这种情况下应该只交换子类的方法,不动父类的方法
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(doInstance));
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(fx_doInstance));
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(self, @selector(doInstance), method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(self, @selector(fx_doInstance), method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
});
}
- 通过
class_addMethod给FXSon类添加方法(class_addMethod不会取代本类中已存在的实现,只会覆盖本类中继承父类的方法实现) -
- 取得新方法
swiMethod的实现和方法类型
- 取得新方法
-
- 往方法名
@selector(fx_doInstance)添加方法
- 往方法名
-
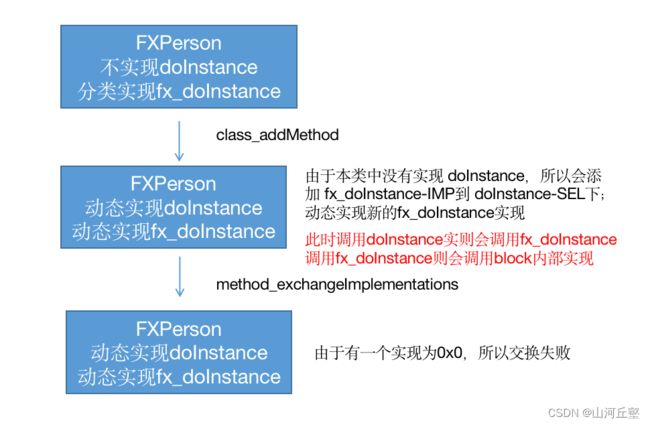
class_addMethod把新方法实现放到旧方法名中,此刻调用doInstance就是调用fx_doInstance,但是调用fx_doInstance会崩溃
- 根据
didAddMethod判断是否添加成功 -
- 添加成功说明之前本类没有实现——
class_replaceMethod替换方法
- 添加成功说明之前本类没有实现——
-
- 添加失败说明之前本类已有实现——
method_exchangeImplementations交换方法
- 添加失败说明之前本类已有实现——
doInstance方法中添加了新的方法实现fx_doInstance方法中想用旧的方法实现替代之前的方法实现,可是找不到doInstance实现,导致class_replaceMethod无效->在fx_doInstance中调用fx_doInstance就会死循环
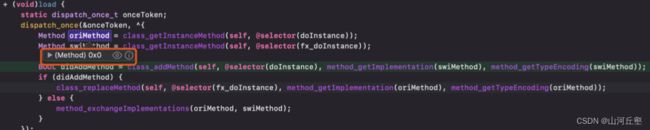
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(doInstance));
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(fx_doInstance));
if (!oriMethod) {
class_addMethod(self, @selector(doInstance), method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
method_setImplementation(swiMethod, imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"方法未实现");
}));
}
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(self, @selector(doInstance), method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(self, @selector(fx_doInstance), method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
});
}
注意事项
使用Method Swizzling有以下注意事项:
- 尽可能在
+load方法中交换方法 - 最好使用
单例保证只交换一次 - 自定义方法名不能产生冲突
- 对于系统方法要调用原始实现,避免对系统产生影响
- 做好注释(因为方法交换比较绕)
- 迫不得已情况下才去使用方法交换
这是一份做好封装的Method Swizzling交换方法
+ (void)FXMethodSwizzlingWithClass:(Class)cls oriSEL:(SEL)oriSEL swizzledSEL:(SEL)swizzledSEL {
if (!cls) NSLog(@"传入的交换类不能为空");
Method oriMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, oriSEL);
Method swiMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL);
if (!oriMethod) {
class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
method_setImplementation(swiMethod, imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"方法未实现");
}));
}
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(cls, oriSEL, method_getImplementation(swiMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swiMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(cls, swizzledSEL, method_getImplementation(oriMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(oriMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(oriMethod, swiMethod);
}
}
某个方法进行多次交换,最终的调用顺序是怎样的?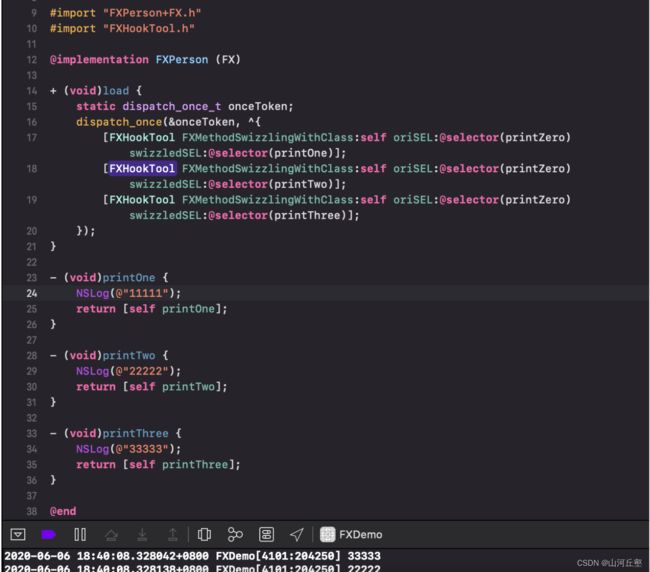
补充面试题二
问:如果发现方法交换之后不生效,应该怎么排查?
答:解决的方案有多种,主要从两个方向进行思考
- 方法交换的
class有没有问题 - 方法交换的
method有没有问题