手撕单链表练习
Topic 1:
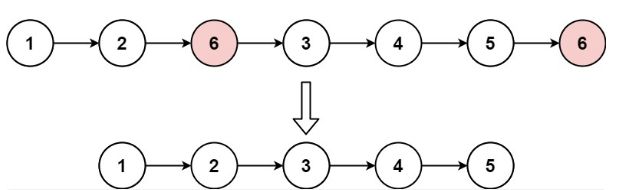
LeetCode——203. 移除链表元素
203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
移除链表中的数字6
操作很简单,我们只需要把2的指向地址修改就好了,原来的指向地址是6现在改为3
这个思路是完全正确的,但是在链表中增加或删除元素是很麻烦的,我们需要判断前后是否为空指针,情况很多。
我们利用这个思路,可以推广另外的做法,把不是6的元素尾插到一个新链表,这样就可以去除所有6
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* cur =head;//利用另外的变量遍历
//哨兵防止空指针
struct ListNode* newnode=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newnode->next=NULL;
struct ListNode* tail=newnode;//记录下次尾插的作用
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val!=val)
{
tail->next=cur;//尾插到哨兵后面
tail=tail->next;//尾向后
cur=cur->next;//指针向后
}
else
{
struct ListNode* tmp=cur->next;//存下一个,我们释放当前位置
free(cur);
cur=tmp;
}
}
tail->next=NULL;//到尾了
head=newnode->next;//去除哨兵
free(newnode);
return head;
}Topic 2:
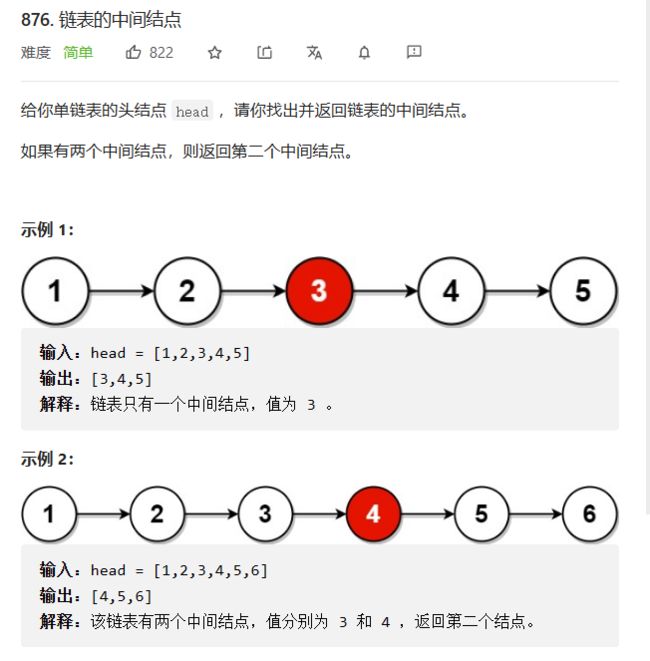
LeetCode——876. 链表的中间结点
876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
找中间很简单,但是假如我们要求时间复杂度为O(N)
我们应该怎么去做?小明一次走一步,小华一次走两步,当小华走完全程的时候,小明走的路程刚刚好是全部路程的一半。通过这个例子,我们可以明白,我们可以定义两个指针来进行查找中间的节点。这种方法叫做快慢指针。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast=head;
struct ListNode* slow=head;
while(fast && fast->next)//当元素是奇数个时fast->next为NULL;当元素为偶数个fast为NULL是结束标志
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}Topic 3:
链表中倒数第k个结点
链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
链表的倒数第k个元素
我们先处理极端情况:链表为空的时候;k大于链表元素个数
把极端情况处理完,我们思考,当时间复杂度为O(N)时,我们应该怎么样得到倒数第k的节点。倒数第k个就是正数的第n-k个,我们定义两个指针,一个先走k步,然后两个指针同时走,当先走k步的指针到结尾的时候,我们第二个指针就是走到了n-k的位置。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
struct ListNode* fast=pListHead;
struct ListNode* slow=pListHead;
if(pListHead==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while(k--)//先走k步
{
if(fast==NULL)//链表的元素小于k
{
return NULL;
}
fast=fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}Topic 4:
链表分割
我们先解读题目,给一个链表,给定一个值x,大于x的放后面,小于x的放前面。不改变原来的数据顺序即,原来小于x的值是,4 2 1,我们不改变想对位置 4 2 1.
题目理解清楚了,我们怎么做呢,我们创建两个链表,一个存小于x的值,一个存大于等于x的值,然后连接起来,这样他们的相对位置就没有改变。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
struct ListNode* gguard;//存大于等于x的数据得哨兵
struct ListNode* lguard;//存小于x的哨兵
struct ListNode* gtail;//存大于x的尾
struct ListNode* ltail;//存小于x的尾
struct ListNode* cur=pHead;
gguard=gtail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));//申请哨兵
lguard=ltail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));//申请哨兵
gtail->next=ltail->next=NULL;//哨兵后面一个置空
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val>=x)
{
gtail->next=cur;//哨兵后面接插入的链表
gtail=gtail->next;//尾向后移
}
else
{
ltail->next=cur;
ltail=ltail->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
ltail->next=gguard->next;//连接两个链表
gtail->next=NULL;//新链表的最后要置空
pHead=lguard->next;
free(lguard);
free(gguard);
return pHead;
}
};Topic 5:
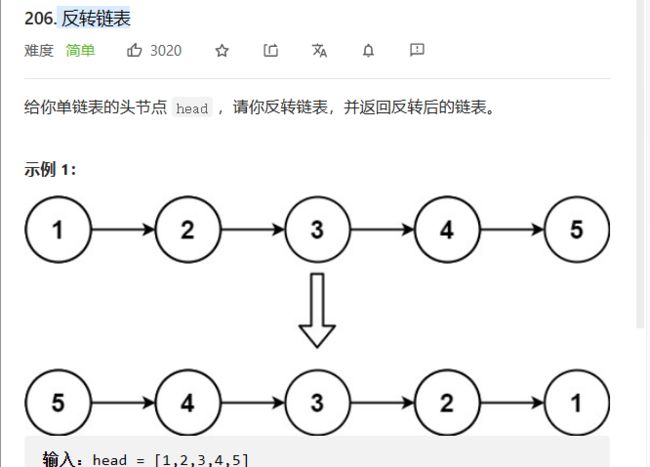
反转链表
206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
反转链表,我们可以利用头插的思路,即我们建立一个新的链表,把一个一个元素头插到第一个,最后插入的元素就是新的头,第一个插入的元素就是新的尾。头插最最要的是更新新的头,新的头就是新插入的元素的地址。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* newnode=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next=cur->next;//存下一个,防止找不到
cur->next=newnode;//将链表第一个元素指向newnode指针,下面依次指向
newnode=cur;//更新newnode,让newnode一直指向链表的开头
cur=next;//链表向后移
}
return newnode;
}Topic 6:
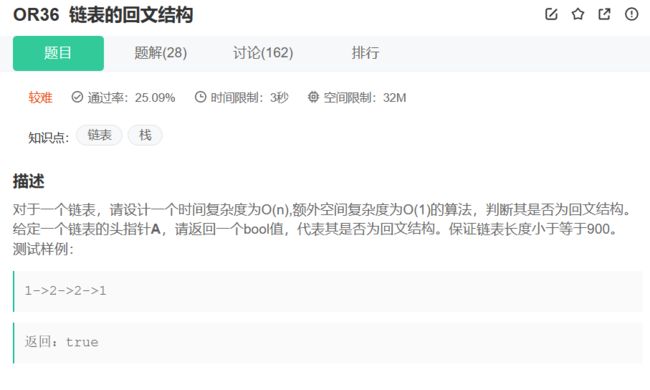
链表的回文结构
链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
链表的回文,怎么判断。我们最直接的方法是,找到中间节点,反转中间节点,得到翻转的链表,与前半段链表比较。如果前半段链表与,后半段链表翻转后的元素都相等,说明这个链表是回文链表。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* newnode=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next=cur->next;
cur->next=newnode;
newnode=cur;
cur=next;
}
return newnode;
}
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast=head;
struct ListNode* slow=head;
while(fast && fast->next)//当元素是奇数个时fast->next为NULL;当元素为偶数个fast为NULL是结束标志
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* mid=middleNode(head);//找到中间节点
struct ListNode* rhead=reverseList(mid);//反转中间节点后的元素
while(rhead)
{
if(head->val==rhead->val)
{
head=head->next;
rhead=rhead->next;
}
else
{
return false;//不相等说明不是回文
}
}
return true;
}
};Topic 7:
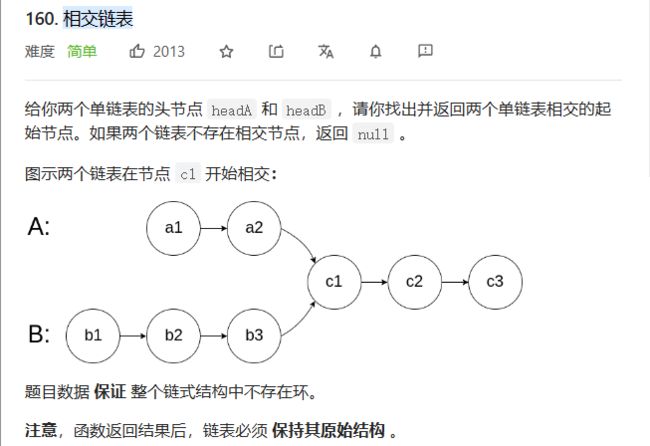
相交链表
160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
怎么判断链表相交,我们需要看链表的地址是否有相等的,如果我们利用两个for循环来实现判断是否有相等的地址,我们的时间复杂度就是O(N^2),,这个时间复杂度是很大的。我们还能通过什么方法来判断呢?相交的链表有共同的特点,就是它们有共同的尾,我们只需要判断尾的地址是否相等就好,如果尾的地址相等,我们就说明它们是相交的链表。
相交的链表,如何寻找第一个交点,全部遍历一遍,这个好像不太可能。既然链表有交点,第一个交点到链表尾的距离相等,而头到链表交点的距离就不一定相等了,它们的差值刚刚好是两个链表距离的差值。我们让长链表先走它们的差值,然后一起走,等它们的地址相等的时候就是它们的第一个交点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode* cur1=headA;
struct ListNode* cur2=headB;
int n1=1;//赋值1是因为统计链表长度的时候,我们的最后的一个位置,我们统计到
int n2=1;
while(cur1->next)//找headA的尾
{
cur1=cur1->next;
++n1;
}
while(cur2->next)//找headB的尾
{
cur2=cur2->next;
++n2;
}
if(cur1!=cur2)
{
return NULL;
}
int dif=abs(n1-n2);//让长的先走
cur1=headA;
cur2=headB;
if(n1>n2)
{
while(dif)
{
cur1=cur1->next;
dif--;
}
}
else
{
while(dif)
{
cur2=cur2->next;
dif--;
}
}
while(cur1!=cur2)
{
cur1=cur1->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
return cur1;
}