Spring Boot Starter 剖析与实践 | 京东云技术团队
引言
对于 Java 开发人员来说,Spring 框架几乎是必不可少的。它是一个广泛用于开发企业应用程序的开源轻量级框架。近几年,Spring Boot 在传统 Spring 框架的基础上应运而生,不仅提供了 Spring 的全部功能,还使开发人员更加便捷地使用。在使用 Spring Boot 时,我们经常会接触到各种 Spring Boot Starter,例如 spring-boot-starter-web。只需将该依赖加入项目中,我们就可以开始开发应用;在引入 spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc 后,只需在配置文件中填写数据库连接信息,即可连接数据库。此外,您还可以随意切换数据源组件依赖,而无需修改业务代码。Spring Boot Starter 是如何适配的呢?我们能否自己实现一个 Spring Boot Starter 呢?本文将剖析 Spring Boot Starter 的原理,并自定义实现一个 Spring Boot Starter 组件。
一、Spring Boot Starter 是什么?
Spring Boot Starter 是 Spring Boot 中比较重要的概念, 是一种依赖描述符,它可以帮助您简化配置。当需要构建一个 Web 应用程序时,不必再遍历所有的依赖包,一个一个地添加到项目的依赖管理中,而是只需要一个配置spring-boot-starter-web,如以下示例:
从上面示例来看,我们使用了相当少的代码创建了一个 REST 应用程序。Spring 官方提供了许多 Starter,同时第三方也可以自定义 Starter,官方为了加以区分,Starter 从名称上进行了如下规范:spring-boot-starter-xxx;第三方提供的 starter 名称为:xxx-spring-boot-starter。
二、Spring Boot Starter 剖析
前面介绍了 Starter 的概念以及如何快速创建 REST 应用程序。只需添加一个依赖和几行代码,就能完成 REST 接口开发。那么,在没有 Spring Boot 和 Starter 的情况下,我们该如何进行开发呢?Spring Boot Starter 的工作原理又是什么?接下来,我们将通过开发 Web 服务和 Dubbo 服务作为例子,分别剖析纯 Spring 和 Spring Boot Starter。
Spring
环境依赖
-
JDK 1.8
-
Maven 3
-
Tomcat 8(需要依靠 Web 容器服务器才能启动)
-
spring-webmvc 4.3.30.RELEASE
-
dubbo 2.7.23
开发流程
-
首先介绍一下,这是一个标准的 Maven 目录结构与
demo-service依赖内容org.springframework spring-webmvc 4.3.30.RELEASE javax.servlet servlet-api 2.5 com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind 2.9.8 org.apache.dubbo dubbo 2.7.23 org.apache.curator curator-x-discovery 5.1.0 org.apache.zookeeper zookeeper 3.8.0 com.demo demo-api 1.0-SNAPSHOT -
由于在 Spring XML 下还需要依靠 Java Web 和 Web 容器运行,还需要
web/WEB-INF/web.xmlWeb 配置文件,内容配置了 SpringMVC 入口org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener contextConfigLocation classpath:dubbo.xml springmvc org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet contextConfigLocation classpath:mvc.xml springmvc / -
SpringMVC 配置文件
mvc.xml与 Dubbo 配置文件dubbo.xml -
编写 Controller 接口与 Dubbo RPC 接口
package com.demo.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping(value = "/say/hello") public HelloEntity sayHello() { return new HelloEntity("Hello World"); } }package com.demo.provider; import com.demo.api.DemoService; import com.demo.dto.HelloEntity; public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Override public HelloEntity sayHello() { return new HelloEntity("Hello World"); } } -
以上还无法单独运行,需要将以上打包成
war包放入到 Tomcat 才可运行。
剖析
从上面的开发流程中,我们可以看到入口都在 web.xml 中。其中有一个监听器和一个 Servlet,以及初始化参数 dubbo.xml 和 mvc.xml。在 Spring Boot 出现之前,Spring 通常使用 XML 配置方式描述 Bean,或者在 XML 中配置注解驱动和上下文扫描方式解析 Bean。因此,我们可以看出这里有两个 XML 文件。经过分析源代码,我们整理出了以下 XML 标签解析到 Bean 解析的流程。如下:
-
由 Tomcat 启动加载
web.xml并通过监听器和 Servlet 让 Spring 加载 XML 并解析。 -
直到
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement开始解析自定义标签,找到mvc:xxx或dubbo:xxx标签找到了 XML 命名空间。 -
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver处理逻辑:以懒加载方式加载所有 jar 中META-INF/spring.handlers(路径必须得是这个)并缓存到handlerMappings,通过命名空间 URI 找到与之对应的处理类,SpringMVC 与 Dubbo 命名空间处理类分别为MvcNamespaceHandler和DubboNamespaceHandler -
MvcNamespaceHandler和DubboNamespaceHandler都分别实现了NamespaceHandler#init方法,内容如下:
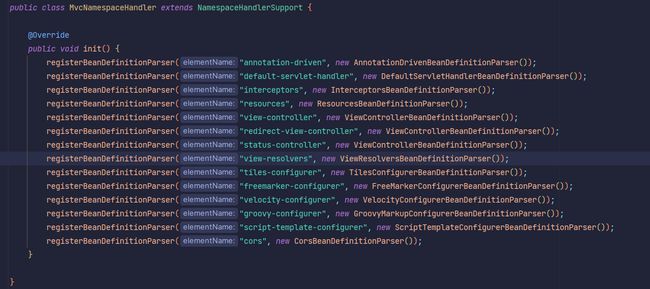
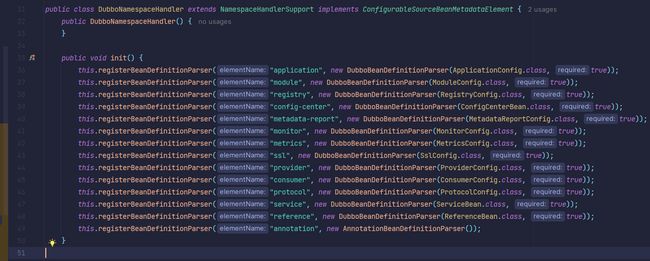
init方法将 SpringMVC 和 Dubbo 标签对应的BeanDefinitionParser注册到了NamespaceHandlerSupport#parsers中。在上一步中,DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver根据标签获取到了该标签的BeanDefinitionParser,从而将对应的 Bean 注册到了 Spring IOC 容器中。注册逻辑不是本文的重点,这里就不再赘述。至此,SpringMVC 和 Dubbo 的加载流程已经完成。
从以上加载流程中,我们可以看出,在没有 Spring Boot 之前,Spring 主要依靠 XML 配置来启动。它会加载 XML 中的自定义标签,找到对应的命名空间,然后扫描 classpath 下的 META-INF/spring.handlers,找到命名空间处理类来解析当前标签。
Spring Boot
环境依赖
-
JDK 1.8
-
Maven 3
-
spring-boot 2.6.9
-
dubbo 2.7.23
开发流程
-
目录结构与 Maven
demo-spring-boot依赖内容
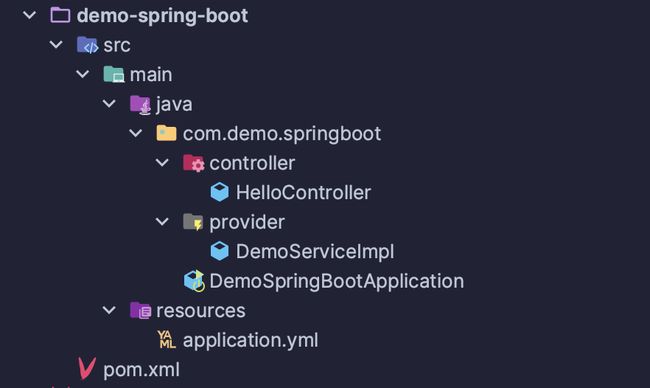
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.apache.dubbo dubbo-spring-boot-starter 2.7.23 org.apache.curator curator-x-discovery 5.1.0 org.apache.zookeeper zookeeper 3.8.0 com.demo demo-api 1.0-SNAPSHOT -
应用程序入口
DemoSpringBootApplication@SpringBootApplication public class DemoSpringBootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoSpringBootApplication.class, args); } } -
application.yml文件内容只有 Dubbo 的配置dubbo: application: name: demo-provider protocol: port: 20880 name: dubbo registry: address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 -
编写 Controller 接口与 Dubbo RPC 接口
package com.demo.controller; import com.demo.dto.HelloEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping(value = "/say/hello") public HelloEntity sayHello() { return new HelloEntity("Hello World"); } }package com.demo.provider; import com.demo.api.DemoService; import com.demo.dto.HelloEntity; @DubboService public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Override public HelloEntity sayHello() { return new HelloEntity("Hello World"); } } -
由于
spring-boot-starter-web已经内嵌 tomcat ,只需要直接运行DemoSpringBootApplication#main方法即可运行应用
剖析
从开发流程上没办法第一时间找到解析入口,唯一入口就是在DemoSpringBootApplication,经过源代码分析得出以下流程:
-
应用
DemoSpringBootApplication类上有@SpringBootApplication注解,而该注解由以下三个注解组成:-
@SpringBootConfiguration,标注当前类为一个配置类,与[@Configuration](https://my.oschina.net/pointdance)注解功能一致 ,被[@Configuration](https://my.oschina.net/pointdance)注解的类对应 Spring 的 XML 版的容器。 -
@EnableAutoConfiguration,开启启动自动装配的关键,由@AutoConfigurationPackage与@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)组成 -
@ComponentScan,按照当前类路径扫描含有@Service、@Controller等等注解的类,等同于 Spring XML 中的context:component-scan。
-
-
Spring Boot 自动装配由
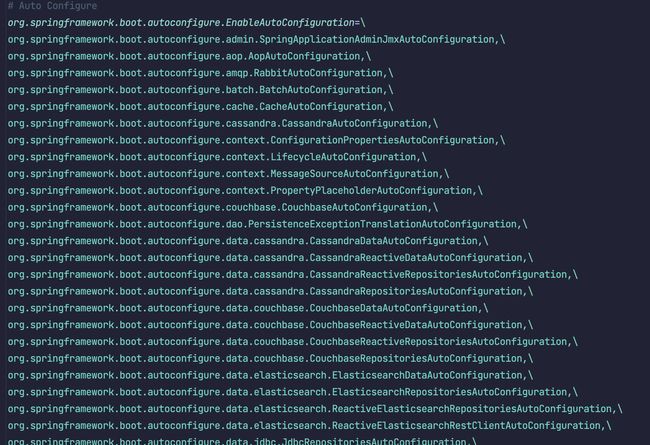
@EnableAutoConfiguration导入的AutoConfigurationImportSelector类,会调用SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames从 ClassPath 下扫描所有 jar 包的META-INF/spring.factories内容,由于传入的EnableAutoConfiguration.class,只会返回org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfigurationkey 的值,得到一个全限定类名字符串数组configurations。 -
configurations经过去重与声明式排除后,会进行以下进行过滤自动装配:configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations)分成两部分:获取过滤器和执行过滤。
-
getConfigurationClassFilter(),也是通过SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames在META-INF/spring.factories找到 Key 为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter的值,目前只有:OnBeanCondition、OnClassCondition、OnClassCondition三个过滤器。 -
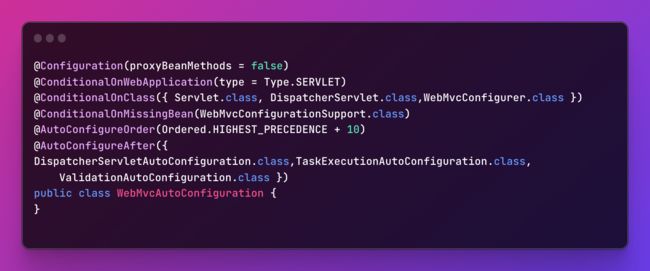
执行过滤,会根据配置类上含有
@ConditionOnBean、@ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnWebApplication等等条件注解来过滤掉部分配置类。比如WebMvcAutoConfiguration指定需要在@ConditionOnWebApplication下才生效。
-
-
在引入各类 Configuration 的配置类后,配置类结合
@Bean来完成 Spring Bean 解析和注入,同时 Spring Boot 还提供了许多@ConditionalXXX给开发者完成灵活注入。
以上就是 Spring Boot 的自动装配过程。Spring Boot 利用被 @Configuration 注解的配置类来代替 Spring XML 完成 Bean 的注入。然后,SpringFactoriesLoader 会最终加载 META-INF/spring.factories 中的自动配置类,实现自动装配过程。依靠“约定大于配置”的思想,如果开发的 Starter 想要生效,就需要按照 Spring Boot 的约定。
小结
通过对比 Spring 与 Spring Boot 的开发流程,我们可以发现 Spring Boot 在完成 Web 与 Dubbo 独立应用开发时,使用了相对较少的代码和配置。这得益于 Spring Boot Starter 的自动装配能力,它是 Spring Boot 的主要功能。通过消除定义一些属于自动配置类部分的需求,自动配置可以帮助简化开发流程并加速开发速度。
SPI
我们从上面剖析发现,两者都使用了一项机制去加载引入的 jar 包中的配置文件从而加载对应类,那就是SPI(Service Provider Interface)
SPI (Service Provider Interface), 是 Java 内置的一种服务提供发现机制,提高框架的扩展性。
Java SPI
Java 内置的 SPI 通过java.util.ServiceLoader类解析 Classpath 和 jar 包的META-INF/services目录下的以接口全限定名命名的文件,并加载该文件中指定的接口实现类,以此完成调用。
但是 Java SPI 会有一定不足:
-
不能做到按需加载,需要遍历所有的实现并实例化,然后在循环中找到所需要的实现。
-
多个并发多线程使用
ServiceLoader类的实例不安全 -
加载不到实现类时抛出并不是真正原因的异常,错误难定位。
Spring SPI
Spring SPI 沿用了 Java SPI ,但是在实现上和 Java SPI 存在差异,但是核心机制相同,在不修改 Spring 源码前提下,可以做到对 Spring 框架的扩展开发。
-
在 Spring XML 中,由
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver负责解析spring.handlers生成 namespaceUri 和 NamespaceHandler 名称的映射,等有需要时在进行实例化。 -
在 Spring Boot 中,由
SpringFactoriesLoader负责解析spring.factories文件,并将指定接口的所有实现类/全限定类名返回。
Spring Boot 2.7.0
在本文中 Spring Boot 自动装配使用了 SPI 来加载到EnableAutoConfiguration所指定的自动装配的类名,但在 Spring Boot2.7.0之后自动装配 SPI 机制有所改动,META-INF/spring.factories将废弃,同时在 Spring Boot 3 以上会将相关代码移除,改动如下:
-
新的注解:
@AutoConfiguration代替@Configuration -
读取自动装配的类文件位置改为:
META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports,并且实现类全限定类名按照一行一个 -
由
org.springframework.boot.context.annotation.ImportCandidates#load负责解析META-INF/spring/%s.imports,其中%s是接口名的占位符
三、Spring Boot Stater 实践
在使用spring-boot-starter-jdbc或者spring-boot-starter-jpa等数据库操作时,通常会引入一个数据库数据源连接池,比如:HikariCP、DBCP等,同时可随意切换依赖而不需要去更改任何业务代码,开发人员也无需关注底层实现,在此我们自定义一个 Starter 同时也实现这种兼容。因为我们以开发一个分布式锁的 Starter 并拥有多个实现:Zookeeper、Redis。 在此使用 Spring Boot 2.6.9 版本。
开发
项目结构与 Maven 依赖
└── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com.demo.distributed.lock
│ │ ├── api
│ │ │ ├── DistributedLock.java
│ │ │ └── LockInfo.java
│ │ ├── autoconfigure
│ │ │ ├── DistributedLockAutoConfiguration.java
│ │ │ └── DistributedLockProperties.java
│ │ ├── redis
│ │ │ └── RedisDistributedLockImpl.java
│ │ └── zookeeper
│ │ └── ZookeeperDistributedLockImpl.java
│ └── resources
│ └── META-INF
│ └── spring.factories
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-autoconfigure
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
org.apache.curator
curator-framework
5.1.0
provided
org.apache.curator
curator-recipes
5.1.0
provided
org.redisson
redisson
3.23.1
provided
在依赖里可以看到 Zookeeper 和 Redis 依赖关系被设置为provided,作用为编译与测试阶段使用,不会随着项目一起发布。即打包时不会带上该依赖。该设置在 Spring Boot Starter 作用较大。
分布式锁接口与实现
接口
public interface DistributedLock {
/**
* 加锁
*/
LockInfo tryLock(String key, long expire, long waitTime);
/**
* 释放锁
*/
boolean release(LockInfo lock);
}
Redis 实现
public class RedisDistributedLockImpl implements DistributedLock {
private final RedissonClient client;
public RedisDistributedLockImpl(RedissonClient client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
public LockInfo tryLock(String key, long expire, long waitTime) {
//do something
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean release(LockInfo lock) {
//do something
return true;
}
}
Zookeeper 实现
public class ZookeeperDistributedLockImpl implements DistributedLock {
private final CuratorFramework client;
public ZookeeperDistributedLockImpl(CuratorFramework client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
public LockInfo tryLock(String key, long expire, long waitTime) {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean release(LockInfo lock) {
return false;
}
}
DistributedLockAutoConfiguration 配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DistributedLockProperties.class)
@Import({DistributedLockAutoConfiguration.Zookeeper.class, DistributedLockAutoConfiguration.Redis.class})
public class DistributedLockAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(CuratorFramework.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DistributedLock.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "distributed.lock.type", havingValue = "zookeeper",
matchIfMissing = true)
static class Zookeeper {
@Bean
CuratorFramework curatorFramework(DistributedLockProperties properties) {
//build CuratorFramework client
return null;
}
@Bean
ZookeeperDistributedLockImpl zookeeperDistributedLock(CuratorFramework client) {
return new ZookeeperDistributedLockImpl(client);
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RedissonClient.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DistributedLock.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "distributed.lock.type", havingValue = "redis",
matchIfMissing = true)
static class Redis {
@Bean
RedissonClient redissonClient(DistributedLockProperties properties) {
//build RedissonClient client
return null;
}
@Bean
RedisDistributedLockImpl redisDistributedLock(RedissonClient client) {
return new RedisDistributedLockImpl(client);
}
}
}
-
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DistributedLockProperties.class)开启配置类 Properties 信息,会将配置文件里的信息注入 Properties 类里。 -
@Configuration配置注解 -
@ConditionalOnClass(CuratorFramework.class)条件注解,要求存在CuratorFramework类当前配置类才生效,Redis 的子配置类同理。 -
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DistributedLock.class)条件注解,Spring 不存在DistributedLockBean 当前配置类才生效,Redis 的子配置类同理。 -
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "distributed.lock.type", havingValue = "zookeeper", matchIfMissing = true)条件注解,这里判断配置文件distributed.lock.type等于zookeeper才生效,当如果没配置则默认当做zookeeper,Redis 的子配置类同理。 -
@Bean将方法返回的 Bean 注入到 Spring IOC 容器里,方法入参中含依赖的 Bean
spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.demo.distributed.lock.autoconfigure.DistributedLockAutoConfiguration
我们只需要将该文件放到resource/META-INF/spring.factories下,就会被 Spring Boot 加载,这也是 Spring Boot 的约定大于配置的思想。
使用
Maven 依赖关系
com.demo
distributed-lock-spring-boot-starter
1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
dev
true
org.redisson
redisson
3.23.1
test
org.apache.curator
curator-framework
5.1.0
org.apache.curator
curator-recipes
5.1.0
此处结合 Maven profile 功能按照不同环境依赖不同分布式锁底层实现,同时 Spring Boot 也提供了 Spring Boot Profile 加载不同配置,可以从开发、测试、生产环境使用不同底层了,同时 Maven profile 可以根据-P指定加载不同的依赖进行打包,解决了不同环境使用不同分布式锁实现。
代码使用
private final DistributedLock distributedLock;
public DemoServiceImpl(DistributedLock distributedLock) {
this.distributedLock = distributedLock;
}
public void test() {
LockInfo lock = null;
try {
lock = distributedLock.tryLock("demo", 1000, 1000);
//do something
} finally {
if (lock != null) {
distributedLock.release(lock);
}
}
}
业务代码中由于依赖的是接口,结合 Spring Boot Starter 条件注解 + Maven Profile 不管依赖哪个分布式锁实现,都无需去修改代码。
四、总结
本文介绍了在没有 Spring Boot 和 Starter 之前,开发人员在使用传统的 Spring XML 开发 Web 应用时需要引用许多依赖,并且需要大量编写 XML 代码来描述 Bean 以及它们之间的依赖关系。也了解了如何利用 SPI 加载自定义标签来加载 Bean 并进行注入。而 Spring Boot Starter 则提供了一种更加现代化的配置方式,它通过 SPI 机制加载自动装配的 @Configuration 配置类来代替传统的 Spring XML 完成 Bean 的注入,从而消除了大量的 XML 配置。最后,我们通过自定义开发了一个分布式锁 Spring Boot Starter 组件,利用一系列的 @ConditionalXXX 注解和 Maven Profile 来完成开发。这样,我们可以兼容多种分布式锁实现,并且在不同环境下使用不同的分布式锁实现,而无需修改业务代码。
作者:京东零售 陈炎清
来源:京东云开发者社区