FPGA利用查找表实现sin cos函数
1.生成0到360度的sin和 cos函数的coe文件
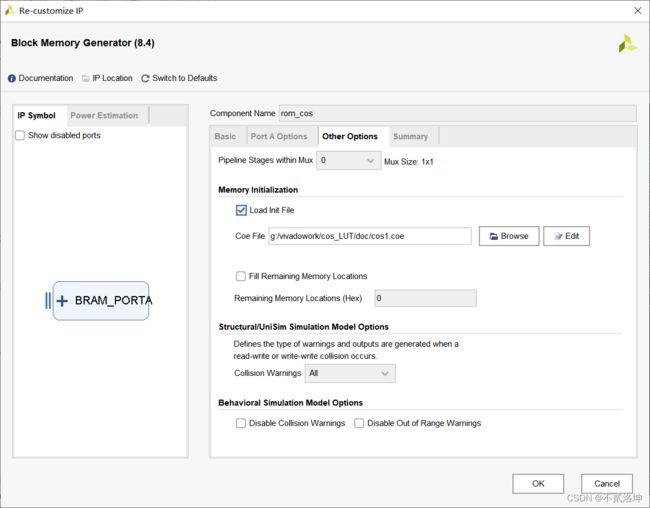
2.导入ROM里面
3.编写Verilog程序
4.进行仿真或者逻辑分析仪
1.sin函数
clear;
clc;
Quantify_bit=16; % 量化位数
theta=0:1:360; % 度
L=length(theta); % 采样点数
y=sind(theta);
yt=round(y*(2^(Quantify_bit-1)-1)); % 16bit量化
% 在.coe文件中
% 第一行为定义数据格式, 2代表 ROM 的数据格式为二进制。
% 从第 3 行开始到第最后一行,是这个 L(数据长度为1024)* ADC_bit(16bit) 大小 ROM 的初始化数据。
% 第一行到倒数第二行的数字后面用逗号,最后一行数字结束用分号。
fid=fopen('sin1.coe','w'); % w表示write
fprintf(fid,'Memory_Initialization_Radix = 2;\r\n'); % 二进制
fprintf(fid,'Memory_Initialization_Vector = \r\n');
for p=1:L
B_s=dec2bin(yt(p)+(yt(p)<0)*2^Quantify_bit,Quantify_bit);
for q=1:Quantify_bit % 12位,依次判断这12位的数值
if B_s(q)=='1'
data=1;
else
data=0;
end
fprintf(fid,'%d',data);
end
% 下面if语句的目的
% 每行数字后面用逗号(,),最后一行数字结束用分号(;)
if (pcos函数
clear;
clc;
Quantify_bit=16; % 量化位数
theta=0:1:360; % 度
L=length(theta); % 采样点数
y=cosd(theta);
yt=round(y*(2^(Quantify_bit-1)-1)); % 16bit量化
% 在.coe文件中
% 第一行为定义数据格式, 2代表 ROM 的数据格式为二进制。
% 从第 3 行开始到第最后一行,是这个 L(数据长度为1024)* ADC_bit(16bit) 大小 ROM 的初始化数据。
% 第一行到倒数第二行的数字后面用逗号,最后一行数字结束用分号。
fid=fopen('cos1.coe','w'); % w表示write
fprintf(fid,'Memory_Initialization_Radix = 2;\r\n'); % 二进制
fprintf(fid,'Memory_Initialization_Vector = \r\n');
for p=1:L
B_s=dec2bin(yt(p)+(yt(p)<0)*2^Quantify_bit,Quantify_bit);
for q=1:Quantify_bit % 12位,依次判断这12位的数值
if B_s(q)=='1'
data=1;
else
data=0;
end
fprintf(fid,'%d',data);
end
% 下面if语句的目的
% 每行数字后面用逗号(,),最后一行数字结束用分号(;)
if (p2.
sin类似
添加ila的IP
3.
top文件
module top(
input sys_clk, //50MHz时钟
input rst_n //复位,低电平有效
);
/*
函数功能:
产生余弦值
*/
wire [15:0] cos_value; //ROM读出数据 每个数据有12bit
reg [8:0] cos_addr; //ROM输入地址 361个数据,需要2^9个地址
//产生ROM地址读取数据
always @ (posedge sys_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
cos_addr <= 10'd0;
else
cos_addr <= cos_addr+1'b1;
end
//实例化ROM
rom_cos rom_cos_inst
(
.clka (sys_clk ), //inoput clka
.addra (cos_addr ), // input wire [8 : 0] addra 361个数据,需要2^9个地址
.douta (cos_value ) // output wire [15 : 0] douta
);
/*
函数功能:
产生正弦值
*/
wire [15:0] sin_value; //ROM读出数据 每个数据有12bit
reg [8:0] sin_addr; //ROM输入地址 1024个数据,需要2^10个地址
//产生ROM地址读取数据
always @ (posedge sys_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
sin_addr <= 10'd0;
else
sin_addr <= sin_addr+1'b1;
end
//实例化ROM
rom_sin rom_sin_inst
(
.clka (sys_clk ), //inoput clka
.addra (sin_addr ), // input wire [8 : 0] addra 361个数据,需要2^9个地址
.douta (sin_value ) // output wire [15 : 0] douta
);
/*
函数功能:
查表计算某角度的正弦值、余弦值
*/
wire [15:0] data_value_sin;
wire [15:0] data_value_cos;
reg [8:0] theta;
always @(posedge sys_clk or negedge rst_n) begin// 角度
if(!rst_n)
theta <= 9'd60;
else if(theta < 9'd300)
theta <= theta + 9'd30;
else
theta <= 9'd180;
end
//查表得到余弦值
rom_cos rom_cos_data_inst
(
.clka (sys_clk ), //inoput clka
.addra (theta ), // input wire [8 : 0] addra 361个数据,需要2^9个地址
.douta (data_value_cos ) // output wire [15 : 0] douta
);
//查表得到正弦值
rom_sin rom_sin_data_inst
(
.clka (sys_clk ), //inoput clka
.addra (theta ), // input wire [8 : 0] addra 361个数据,需要2^9个地址
.douta (data_value_sin ) // output wire [15 : 0] douta
);
//实例化逻辑分析仪
ila_0 ila_0_inst (
.clk(sys_clk), // input wire clk
.probe0(cos_addr ), // input wire [8:0] probe0
.probe1(cos_value), // input wire [15:0] probe1
.probe2(sin_addr ), // input wire [8:0] probe2
.probe3(sin_value), // input wire [15:0] probe3
.probe4(data_value_sin), // input wire [`15:0] probe4
.probe5(data_value_cos) // input wire [15:0] probe5
);
endmoduletop1_tb文件
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module top1_tb();
reg sys_clk;
reg rst_n;
initial begin
sys_clk = 1'b0;
rst_n = 1'b0;
#20
rst_n = 1'b1;
end
always #10 sys_clk = ~sys_clk;
top u_top(
.sys_clk(sys_clk), //50MHz时钟
.rst_n(rst_n) //复位,低电平有效
);
endmodule4.
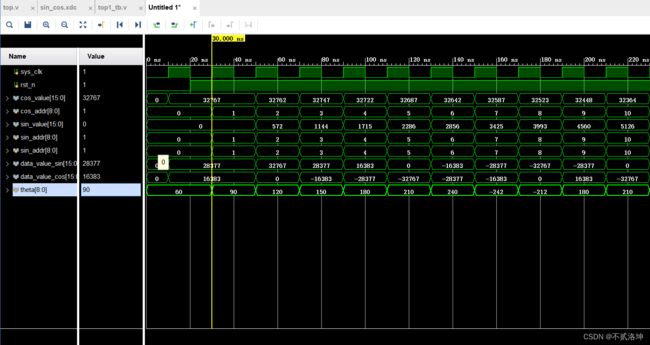
最后结果,theta=60的时候,data_value_sin = 28377,这是量化后的值,除以2^15 -1=32767,28377/32767=0.866=根号3除以2
data_value_cos = 16383,16383/32767=0.49998约等于0.5