Tarjan 算法的 Python 实现
本文介绍求解有向图强连通分量的线性时间的 Tarjan 算法,并提供 Python 代码。
相关概念
强连通:节点在有向图中可以互相到达
强连通图:任意两个节点都强连通的有向图
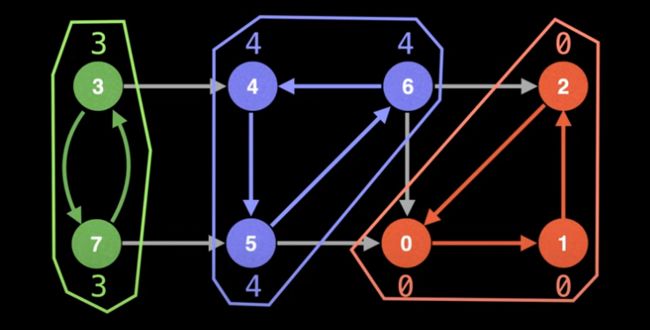
强连通分量(strongly connected component, SCC):有向图的极大强连通子图
low-link value (LLV, 中文直译:低链接值):在深度优先搜索(DFS)过程中,某一节点所能到达的最小节点编号(含自身)
算法流程
- 开始深度优先搜索:访问一个未访问过的节点,编号自增长,初始化其 LLV 为编号,然后将节点标记为已访问,并压入栈中;
- 深度优先搜索回调:若相邻节点(前向)在栈中,更新当前节点的 LLV 值;
- 相邻节点访问结束:若当前节点是一个强连通分量(SCC)的起始节点,则执行出栈操作直到当前节点出栈。
注意:
已经访问过所有相邻节点(出度)的节点,不再考虑到达它的路径(入度),如此可以确保单向相连的节点不在同一个强连通分量。
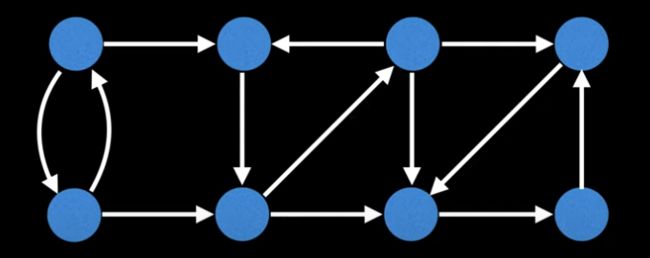
算例
代码实现
node.py
from typing import List
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, id: int, parents: List[int], descendants: List[int]) -> None:
"""
node initialise
:param id: node ID
:param parents: from which nodes can come to current node directly
:param descendants: from current node can go to which nodes directly
"""
self.id = id
self.parents = parents
self.descendants = descendants
algorithm.py
from typing import Dict
from node import Node
class Tarjan(object):
"""
Tarjan's algorithm
"""
def __init__(self, nodes: Dict[int, Node]) -> None:
"""
data initialise
:param nodes: node dictionary
"""
self.nodes = nodes
# intermediate data
self.unvisited_flag = -1
self.serial = 0 # serial number of current node
self.num_scc = 0 # current SCC
self.serials = {i: self.unvisited_flag for i in nodes.keys()} # each node's serial number
self.low = {i: 0 for i in nodes.keys()} # each node's low-link value
self.stack = [] # node stack
self.on_stack = {i: False for i in nodes.keys()} # if each node on stack
# run algorithm
self.list_scc = [] # final result
self._find_scc()
def _find_scc(self):
"""
algorithm main function
"""
for i in self.nodes.keys():
self.serials[i] = self.unvisited_flag
for i in self.nodes.keys():
if self.serials[i] == self.unvisited_flag:
self._dfs(node_id_at=i)
# result process
dict_scc = {}
for i in self.low.keys():
if self.low[i] not in dict_scc.keys():
dict_scc[self.low[i]] = [i]
else:
dict_scc[self.low[i]].append(i)
self.list_scc = list(dict_scc.values())
def _dfs(self, node_id_at: int):
"""
algorithm recursion function
:param node_id_at: current node ID
"""
self.stack.append(node_id_at)
self.on_stack[node_id_at] = True
self.serials[node_id_at] = self.low[node_id_at] = self.serial
self.serial += 1
# visit all neighbours
for node_id_to in self.nodes[node_id_at].descendants:
if self.serials[node_id_to] == self.unvisited_flag:
self._dfs(node_id_at=node_id_to)
# minimise the low-link number
if self.on_stack[node_id_to]:
self.low[node_id_at] = min(self.low[node_id_at], self.low[node_id_to])
# After visited all neighbours, if reach start node of current SCC, empty stack until back to start node.
if self.serials[node_id_at] == self.low[node_id_at]:
node_id = self.stack.pop()
self.on_stack[node_id] = False
self.low[node_id] = self.serials[node_id_at]
while node_id != node_id_at:
node_id = self.stack.pop()
self.on_stack[node_id] = False
self.low[node_id] = self.serials[node_id_at]
self.num_scc += 1
main.py
from node import Node
from algorithm import Tarjan
# params
# case 1
num_node = 8
connections = [
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]
]
# # case 2
# num_node = 6
# connections = [
# [0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
# [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
# [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
# [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
# ]
# nodes
nodes = {i: Node(id=i, parents=[j for j in range(num_node) if connections[j][i]],
descendants=[j for j in range(num_node) if connections[i][j]]) for i in range(num_node)}
# algorithm
tarjan = Tarjan(nodes=nodes)
print()
print("strongly connected components:")
for scc in tarjan.list_scc:
print(scc)
print()