UART的verilog实现
1 串口的协议
串口的全称是通用异步收发传输器,主要用于数据间的串行传递,是一种全双工传输模式。它在发送数据时将并行的数据转换成串行数据来传输,在接收数据时,将收到的串行数据转化为并行数据。
uart在发送或者接收过程中的一帧数据由4部分组成,包括起始位、数据位、奇偶校验位和停止位。其中起始位标志着一帧数据的开始,停止位标志着一帧数据的结束。数据位是一帧数据中的有效数据,校验位可以分为奇校验还是偶校验。
起始位:
tx传输信号默认是低电平,当出现一个下降沿,且持续一个bit的时间的低电平,则认为传输了一个起始位
数据位
是传输的有效数据,数据的位宽是可以选择的,6,7,8位。
校验位:
可以对传输的数据的正确性进行一定程度的检查
停止位:
持续一个bit时间长的高电平,则认为是数据的结束
波特率
对于波特率,表示一秒内需要传输多少bit的数据,比如9600bps,就是表示一秒要传播9600bit。
2 串口发送模块
| clk | 时钟 |
|---|---|
| rst_n | 复位 |
| tx_data | 发送的一字节的数据 |
| tx_en | 发送数据的使能信号,为一个高脉冲 |
| byte_finish | 成功发射了一字节的数据 |
| tx | 发送的信号 |
设计的整体思路
总体思路是设计一个状态机,有五个状态,空闲状态(IDLE),开始状态(START)、发送数据(SEND_DATA)、校验(EVEN_ODD_CHECK)和停止(STOP)。
首先对于全局的数据放在一个文件中config.v中,其中代码如下:
`define CLK_FRE 50_000_000 //输入的时钟频率
`define BAUD_RATE 115200 //波特率
`define EVEN_CHECK 1 //1 :偶校验 0:奇校验
uart_tx的模块代码如下:
`include "config.v"
module uart_tx (
input wire clk ,
input wire rst_n ,
input wire [7:0] tx_data ,
input wire tx_en ,
output wire byte_finish ,
output reg tx
);
localparam IDLE = 5'b00001 , //空闲
START = 5'b00010 , //起始
SEND_DATA = 5'b00100 , //发送数据
EVEN_OLD_CHECK = 5'b01000 , //奇偶校验
STOP = 5'b10000 ; //停止
localparam CNT_MAX = `CLK_FRE / `BAUD_RATE ;
reg [31:0] cnt ;
reg [4:0] state ;
reg [4:0] nx_state ;
reg [2:0] cnt_data ;
reg even_check ;
reg odd_check ;
wire start_finish; //起始位结束信号
wire bit_flag ; //发送每个数据的bit信号
wire byte_flag ; //成功发送一字节数据的标致
wire check_flag ; //奇偶校验的标志
wire stop_flag ; //停止位的标志
wire check ; //要发送的奇偶校验信号
assign start_finish = (state == START) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign bit_flag = (state == SEND_DATA) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign byte_flag = bit_flag && (cnt_data == 3'd7) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign check_flag = ((state == EVEN_OLD_CHECK) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1)) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign stop_flag = ((state == STOP) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1)) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign check = `EVEN_CHECK ? even_check : odd_check;
//状态转移(时序逻辑)
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
state <= nx_state;
end
end
//状态跳转(组合逻辑)
always @(*) begin
//nx_state <= IDLE;
case(state)
IDLE: nx_state = (tx_en) ? START : IDLE;
START: nx_state = (start_finish) ? SEND_DATA : START;
SEND_DATA: nx_state = byte_flag ? EVEN_OLD_CHECK : SEND_DATA;
EVEN_OLD_CHECK: nx_state = check_flag ? STOP : EVEN_OLD_CHECK;
STOP: nx_state = stop_flag ? IDLE : STOP;
default: nx_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
//对cnt计数器赋值
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
case(state)
IDLE: cnt <= 'd0;
START: begin
if(nx_state == START) begin
cnt <= cnt + 1'b1;
end
else if(nx_state == SEND_DATA) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt;
end
end
SEND_DATA:begin
if(nx_state == SEND_DATA) begin
if(bit_flag) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt + 1'b1;
end
end
else if(nx_state == EVEN_OLD_CHECK) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt;
end
end
EVEN_OLD_CHECK: cnt <= (nx_state == EVEN_OLD_CHECK) ? cnt + 1'b1 : (nx_state == STOP) ? 'd0 : cnt;
STOP: cnt <= (nx_state == STOP) ? cnt + 1'b1 : 1'b0;
default:cnt <= 'd0;
endcase
end
end
//统计发送的数据的bit数
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt_data <= 3'd0;
end
else if((state == SEND_DATA) && (cnt_data == 3'd7) && (bit_flag)) begin
cnt_data <= 'd0;
end
else if((state == SEND_DATA) && (cnt_data < 3'd7) && (bit_flag)) begin
cnt_data <= cnt_data + 1'b1;
end
else begin
cnt_data <= cnt_data;
end
end
//生成奇校验还是偶校验
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
even_check <= 1'b0;
odd_check <= 1'b0;
end
else if(tx_en) begin
even_check <= ^tx_data;
odd_check <= ~(^tx_data);
end
else begin
even_check <= even_check;
odd_check <= odd_check;
end
end
assign byte_finish = stop_flag;
//发送数据
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
tx <= 1'b1;
end
else begin
case(nx_state)
IDLE: tx <= 1'b1;
START: tx <= 1'b0;
SEND_DATA: tx <= bit_flag ? tx_data[cnt_data+1] : tx_data[cnt_data];
EVEN_OLD_CHECK:tx <= check;
STOP: tx <= 1'b1;
default: tx <= 1'b1;
endcase
end
end
endmodule
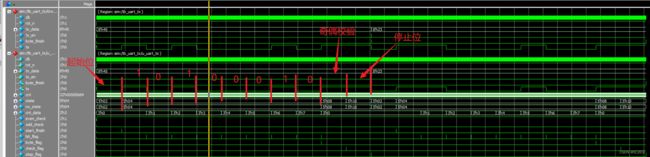
testbench如下:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
`define CLK_CYCLE 20
module tb_uart_tx;
reg clk ;
reg rst_n ;
reg [7:0] tx_data ;
reg tx_en ;
wire byte_finish ;
wire tx ;
uart_tx u_uart_tx(
. clk (clk),
. rst_n (rst_n),
. tx_data (tx_data),
. tx_en (tx_en),
. byte_finish (byte_finish),
. tx (tx)
);
initial begin
clk = 1'b0;
rst_n = 1'b0;
tx_data = 8'h00;
tx_en = 1'b0;
#30
rst_n = 1'b1;
#100
repeat (2) @(posedge clk);
tx_en = 1'b1;
tx_data = 8'h45;
@(posedge clk);
tx_en = 1'b0;
@(negedge byte_finish);
tx_en = 1'b1;
tx_data = 8'h23;
@(posedge clk);
tx_en = 1'b0;
@(byte_finish);
#100
$finish;
end
always #(`CLK_CYCLE / 2) clk = ~clk;
endmodule
3 串口接收模块
信号的解释:
| clk | 时钟 |
|---|---|
| rst_n | 复位 |
| tx | 接受到的单bit信号 |
| rx_data | 接收到的一个字节数据 |
| byte_finish | 一个字节数据接收的完成信号 |
| error | 基于奇偶校验,判断接收的数据是否可信 |
设计的整体思路
总体思路是设计一个状态机,有五个状态,空闲状态(IDLE),开始状态(START)、接收数据(RV_DATA)、校验(CHECK)和停止(STOP)。需要指出的一点是,对于数据采样,选择一个bit信号中间采样,这样采样的数据才是较为可靠的。
uart_rx的模块如下:
`include "config.v"
module uart_rx(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst_n ,
input wire tx ,
output wire [7:0] rx_data ,
output reg error ,
output wire byte_finish
);
localparam IDLE = 5'b00001 , //空闲
START = 5'b00010 , //开始
RV_DATA = 5'b00100 , //接收数据
CHECK = 5'b01000 , //奇偶校验
STOP = 5'b10000 ; //停止
localparam CNT_MAX = `CLK_FRE / `BAUD_RATE ;
reg tx_dly ;
reg [31:0] cnt ;
reg [4:0] state ;
reg [4:0] nx_state ;
reg [2:0] cnt_bit ;
reg [7:0] rv_data ;
reg even_check ;
reg odd_check ;
wire tx_negedge ;
wire start_end ;
wire bit_flag ;
wire rv_end ;
wire sample_flag ; //采样数据的信号
wire check ;
wire check_end ;
wire stop_end ;
assign start_end = (state == START) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 2);
assign bit_flag = (state == RV_DATA) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1);
assign rv_end = (state == RV_DATA) && (bit_flag) && (cnt_bit == 3'd7);
assign sample_flag = ((state == RV_DATA) ) && (cnt == CNT_MAX / 2 - 1);
assign check = `EVEN_CHECK ? even_check : odd_check;
assign check_end = (state == CHECK) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1);
assign stop_end = (state == STOP) && (cnt == CNT_MAX - 1);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
tx_dly <= 1'b1;
end
else begin
tx_dly <= tx;
end
end
assign tx_negedge = ((tx_dly) && (!tx)) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
state <= nx_state;
end
end
always @(*) begin
case(state)
IDLE: nx_state = tx_negedge ? START : IDLE;
START: nx_state = start_end ? RV_DATA : START;
RV_DATA:nx_state = rv_end ? CHECK : RV_DATA;
CHECK: nx_state = check_end ? STOP : CHECK;
STOP: nx_state = stop_end ? IDLE : STOP;
default:nx_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
case(state)
IDLE: cnt <= 'd0;
START: begin
if(nx_state == START) begin
cnt <= cnt + 1'b1;
end
else if(nx_state == RV_DATA) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt;
end
end
RV_DATA:begin
if(nx_state == RV_DATA) begin
if(bit_flag) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt + 1'b1;
end
end
else if(nx_state == CHECK) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt;
end
end
CHECK: cnt <= (nx_state == CHECK) ? cnt + 1'b1 : 'd0;
STOP : cnt <= (nx_state == STOP) ? cnt + 1'b1 : 'd0;
default:cnt <= 'd0;
endcase
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt_bit <= 3'd0;
end
else if((bit_flag) && (nx_state == CHECK)) begin
cnt_bit <= 3'd0;
end
else if(bit_flag) begin
cnt_bit <= cnt_bit + 1'b1;
end
else begin
cnt_bit <= cnt_bit;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
rv_data <= 8'h00;
end
else if(state == IDLE) begin
rv_data <= 8'h00;
end
else if(sample_flag) begin
rv_data <= {tx, rv_data[7:1]};
end
else begin
rv_data <= rv_data;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
odd_check <= 1'b0;
even_check <= 1'b0;
end
else if(nx_state == CHECK) begin
even_check <= ^rv_data;
odd_check <= ~(^rv_data);
end
else begin
even_check <= even_check;
odd_check <= odd_check;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
error <= 1'b0;
end
else if(nx_state == IDLE) begin
error <= 1'b0;
end
else if(nx_state == STOP) begin
error <= 1'b0;
end
else if((nx_state == CHECK) && sample_flag) begin
error <= (tx != check) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
end
else begin
error <= error;
end
end
assign rx_data = rv_data;
assign byte_finish = (state == STOP) && (nx_state == IDLE);
endmodule
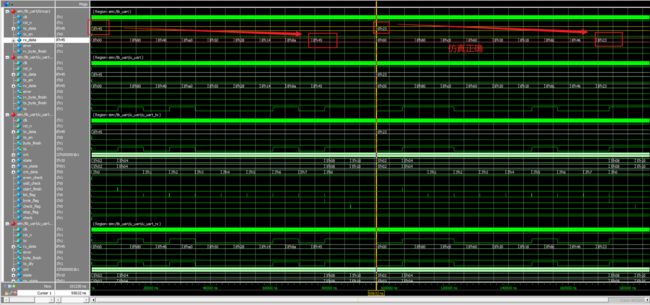
4 uart发送和接收模块的联合仿真
uart的顶层如下:

uart模块代码如下,就是把发送和接收模块连接
module uart(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst_n ,
input wire [7:0] tx_data ,
input wire tx_en ,
output wire [7:0] rx_data ,
output wire error ,
output wire rv_byte_finish
);
wire tx_byte_finish ;
wire tx ;
uart_tx u_uart_tx(
. clk (clk),
. rst_n (rst_n),
. tx_data (tx_data),
. tx_en (tx_en),
. byte_finish (tx_byte_finish),
. tx (tx)
);
uart_rx u_uart_rx(
. clk (clk),
. rst_n (rst_n),
. tx (tx),
. rx_data (rx_data),
. error (error),
. byte_finish (rv_byte_finish)
);
endmodule
仿真代码如下:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
`define CLK_CYCLE 20
module tb_uart;
reg clk ;
reg rst_n ;
reg [7:0] tx_data ;
reg tx_en ;
wire [7:0] rx_data ;
wire error ;
wire rv_byte_finish;
uart u_uart(
. clk (clk),
. rst_n (rst_n),
. tx_data (tx_data),
. tx_en (tx_en),
. rx_data (rx_data),
. error (error),
. rv_byte_finish(rv_byte_finish)
);
initial begin
clk = 1'b0;
rst_n = 1'b0;
tx_data = 8'h00;
tx_en = 1'b0;
#30
rst_n = 1'b1;
#100
repeat (2) @(posedge clk);
tx_en = 1'b1;
tx_data = 8'h45;
@(posedge clk);
tx_en = 1'b0;
@(negedge rv_byte_finish);
tx_en = 1'b1;
tx_data = 8'h23;
@(posedge clk);
tx_en = 1'b0;
@(rv_byte_finish);
#100
$finish;
end
always #(`CLK_CYCLE / 2) clk = ~clk;
endmodule
5 总结
感觉自己对状态机的写法以及理解更加好了,至此三大通信协议都完成了。加油加油加油!!!