[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(5): cpphttplib实现网络服务、html页面实现、服务器部署...
在前四篇文章中, 我们实现了从文档文件的清理 到 搜索的所有内容:
- 项目背景: [C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(1): 项目背景介绍、相关技术栈、相关概念介绍…
- 文档解析、处理模块
parser的实现: [C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(2): 文档文本解析模块parser的实现、如何对文档文件去标签、如何获取文档标题… - 文档 正排索引与倒排索引 建立的接口的实现: [C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(3): 建立文档及其关键字的正排 倒排索引、jieba库的安装与使用…
- 文档的 搜索功能 接口的实现: [C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(4): 实现搜索的相关接口、线程安全的单例index接口、cppjieba分词库的使用…
建议先阅读上面四篇文章
后端的主要功能接口完成之后, 就可以结合网络将其设计为服务器 然后部署到网络上了
网络服务
我们使用cpphttplib库 实现搜索引擎服务器. 所以要先安装cpphttplib库
cpphttplib
使用cpphttplib时, gcc版本不能太低. 而CentOS 7默认的版本是4.8.5, 太低了. 所以安装使用cpphttplib之前, 要先升级gcc到至少7.x以上
gcc升级
我们将gcc升级到8.3.1. 非常的简单, 只需要一共6条指令 就可以完成:
# 安装 centos-release-scl
sudo yum install centos-release-scl
# 安装 devtoolset-8-gcc* (gcc8相关软件包)
sudo yum install devtoolset-8-gcc*
# 安装完成, 需要建立软连接
mv /usr/bin/gcc /usr/bin/gcc-4.8.5
ln -s /opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/bin/gcc /usr/bin/gcc
mv /usr/bin/g++ /usr/bin/g++-4.8.5
ln -s /opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/bin/g++ /usr/bin/g++
然后就可以看到:
❯ gcc -v
Using built-in specs.
COLLECT_GCC=gcc
COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/lto-wrapper
Target: x86_64-redhat-linux
Configured with: ../configure --enable-bootstrap --enable-languages=c,c++,fortran,lto --prefix=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr --mandir=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/share/man --infodir=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/share/info --with-bugurl=http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla --enable-shared --enable-threads=posix --enable-checking=release --enable-multilib --with-system-zlib --enable-__cxa_atexit --disable-libunwind-exceptions --enable-gnu-unique-object --enable-linker-build-id --with-gcc-major-version-only --with-linker-hash-style=gnu --with-default-libstdcxx-abi=gcc4-compatible --enable-plugin --enable-initfini-array --with-isl=/builddir/build/BUILD/gcc-8.3.1-20190311/obj-x86_64-redhat-linux/isl-install --disable-libmpx --enable-gnu-indirect-function --with-tune=generic --with-arch_32=x86-64 --build=x86_64-redhat-linux
Thread model: posix
gcc version 8.3.1 20190311 (Red Hat 8.3.1-3) (GCC)
❯ g++ -v
Using built-in specs.
COLLECT_GCC=g++
COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/libexec/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/lto-wrapper
Target: x86_64-redhat-linux
Configured with: ../configure --enable-bootstrap --enable-languages=c,c++,fortran,lto --prefix=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr --mandir=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/share/man --infodir=/opt/rh/devtoolset-8/root/usr/share/info --with-bugurl=http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla --enable-shared --enable-threads=posix --enable-checking=release --enable-multilib --with-system-zlib --enable-__cxa_atexit --disable-libunwind-exceptions --enable-gnu-unique-object --enable-linker-build-id --with-gcc-major-version-only --with-linker-hash-style=gnu --with-default-libstdcxx-abi=gcc4-compatible --enable-plugin --enable-initfini-array --with-isl=/builddir/build/BUILD/gcc-8.3.1-20190311/obj-x86_64-redhat-linux/isl-install --disable-libmpx --enable-gnu-indirect-function --with-tune=generic --with-arch_32=x86-64 --build=x86_64-redhat-linux
Thread model: posix
gcc version 8.3.1 20190311 (Red Hat 8.3.1-3) (GCC)
安装cpphttplib
cpphttplib库的安装非常简单, 因为整个库中 只需要用到一个httplib.h的头文件.
但是, 我们需要选择版本安装, 不能直接安装最新版的. 因为gcc编译器版本不匹配的话 可能 会出现无法编译或运行时错误的情况
这里推荐0.7.16的版本: https://github.com/yhirose/cpp-httplib/tree/v0.7.16
可以直接获取此版本的源码:
❯ wget https://codeload.github.com/yhirose/cpp-httplib/zip/refs/tags/v0.7.16
然后解压出来, 将httplib.h拷贝到项目目录下:
❯ wget https://codeload.github.com/yhirose/cpp-httplib/zip/refs/tags/v0.7.16
--2023-08-08 14:24:23-- https://codeload.github.com/yhirose/cpp-httplib/zip/refs/tags/v0.7.16
Resolving codeload.github.com (codeload.github.com)... 20.205.243.165
Connecting to codeload.github.com (codeload.github.com)|20.205.243.165|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: unspecified [application/zip]
Saving to: ‘v0.7.16’
[ <=> ] 586,948 1.10MB/s in 0.5s
2023-08-08 14:24:25 (1.10 MB/s) - ‘v0.7.16’ saved [586948]
❯ unzip v0.7.16
Archive: v0.7.16
... 解压过程
extracting: cpp-httplib-0.7.16/test/www3/dir/test.html
❯ ll
total 588K
drwxr-xr-x 6 July July 4.0K Nov 30 2020 cpp-httplib-0.7.16
drwxr-xr-x 9 July July 4.0K Aug 7 00:16 cppjieba
drwxr-xr-x 6 July July 4.0K Aug 8 13:52 gitHub
-rw-r--r-- 1 July July 574K Aug 8 14:24 v0.7.16
# 将httplib.h 拷贝到项目目录下:
cp cpp-httplib-0.7.16/httplib.h gitHub/Boost-Doc-Searcher/.
这就算在项目中安装成功了
cpphttplib的简单使用
关于cpphttplib的使用, Github文档有简单的使用介绍
直接使用这段代码 可以实现怎么样的结果呢?
#include 直接访问根url, 没有任何响应. 但是如果我们在url之后添加/hi. 就能看到Hello World!的字样.
这就是我们设定的 申请/hi资源时, 会响应的内容:
httplib::Server::Get()是用来处理HTTP的GET方法的接口.
-
第一个参数, 用来指定处理 申请某内容的请求.
如果传入
/hi, 就会处理 请求的url是wwwRoot/hi的请求. 如果传入/index.html, 就会处理 请求的url是wwwRoot/hi的请求wwwRoot表示web根目录, 没有设置 即为服务器运行路径 -
第二个参数, 是一个回调函数 用来 接收请求 对请求进行处理, 并响应
此回调函数的第一个参数 就是用来接收请求的.
第二个参数, 可以看作一个输出型参数. 是用来填充响应的
在例子中, 使用
httplib::Response::set_content(), 接口设置响应正文以及相应的类型
最后监听指定端口, 就可以通过ip:port的形式访问服务器.
项目网络服务 **
了解了cpphttplib的最基本使用. 就可以为项目创建网络服务了
但是, 创建网络服务之前. 可以先了解一下 搜索引擎的搜索结果是怎么出现的?
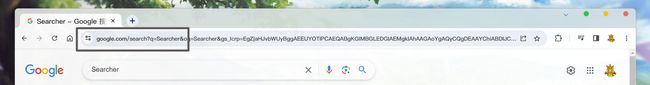
当我们搜索时, 会申请/search这个服务. 并携带了?q=Searcher这个key(q)=value(Searcher)属性.
然后, 就会将搜索结果显示出来.
而cpphttplib提供了检索url中是否存在key的接口, 并且可以通过key获取value值的接口, 所以我们就可以这样来向页面设置内容:
svr.Get("/search", [](const httplib::Request& request, httplib::Response& response) {
if (!request.has_param("word")) {
// url中没有 word 键值
// set_content() 第一个参数是设置正文内容, 第二个参数是 正文内容类型等属性
response.set_content("请输入内容后搜索", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
}
});
然后运行服务器并访问/search:
当url中没有key为word的键值时, 就会显示 请输入内容后搜索
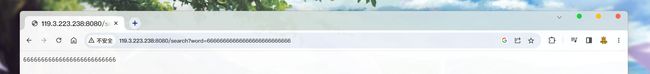
如果有key为word的键值, 因为我们没有做任何操作, 所以不会有任何内容:
除了判断是否存在key, 还可以通过接口获得对应的value:
svr.Get("/search", [](const httplib::Request& request, httplib::Response& response) {
if (!request.has_param("word")) {
// url中没有 word 键值
// set_content() 第一个参数是设置正文内容, 第二个参数是 正文内容类型等属性
response.set_content("请输入内容后搜索", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
}
std::string word = request.get_param_value("word");
response.set_content(word, "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
});
此时, 再携带key=value键对:
就获取到了value的内容, 并设置为了响应内容.
既然可以获取url中的键值, 那么 就可以实现根据键值调用searcher::search()接口, 搜索相关文档:
#include 编译代码 g++ httpServer.cc -lpthread -ljsoncpp
运行程序. 建立索引 等待服务器开启成功之后:
直接在url添加键值 就可以看到直接的搜索结果.
至此, 网络服务的编写就完成了.
下面要做的, 就是通过网页发送请求, 并根据响应构建结果网页.
网页构建
由于博主没有学过前端的代码, 所以做出来的网页只是能用. 也没有能力去解释一些原理或底层的实现. 只能介绍一下基本功能
所以, 直接列出代码:
./wwwRoot/index.html:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<link rel="icon" type="image/svg+xml" href="/favicon.svg" />
<title>Boost库 文档搜索</title>
<style>
/* 去掉网页中的所有的默认内外边距,html的盒子模型 */
* {
background-color: #f5f5f7;
/* 设置外边距 */
margin: 0;
/* 设置内边距 */
padding: 0;
}
/* 将我们的body内的内容100%和html的呈现吻合 */
html,
body {
height: 100%;
}
/* 类选择器.container */
.container {
text-align: center;
/* 设置div的宽度 */
width: 800px;
/* 通过设置外边距达到居中对齐的目的 */
margin: 0px auto;
/* 设置外边距的上边距,保持元素和网页的上部距离 */
margin-top: 100px;
}
/* 复合选择器,选中container 下的 search */
.container .search {
/* 宽度与父标签保持一致 */
width: auto;
/* 高度设置为52px */
height: 52px;
}
.container .result {
margin-top: 30px;
text-align: left;
width: 100%;
}
.container .result .item {
height: auto;
border-radius: 13px;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
margin-top: 15px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
padding-top: 10px;
}
.container .result .item a {
margin-left: 10px;
margin-right: 10px;
/* 设置为块级元素,单独站一行 */
display: block;
background-color: #fff;
/* a标签的下划线去掉 */
text-decoration: none;
/* 设置a标签中的文字的字体大小 */
font-size: 20px;
/* 设置字体的颜色 */
color: #4e6ef2;
word-break: break-all;
}
.container .result .item a:hover {
/*设置鼠标放在a之上的动态效果*/
text-decoration: underline;
}
.container .result .item p {
margin-left: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 10px;
display: block;
background-color: #fff;
font-size: 16px;
word-break: break-all;
font-family: "Lucida Sans", "Lucida Sans Regular", "Lucida Grande",
"Lucida SansUnicode", Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
}
.container .result .item i {
margin-left: 10px;
margin-right: 10px;
/* 设置为块级元素,单独站一行 */
display: block;
font-size: 12px;
/* 取消斜体风格 */
font-style: normal;
background-color: #fff;
color: gray;
word-break: break-all;
}
#INDEXBLOGS {
text-align: center;
width: 75%;
}
.search-box {
width: 666px;
margin: auto;
display: flex;
background-color: #fff;
align-items: center;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 25px;
height: 44px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}
.search-input {
flex: 1;
padding: 0 15px;
border: none;
background-color: #fff;
border: 0px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 25px;
font-size: 16px;
height: 43px;
}
.search-input:focus {
outline: none;
}
.search-button {
padding: 0 18px;
height: 100%;
border: none;
border-radius: 0 25px 25px 0;
background: #fef9f2;
color: #666;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.suggestion {
margin-bottom: 5px;
color: #000000;
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<img
src="https://dxyt-july-image.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/202308080011153.png"
id="INDEXBLOGS"
/>
<p class="suggestion">
服务器配置原因, 若搜索结果过多 可能响应较慢, 请耐心等待哦~
</p>
<div class="search-box">
<input
type="text"
id="search-input"
class="search-input"
placeholder=""
/>
<button onclick="Search()" class="search-button">♥ Search</button>
</div>
<div class="result">
// 这里是展示搜索结果的地方
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 获取输入框元素
const input = document.getElementById("search-input");
// 输入框按键按下事件监听
input.addEventListener("keydown", function (event) {
// 判断按键为回车键
if (event.keyCode === 13) {
// 模拟按钮点击事件
document.querySelector(".search-button").click();
}
});
function Search() {
// 是浏览器的一个弹出框
// alert("hello js!");
// 1. 提取数据, $可以理解成就是JQuery的别称
let query = $(".container .search-input").val();
console.log("query = " + query); //console是浏览器的对话框,可以用来进行查看js数据
//2. 发起http请求,ajax: 属于一个和后端进行数据交互的函数,JQuery中的
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: "/s?word=" + query,
success: function (data) {
console.log(data);
BuildHtml(data);
},
});
}
function BuildHtml(data) {
// 获取html中的result标签
let result_lable = $(".container .result");
// 清空历史搜索结果
result_lable.empty();
for (let elem of data) {
// console.log(elem.title);
// console.log(elem.url);
let a_lable = $("", {
text: elem.title,
href: elem.url,
// 跳转到新的页面
target: "_blank",
});
let i_lable = $("", {
text: elem.url,
});
let p_lable = $(""
, {
text: elem.desc,
});
let div_lable = $("", {
class: "item",
});
a_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
i_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
p_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
div_lable.appendTo(result_lable);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
这个html文件是创建在项目目录下的wwwRoot目录下的:
一个是页面html文件, 一个是图标文件
大概解释一下这个html代码:
-
首先最外层 是html最基本的框架:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
之间的内容, 就是要在页面中显示的内容
-
在 之间. 先设置了一个
可以看作是在页面内容中设置了一个框架, 之后只要在这个内部的 都会显示在这个框架中
-
然后
-
<div class="search-box">
<input
type="text"
id="search-input"
class="search-input"
placeholder=""
/>
<button onclick="Search()" class="search-button">♥ Searchbutton>
div>
又设置了一个并在其内部设置了: 一个搜索框
一个搜索按钮
onclick="Search()"表示点击按钮执行的函数
-
<div class="result">
// 这里是展示搜索结果的地方
div>
搜索框下面就是要展示的内容了
设置了 , 这个内部就是展示搜索结果用的 搜索结果用这个元素item表示:
<div class="item">
<a href="" target="_blank">跳转标题a>
<i>urli>
<p>摘要p>
div>
-
布局设置完毕之后, 就需要使用JavaScript JQuery ajax来发送请求, 接收响应 和 设置搜索结果了
<script>
// 获取输入框元素
const input = document.getElementById("search-input");
// 输入框按键按下事件监听
input.addEventListener("keydown", function (event) {
// 判断按键为回车键
if (event.keyCode === 13) {
// 模拟按钮点击事件
document.querySelector(".search-button").click();
}
});
function Search() {
// 是浏览器的一个弹出框
// alert("hello js!");
// 1. 提取数据, $可以理解成就是JQuery的别称
let query = $(".container .search-input").val();
console.log("query = " + query); //console是浏览器的对话框,可以用来进行查看js数据
//2. 发起http请求,ajax: 属于一个和后端进行数据交互的函数,JQuery中的
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: "/s?word=" + query,
success: function (data) {
console.log(data);
BuildHtml(data);
},
});
}
function BuildHtml(data) {
// 获取html中的result标签
let result_lable = $(".container .result");
// 清空历史搜索结果
result_lable.empty();
for (let elem of data) {
// console.log(elem.title);
// console.log(elem.url);
let a_lable = $("", {
text: elem.title,
href: elem.url,
// 跳转到新的页面
target: "_blank",
});
let i_lable = $("", {
text: elem.url,
});
let p_lable = $(""
, {
text: elem.desc,
});
let div_lable = $("", {
class: "item",
});
a_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
i_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
p_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
div_lable.appendTo(result_lable);
}
}
script>
然后就是Search()函数, 获取search-input搜索框内的数据为query, 然后创建HTTP的GET方法请求, 并携带?word=query 发送给服务器.
然后成功接收到响应之后, 根据响应数据 执行Build()函数 在item元素
编写完index.html之后, 需要在httpServer.cc主函数内, 将服务器的web根文件设置为./wwwRoot/index.html
const std::string& rootPath = "./wwwRoot/index.html";
svr.set_base_dir(rootPath.c_str());
然后再编译运行服务器:
-
没有执行搜索的界面:
-
执行了搜索之后的界面:
搜索结果, 都会按照权重一个个排列在下面
至此, 我们的Boost搜索引擎就可以使用了!
不过, 还有一些地方需要优化和修改
代码优化
当前的搜索引擎还有问题:
-
没有搜索到内容时, 不会有任何反应. 可能会让用户认为服务器没有运作.
所以可以考虑在没有搜索到任何文档的时候, 响应一个没有任何内容的item元素. 并实现, 点击标题 跳转回主页:
/* searcher.hpp */
// 排序之后, allInvertedElemOut 中文档的排序就是倒序了
// 然后 通过遍历此数组, 获取文档id, 根据id获取文档在正排索引中的内容
// 然后再将 所有内容序列化
Json::Value root;
if (allInvertedElemOut.empty()) {
// 如果没有查找到一个文档
Json::Value elem;
elem["url"] = "http://119.3.223.238:8080";
elem["title"] = "Search nothing!";
// 关于文档的内容, 搜索结果中是不展示文档的全部内容的, 应该只显示包含关键词的摘要, 点进文档才显示相关内容
// 而docInfo中存储的是文档去除标签之后的所有内容, 所以不能直接将 doc._content 存储到elem对应key:value中
elem["desc"] = "Search nothing!";
root.append(elem);
// 处理url 都设置为无效值
}
else {
for (auto& elemOut : allInvertedElemOut) {
// 通过Json::Value 对象, 存储文档内容
Json::Value elem;
// 通过elemOut._docId 获取正排索引中 文档的内容信息
ns_index::docInfo_t* doc = _index->getForwardIndex(elemOut._docId);
// elem赋值
elem["url"] = doc->_url;
elem["title"] = doc->_title;
// 关于文档的内容, 搜索结果中是不展示文档的全部内容的, 应该只显示包含关键词的摘要, 点进文档才显示相关内容
// 而docInfo中存储的是文档去除标签之后的所有内容, 所以不能直接将 doc._content 存储到elem对应key:value中
elem["desc"] = getDesc(doc->_content, elemOut._keywords[0]); // 只根据第一个关键词来获取摘要
// for Debug
// 这里有一个bug, jsoncpp 0.10.5.2 是不支持long或long long 相关类型的, 所以需要转换成 double
// 这里转换成 double不会有什么影响, 因为这两个参数只是本地调试显示用的.
elem["docId"] = (double)doc->_docId;
elem["weight"] = (double)elemOut._weight;
root.append(elem);
}
}
此时, 搜索不到内容:
点击就会跳转至主页.
-
可能没有标题:
当搜索到的文章没有标题时, 就不会显示出来. 显示不出来也就无法通过标题跳转至指定的页面:
为什么没有标题呢? 不是因为出错了, 是因为 这篇文章本身就没有标题:
所以, 我们可以考虑修改搜索时获取标题的代码:
/* searcher.hpp */
Json::Value root;
if (allInvertedElemOut.empty()) {
Json::Value elem;
elem["url"] = "http://119.3.223.238:8080";
elem["title"] = "Search nothing!";
// 关于文档的内容, 搜索结果中是不展示文档的全部内容的, 应该只显示包含关键词的摘要, 点进文档才显示相关内容
// 而docInfo中存储的是文档去除标签之后的所有内容, 所以不能直接将 doc._content 存储到elem对应key:value中
elem["desc"] = "Search nothing!";
root.append(elem);
}
else {
for (auto& elemOut : allInvertedElemOut) {
// 通过Json::Value 对象, 存储文档内容
Json::Value elem;
// 通过elemOut._docId 获取正排索引中 文档的内容信息
ns_index::docInfo_t* doc = _index->getForwardIndex(elemOut._docId);
// elem赋值
elem["url"] = doc->_url;
elem["title"] = doc->_title;
if (doc->_title.empty()) {
// 如果无标题, 将标题设置为TITLE
elem["title"] = "TITLE";
}
// 关于文档的内容, 搜索结果中是不展示文档的全部内容的, 应该只显示包含关键词的摘要, 点进文档才显示相关内容
// 而docInfo中存储的是文档去除标签之后的所有内容, 所以不能直接将 doc._content 存储到elem对应key:value中
elem["desc"] = getDesc(doc->_content, elemOut._keywords[0]); // 只根据第一个关键词来获取摘要
// for Debug
// 这里有一个bug, jsoncpp 0.10.5.2 是不支持long或long long 相关类型的, 所以需要转换成 double
// 这里转换成 double不会有什么影响, 因为这两个参数只是本地调试显示用的.
elem["docId"] = (double)doc->_docId;
elem["weight"] = (double)elemOut._weight;
root.append(elem);
}
}
然后, 再搜索:
-
我们之前为了方便观测调试, 把文档的docId和weight也存储并发送了. 现在可以去除
-
在使用parser模块处理文档html文件的时候, 有三个符号被转换成了编码<: < >: > &: &
搜索的结果在页面中显示的时候, < > & 符号会以编码的形式显示. 所以我们可以在构建结果的的时候, 再将其转换回去:
/*index.html*/
for (let elem of data) {
// console.log(elem.title);
// console.log(elem.url);
let a_lable = $("", {
text: elem.title.replace(/</g, "<").replace(/>/g, ">").replace(/&/g, "&"),
href: elem.url,
// 跳转到新的页面
target: "_blank",
});
let i_lable = $("", {
text: elem.url,
});
let p_lable = $(""
, {
text: elem.desc.replace(/</g, "<").replace(/>/g, ">").replace(/&/g, "&"),
});
let div_lable = $("", {
class: "item",
});
a_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
i_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
p_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
div_lable.appendTo(result_lable);
}
添加日志 并 部署服务器
这部分涉及到守护进程相关内容, 建议阅读博主文章了解:
[Linux] 守护进程介绍、服务器的部署、日志文件…
直接在项目中引入两个文件, 这两个文件都是之前实现过 只不过做了一点点修改的. 很简单:
logMessage.hpp:
/* 日志相关 */
#pragma once
#include
daemonize.hpp:
/* 守护进程接口 */
#pragma once
#include
在项目中引入这两个文件之后, 就可以将httpServer.cc设置为守护进程.
并将 整个项目中所有向标准输出和标准错误打印日志的信息, 都改为LOG(LEVEL, MESSAGE, ...)形式 向文件中打印日志:
#include
执行了daemonize()之后, 服务器就会变成守护进程. 只要服务器主机不关机 或者 不主动kill掉进程. 服务就会一直在后台运行. 所有人都可以随时随地访问.
欢迎访问: Boost库 文档搜索
不欢迎搞破坏!!
项目的完整目录结构 以及 完整代码 展示
目录结构
❯ pwd
/home/July/gitCode/gitHub/Boost-Doc-Searcher
❯ tree -L 3
.
├── cppjieba
│ ├── DictTrie.hpp
│ ├── ...(jieba库相关头文件)
│ └── Unicode.hpp
├── cppjiebaDict
│ ├── hmm_model.utf8
│ ├── ...(jieba库提供的分词库)
│ └── user.dict.utf8
├── daemonize.hpp
├── data
│ ├── input
│ │ ├── about.html
│ │ ├── ...(Boost库文档文件)
│ │ └── yap.html
│ └── output
│ └── raw
├── httplib.h
├── httpServer.cc
├── index.hpp
├── LICENSE
├── logMessage.hpp
├── makefile
├── parser
├── parser.cc
├── README.md
├── searcher.hpp
├── searcherServerd
├── serverLog.log
├── util.hpp
└── wwwRoot
├── favicon.svg
└── index.html
64 directories, 287 files
完整代码
整个项目的完整代码已提交至Github: Boost-Doc-Searcher
欢迎收藏使用~
本篇文章至此结束. 但此项目还有扩展内容, 可以关注一下专栏等待后续更新~
感谢阅读~
��������������������
![[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(5): cpphttplib实现网络服务、html页面实现、服务器部署..._第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c60098c5a77f4ecb859b37a43107dbf0.jpg)
![[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(5): cpphttplib实现网络服务、html页面实现、服务器部署..._第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f809561efab4448297774e136c5af11c.jpg)
![[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(5): cpphttplib实现网络服务、html页面实现、服务器部署..._第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/def05c1b72a84989a438b1fd5b5a1449.jpg)



![[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(5): cpphttplib实现网络服务、html页面实现、服务器部署..._第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/0a87e57ff90d4b3aa0a9e408082099cb.gif)
![[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(5): cpphttplib实现网络服务、html页面实现、服务器部署..._第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3e2365d2ad3b4345970d5b2556211c01.jpg)