【SpringBoot】| ORM 操作 MySQL(集成MyBatis)
目录
一:ORM 操作 MySQL
1. 创建 Spring Boot 项目
2. @MapperScan
3. mapper文件和java代码分开管理
4. 事务支持
一:ORM 操作 MySQL
使用MyBatis框架操作数据, 在SpringBoot框架集成MyBatis,使用步骤:
(1)mybatis起步依赖 : 完成mybatis对象自动配置, 对象放在容器中
(2)pom.xml 指定把src/main/java目录中的xml文件包含到classpath中
(3)创建实体类Student
(4)创建Dao接口 StudentDao , 创建一个查询学生的方法
(5)创建Dao接口对应的Mapper文件, xml文件, 写sql语句
(6)创建Service层对象, 创建StudentService接口和它的实现类。 去dao对象的方法,完成数据库的操作
(7)创建Controller对象,访问Service。
(8)写application.properties文件,配置数据库的连接信息。
1. 创建 Spring Boot 项目
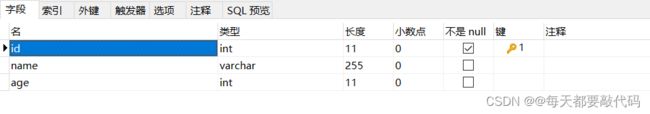
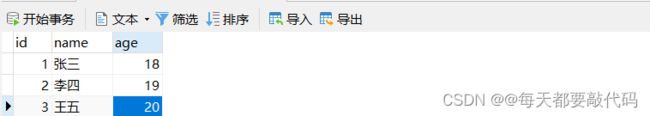
(1)准备数据库表
字段及其类型
插入数据
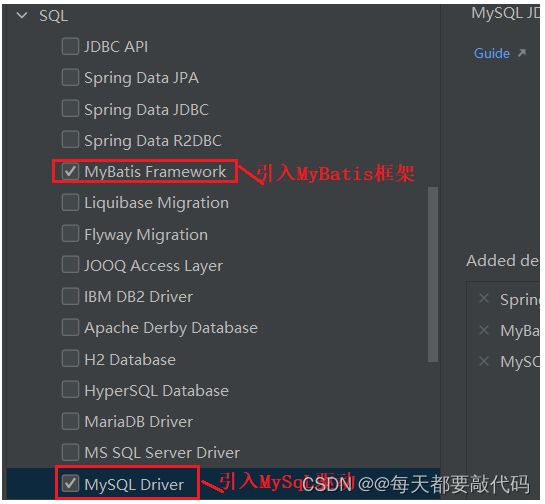
(2)创建一个SpringBoot项目
选择Spring Web依赖
MybatisFramework依赖、MySQL Driver依赖
(3)生成的pom.xml配置和手动添加的resource插件配置
注:resource插件配置是表示将src/java/main下的或者说子包下的*.xml配置文件最终加载到target/classes目录下。
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.7.9
com.zl
study-springboot-mysql
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
2.3.0
com.mysql
mysql-connector-j
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
src/main/java
**/*.xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
(4)实体类
准备一个实体类,类的属性名与数据库中的字段名保持一致。
package com.zl.pojo;
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
(5)创建Dao接口
需要在类上加@Mapper注解:告诉MyBatis这是一个dao接口,创建此接口的代理对象。
package com.zl.dao;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper //用来创建代理对象的
public interface StudentDao {
// 根据id进行查询
Student selectById(@Param("stuId") Integer id);
}
(6)在Dao接口下创建一个同名的StudentDao.xml文件
注:前面我们配置的resource配置就是为这个StudentDao.xml配置服务的!
(7)编写Service接口和对应的实现类
StudentService接口
package com.zl.service;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
public interface StudentService {
// 方法调用
Student queryStudent(Integer id);
}
StudentService接口实现类,编写业务逻辑
package com.zl.service.impl;
import com.zl.dao.StudentDao;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
import com.zl.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service // 交给Spring容器管理
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
// 调用Dao
@Resource // 给属性赋值
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Override
public Student queryStudent(Integer id) {
Student student = studentDao.selectById(id);
return student;
}
}
(8)创建controller去调用service
package com.zl.controller;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
import com.zl.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource
public StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/student/query")
@ResponseBody
public String queryStudent(Integer id){
Student student = studentService.queryStudent(id);
return student.toString();
}
}
(9)连接数据库,需要application.properties配置
useUnicode使用unicode编码,characterEncoding字符集是utf-8,serverTimezone时区。
server.port=9090
server.servlet.context-path=/orm
#连接数据库的配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123(10)执行结果
2. @MapperScan
如果有多个Dao接口,那么需要在每个Dao接口上都加入@Mapper注解,比较麻烦!
StudentDao接口
package com.zl.dao;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface StudentDao {
// 根据id进行查询
Student selectById(Integer id);
}
UserDao接口
package com.zl.dao;
import com.zl.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
// 根据id进行查询
SUser selectById(Integer id);
}
也可以在主类上(启动类上)添加注解包扫@MapperScan("com.zl.dao")
注:basePackages是一个String数组,可以写多个要扫描的包。
package com.zl;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.zl.dao")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
细节:
如果我们导入一个项目,对于IDEA是不能识别resources的,图标如下:
右击鼠标----》Mark Directory as-----》 Resources Root即可
此时的图标如下:
3. mapper文件和java代码分开管理
现在的xml文件和java代码是放在同一个包下管理的!
也可以分开存储,把xml文件放到resources目录下!在resources下创建一个mapper目录,把所有的*.xml全都放进去;但是此时就找不到了,需要我们去配置指定。
此时需要在application.properties文件里指定:
#指定mapper文件的位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml注:此时低版本的Springboot可能出现application.properties文件没有编译到target/classes目录的情况下,此时就需要修改resources插件配置:
src/main/resources
**/*.properties
**/*.xml
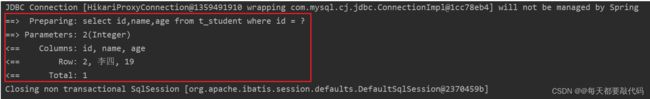
要想看到SQL语句的信息,需要在application.properties中添加日志框架
#指定mybatis的日志,使用StdOutImpl输出到控制台
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl此时就可以看到SQL语句的日志信息
4. 事务支持
Spring框架中的事务:
(1)使用管理事务的对象: 事务管理器(接口, 接口有很多的实现类)
例:使用Jdbc或mybatis访问数据库,使用的事务管理器:DataSourceTransactionManager
(2)声明式事务: 在xml配置文件或者使用注解说明事务控制的内容
控制事务: 隔离级别,传播行为, 超时时间等
(3)事务处理方式:
①Spring框架中的@Transactional;
②aspectj框架可以在xml配置文件中,声明事务控制的内容;
SpringBoot使用事务非常简单,底层依然采用的是 Spring 本身提供的事务管理
①在业务方法的上面加入@Transactional , 加入注解后,方法有事务功能了。
②在主启动类的上面 ,加入@EnableTransactionManager,开启事务支持。
注:只加上@Transactional也能完成事务的功能,对于@EnableTransactionManager建议也加上。
第一步:创建一个SpringBoot项目,引入:Spring Web、MybatisFramework、MySQL Driver
第二步:使用mybatis逆向工程插件生成个pojo类、dao接口
①添加Mybatis逆向工程的插件
注:这个插件是需要MySQL驱动依赖的,如果这里没有引入MySQL驱动的依赖,那么下面的generatorConfig.xml配置中就需要
标签去指定连接数据库的JDBC驱动包所在位置,指定到你本机的完整路径 ,例如: 。
org.mybatis.generator
mybatis-generator-maven-plugin
1.4.1
true
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.23
②编写generatorConfig.xml配置文件
注:如果下面的generatorConfig.xml配置文件放到src的resources目录下,那么配置文件的名字必须是generatorConfig.xml(不区分大小写),并且不需要上面的
标签去指定。 注:如果我们把generatorConfig.xml配置文件直接放到项目的根目录下(和src同级目录),那么此时generatorConfig.xml配置文件的名字随意,但是必须使用上面的
标签去指定一下(两者保持一致即可)。 注:当然也可以不直接放到项目的根目录下,例如:放到src/main目录下,那么对于
标签就需要指定src/main/generatorConfig.xml(两者也要保持一致) 注:对于高版本的MySQL驱动,对于URL后面必须跟上时区,但是在xml中是无法识别&,所以需要使用&去替换,例如:
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8"最终会生成*.xml配置,要想让它最终编译后放到target/classes中,就需要配置处理资源目录
src/main/java
**/*.xml
**/*.properties
src/main/resources
**/*.xml
**/*.properties
generatorConfig.xml配置
双击插件,执行结果如下:
第三步:编写application.properties配置
注:如果StudentMapper.xml的目录与StudentMapper目录保持一致,就不需要以下这个配置mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml;这里我们是自己定义的mapper目录,把mapper.xml文件放进去了,所以需要我们指定出来它的位置!
#设置端口
server.port=8082
#配置项目根路径context-path
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
#配置数据库
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123
#配置mybatis
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
#配置日志
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl第四步:编写service接口和实现类
StudentService接口
package com.zl.service;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
public interface StudentService {
int addStudent(Student student);
}
StudentService接口的实现类StudentServiceImpl
package com.zl.service.impl;
import com.zl.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
import com.zl.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service // 交给Spring容器管理
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Resource // 属性赋值
private StudentMapper studentDao;
@Transactional // 事务控制
@Override
public int addStudent(Student student) {
System.out.println("准备执行sql语句");
int count = studentDao.insert(student);
System.out.println("已完成sql语句的执行");
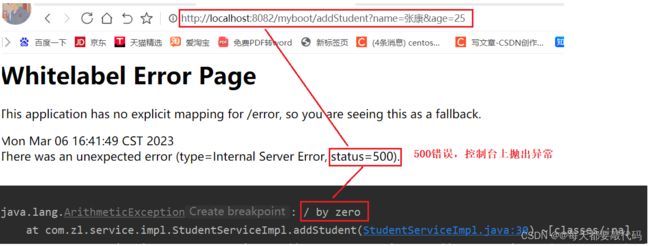
// 模拟异常,回滚事务
int sum = 10 / 0;
return count;
}
}
第五步:编写controller类去调用service
package com.zl.controller;
import com.zl.pojo.Student;
import com.zl.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/addStudent")
@ResponseBody
public String addStudent(String name,Integer age){
Student s = new Student();
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
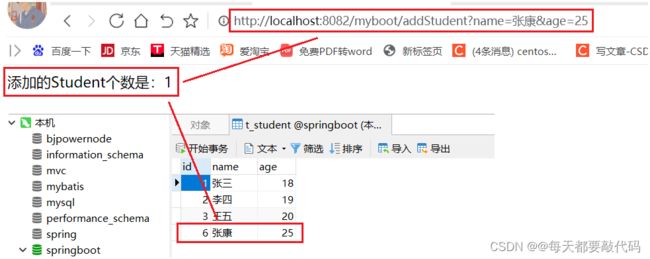
int count = studentService.addStudent(s);
return "添加的Student个数是:"+count;
}
}
第六步:在启动类上面加上包扫描注解和启动事务管理器注解
package com.zl;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.zl.mapper") // 添加包扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement // 启动事务管理器
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
第七步:进行测试
有异常发生,会回滚事务,无法插入数据
无异常发生,正常插入数据