Opencv特征检测之ORB算法原理及应用详解
Opencv特征检测之ORB算法原理及应用详解
- 特征是图像信息的另一种数字表达形式。一组好的特征对于在指定
任务上的最终表现至关重要。 - 视觉里程 (VO) 的主要问题是如何根据图像特征来估计相机运动。但是,整幅图像用来计算分析通常比较耗时,故而转换为分析图像中的特征点的运动。
- 计算机视觉领域的研究者们在长年的研究中,设计了许多更加稳定的局部图像特征,如著名的SIFT, SURF,ORB 等等。相比于朴素的角点,这些人工设计的特征点能够拥有如下的性质:
- 可重复性(Repeatability):相同的“区域”可以在不同的图像中被找到。
- 可区别性(Distinctiveness):不同的“区域”有不同的表达。
- 高效率(Efficiency):同一图像中,特征点的数量应远小于像素的数量。
- 本地性(Locality):特征仅与一小片图像区域相关。
- 特征点由关键点(Key-point)和描述子(Descriptor)两部分组成。比方说,当我们谈论 SIFT 特征时,是指“提取 SIFT 关键点,并计算 SIFT 描述子”两件事情。关键点是指该特征点在图像里的位置,有些特征点还具有朝向、大小等信息。描述子通常是一个向量,按照某种人为设计的方式,描述了该关键点周围像素的信息。描述子是按照“外观相似的特征应该有相似的描述子”的原则设计的。因此,只要两个特征点的描述子在向量空间上的距离相近,就可以认为它们是同样的特征点。
- 下文将详细讲述ORB算法(关键点+特征描述子)原理。
1. ORB 简介
- ORB论文:https://www.gwylab.com/download/ORB_2012.pdf
- 历史上,研究者提出过许多图像特征。它们有些很精确,在相机的运动和光照变化下仍具有相似表达,但相应地需要较大的计算量。其中,SIFT(尺度不变特征变换,Scale Invariant FeatureTransform) 当属最为经典的一种。它充分考虑了在图像变换过程中出现的光照,尺度,旋转等变化,但随之而来的是极大的计算量。由于整个 SLAM 过程中,图像特征的提取与匹配仅仅是诸多环节中的一个,到目前(2016 年)为止,普通 PC 的 CPU还无法实时地计算 SIFT 特征,进行定位与建图。所以在 SLAM 中我们甚少使用这种“奢侈”的图像特征。
- 另一些特征,则考虑适当降低精度和鲁棒性,提升计算的速度。例如 FAST 关键点属于计算特别快的一种特征点(注意这里“关键点”的用词,说明它没有描述子)。而 ORB(Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)特征则是目前看来非常具有代表性的实时图像特征。它改进了 FAST 检测子 [33] 不具有方向性的问题,并采用速度极快的二进制描述子BRIEF,使整个图像特征提取的环节大大加速。根据作者在论文中的测试,在同一幅图像中同时提取约 1000 个特征点的情况下,ORB 约要花费 15.3ms,SURF 约花费 217.3ms,SIFT 约花费 5228.7ms。由此可以看出 ORB 在保持了特征子具有旋转,尺度不变性的同时,速度方面提升明显,对于实时性要求很高的 SLAM 来说是一个很好的选择。大部分特征提取都具有较好的并行性,可以通过 GPU 等设备来加速计算。经过 GPU加速后的 SIFT,就可以满足实时计算要求。但是,引入 GPU 将带来整个 SLAM 成本的提升。由此带来的性能提升,是否足以抵去付出的计算成本,需要系统的设计人员仔细考量。在目前的 SLAM 方案中,ORB 是质量与性能之间较好的折中,因此我们以 ORB 为代表,介绍提取特征的整个过程。
2. ORB原理

\quad \quad ORB特征亦由关键点和描述子两部分组成。它的关键点称为“OrientedFAST”,是一种改进的FAST角点,什么是FAST角点我们将在下文介绍。它的描述子称为BRIEF (BinaryRobustIndependentElementaryFeatures)。因此,提取ORB特征分为两个步骤:
- FAST 角点提取:找出图像中的” 角点”。相较于原版的 FAST, ORB 中计算了特征
点的主方向,为后续的 BRIEF 描述子增加了旋转不变特性。 - BRIEF 描述子:对前一步提取出特征点的周围图像区域进行描述。
下面我们分别介绍 FAST 和 BRIEF。
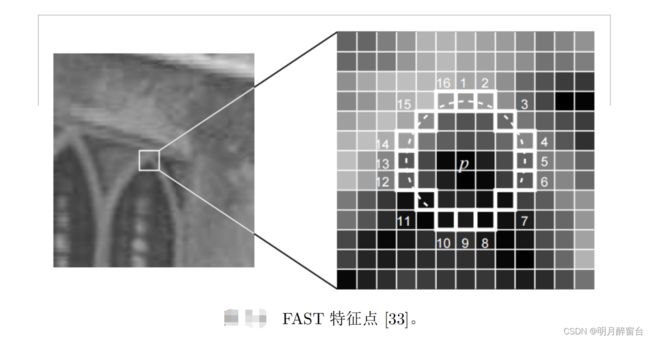
2.1 FAST关键点
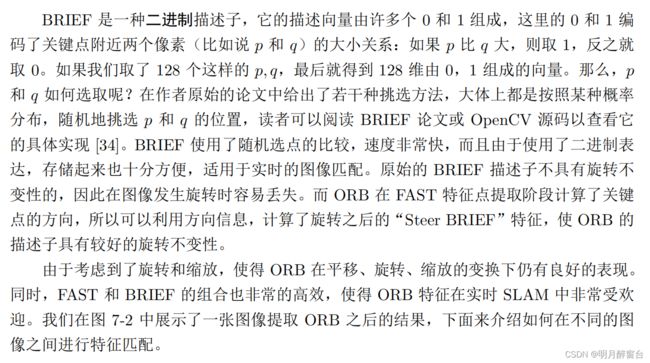
2.2 BRIEF 描述子
在提取 Oriented FAST 关键点后,我们对每个点计算其描述子。ORB 使用改进的BRIEF 特征描述。我们先来讲 BRIEF 是什么。
2.3 ORB算法具体实现
2.4 Opencv源码解析
- API简介
//ORB类定义:位置..\features2d.hpp
static Ptr<ORB> cv::ORB::create (
int nfeatures = 500, //需要的特征点总数;
float scaleFactor = 1.2f, //尺度因子;
int nlevels = 8, //金字塔层数;
int edgeThreshold = 31, //边界阈值;
int firstLevel = 0, //起始层;
int WTA_K = 2, //描述子形成方法,WTA_K=2表示,采用两两比较;
int scoreType = ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, //角点响应函数,可以选择Harris或者Fast的方法;
int patchSize = 31, //特征点邻域大小;
int fastThreshold = 20) //FAST阈值
- 源码:
- 头文件类定义如下:
/*!
ORB implementation.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS_W ORB : public Feature2D
{
public:
// the size of the signature in bytes
enum { kBytes = 32, HARRIS_SCORE=0, FAST_SCORE=1 };
CV_WRAP explicit ORB(int nfeatures = 500, float scaleFactor = 1.2f, int nlevels = 8, int edgeThreshold = 31,//构造函数
int firstLevel = 0, int WTA_K=2, int scoreType=ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, int patchSize=31 );
// returns the descriptor size in bytes
int descriptorSize() const; //描述子占用的字节数,默认32字节
// returns the descriptor type
int descriptorType() const;//描述子类型,8位整形数
// Compute the ORB features and descriptors on an image
void operator()(InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints) const;
// Compute the ORB features and descriptors on an image
void operator()( InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, //提取特征点与形成描述子
OutputArray descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints=false ) const;
AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
protected:
void computeImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, Mat& descriptors ) const;//计算描述子
void detectImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;//检测特征点
CV_PROP_RW int nfeatures;//特征点总数
CV_PROP_RW double scaleFactor;//尺度因子
CV_PROP_RW int nlevels;//金字塔内层数
CV_PROP_RW int edgeThreshold;//边界阈值
CV_PROP_RW int firstLevel;//开始层数
CV_PROP_RW int WTA_K;//描述子形成方法,默认WTA_K=2,两两比较
CV_PROP_RW int scoreType;//角点响应函数
CV_PROP_RW int patchSize;//邻域Patch大小
};
- 特征提取及形成描述子:通过这个函数对图像提取Fast特征点或者计算特征描述子
_image:输入图像;
_mask:掩码图像;
_keypoints:输入角点;
_descriptors:如果为空,只寻找特征点,不计算特征描述子;
_useProvidedKeypoints:如果为true,函数只计算特征描述子;
/** Compute the ORB features and descriptors on an image
* @param img the image to compute the features and descriptors on
* @param mask the mask to apply
* @param keypoints the resulting keypoints
* @param descriptors the resulting descriptors
* @param do_keypoints if true, the keypoints are computed, otherwise used as an input
* @param do_descriptors if true, also computes the descriptors
*/
void ORB::operator()( InputArray _image, InputArray _mask, vector<KeyPoint>& _keypoints,
OutputArray _descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints) const
{
CV_Assert(patchSize >= 2);
bool do_keypoints = !useProvidedKeypoints;
bool do_descriptors = _descriptors.needed();
if( (!do_keypoints && !do_descriptors) || _image.empty() )
return;
//ROI handling
const int HARRIS_BLOCK_SIZE = 9;//Harris角点响应需要的边界大小
int halfPatchSize = patchSize / 2;.//邻域半径
int border = std::max(edgeThreshold, std::max(halfPatchSize, HARRIS_BLOCK_SIZE/2))+1;//采用最大的边界
Mat image = _image.getMat(), mask = _mask.getMat();
if( image.type() != CV_8UC1 )
cvtColor(_image, image, CV_BGR2GRAY);//转灰度图
int levelsNum = this->nlevels;//金字塔层数
if( !do_keypoints ) //不做特征点检测
{
// if we have pre-computed keypoints, they may use more levels than it is set in parameters
// !!!TODO!!! implement more correct method, independent from the used keypoint detector.
// Namely, the detector should provide correct size of each keypoint. Based on the keypoint size
// and the algorithm used (i.e. BRIEF, running on 31x31 patches) we should compute the approximate
// scale-factor that we need to apply. Then we should cluster all the computed scale-factors and
// for each cluster compute the corresponding image.
//
// In short, ultimately the descriptor should
// ignore octave parameter and deal only with the keypoint size.
levelsNum = 0;
for( size_t i = 0; i < _keypoints.size(); i++ )
levelsNum = std::max(levelsNum, std::max(_keypoints[i].octave, 0));//提取特征点的最大层数
levelsNum++;
}
// Pre-compute the scale pyramids
vector<Mat> imagePyramid(levelsNum), maskPyramid(levelsNum);//创建尺度金字塔图像
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
{
float scale = 1/getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor); //每层对应的尺度
/*
static inline float getScale(int level, int firstLevel, double scaleFactor)
{
return (float)std::pow(scaleFactor, (double)(level - firstLevel));
}
*/
Size sz(cvRound(image.cols*scale), cvRound(image.rows*scale));//每层对应的图像大小
Size wholeSize(sz.width + border*2, sz.height + border*2);
Mat temp(wholeSize, image.type()), masktemp;
imagePyramid[level] = temp(Rect(border, border, sz.width, sz.height));
if( !mask.empty() )
{
masktemp = Mat(wholeSize, mask.type());
maskPyramid[level] = masktemp(Rect(border, border, sz.width, sz.height));
}
// Compute the resized image
if( level != firstLevel ) //得到金字塔每层的图像
{
if( level < firstLevel )
{
resize(image, imagePyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
if (!mask.empty())
resize(mask, maskPyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
}
else
{
resize(imagePyramid[level-1], imagePyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
if (!mask.empty())
{
resize(maskPyramid[level-1], maskPyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
threshold(maskPyramid[level], maskPyramid[level], 254, 0, THRESH_TOZERO);
}
}
copyMakeBorder(imagePyramid[level], temp, border, border, border, border,//扩大图像的边界
BORDER_REFLECT_101+BORDER_ISOLATED);
if (!mask.empty())
copyMakeBorder(maskPyramid[level], masktemp, border, border, border, border,
BORDER_CONSTANT+BORDER_ISOLATED);
}
else
{
copyMakeBorder(image, temp, border, border, border, border,//扩大图像的四个边界
BORDER_REFLECT_101);
if( !mask.empty() )
copyMakeBorder(mask, masktemp, border, border, border, border,
BORDER_CONSTANT+BORDER_ISOLATED);
}
}
// Pre-compute the keypoints (we keep the best over all scales, so this has to be done beforehand
vector < vector<KeyPoint> > allKeypoints;
if( do_keypoints )//提取角点
{
// Get keypoints, those will be far enough from the border that no check will be required for the descriptor
computeKeyPoints(imagePyramid, maskPyramid, allKeypoints, //对每一层图像提取角点,见下面(1)的分析
nfeatures, firstLevel, scaleFactor,
edgeThreshold, patchSize, scoreType);
// make sure we have the right number of keypoints keypoints
/*vector temp;
for (int level = 0; level < n_levels; ++level)
{
vector& keypoints = all_keypoints[level];
temp.insert(temp.end(), keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end());
keypoints.clear();
}
KeyPoint::retainBest(temp, n_features_);
for (vector::iterator keypoint = temp.begin(),
keypoint_end = temp.end(); keypoint != keypoint_end; ++keypoint)
all_keypoints[keypoint->octave].push_back(*keypoint);*/
}
else //不提取角点
{
// Remove keypoints very close to the border
KeyPointsFilter::runByImageBorder(_keypoints, image.size(), edgeThreshold);
// Cluster the input keypoints depending on the level they were computed at
allKeypoints.resize(levelsNum);
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = _keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = _keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
allKeypoints[keypoint->octave].push_back(*keypoint); //把角点信息存入allKeypoints内
// Make sure we rescale the coordinates
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level) //把角点位置信息缩放到指定层位置上
{
if (level == firstLevel)
continue;
vector<KeyPoint> & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
float scale = 1/getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
keypoint->pt *= scale; //缩放
}
}
Mat descriptors;
vector<Point> pattern;
if( do_descriptors ) //计算特征描述子
{
int nkeypoints = 0;
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
nkeypoints += (int)allKeypoints[level].size();//得到所有层的角点总数
if( nkeypoints == 0 )
_descriptors.release();
else
{
_descriptors.create(nkeypoints, descriptorSize(), CV_8U);//创建一个矩阵存放描述子,每一行表示一个角点信息
descriptors = _descriptors.getMat();
}
const int npoints = 512;//取512个点,共256对,产生256维描述子,32个字节
Point patternbuf[npoints];
const Point* pattern0 = (const Point*)bit_pattern_31_;//训练好的256对数据点位置
if( patchSize != 31 )
{
pattern0 = patternbuf;
makeRandomPattern(patchSize, patternbuf, npoints);
}
CV_Assert( WTA_K == 2 || WTA_K == 3 || WTA_K == 4 );
if( WTA_K == 2 ) //WTA_K=2使用两个点之间作比较
std::copy(pattern0, pattern0 + npoints, std::back_inserter(pattern));
else
{
int ntuples = descriptorSize()*4;
initializeOrbPattern(pattern0, pattern, ntuples, WTA_K, npoints);
}
}
_keypoints.clear();
int offset = 0;
for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)//依次计算每一层的角点描述子
{
// Get the features and compute their orientation
vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
int nkeypoints = (int)keypoints.size();//本层内角点个数
// Compute the descriptors
if (do_descriptors)
{
Mat desc;
if (!descriptors.empty())
{
desc = descriptors.rowRange(offset, offset + nkeypoints);
}
offset += nkeypoints; //偏移量
// preprocess the resized image
Mat& workingMat = imagePyramid[level];
//boxFilter(working_mat, working_mat, working_mat.depth(), Size(5,5), Point(-1,-1), true, BORDER_REFLECT_101);
GaussianBlur(workingMat, workingMat, Size(7, 7), 2, 2, BORDER_REFLECT_101);//高斯平滑图像
computeDescriptors(workingMat, keypoints, desc, pattern, descriptorSize(), WTA_K);//计算本层内角点的描述子,(3)
}
// Copy to the output data
if (level != firstLevel) //角点位置信息返回到原图上
{
float scale = getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
keypoint->pt *= scale;
}
// And add the keypoints to the output
_keypoints.insert(_keypoints.end(), keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end());//存入描述子信息,返回
}
}
2.4.1 提取角点
imagePyramid:即构造好的金字塔
/** Compute the ORB keypoints on an image
* @param image_pyramid the image pyramid to compute the features and descriptors on
* @param mask_pyramid the masks to apply at every level
* @param keypoints the resulting keypoints, clustered per level
*/
static void computeKeyPoints(const vector<Mat>& imagePyramid,
const vector<Mat>& maskPyramid,
vector<vector<KeyPoint> >& allKeypoints,
int nfeatures, int firstLevel, double scaleFactor,
int edgeThreshold, int patchSize, int scoreType )
{
int nlevels = (int)imagePyramid.size(); //金字塔层数
vector<int> nfeaturesPerLevel(nlevels);
// fill the extractors and descriptors for the corresponding scales
float factor = (float)(1.0 / scaleFactor);
float ndesiredFeaturesPerScale = nfeatures*(1 - factor)/(1 - (float)pow((double)factor, (double)nlevels));//
int sumFeatures = 0;
for( int level = 0; level < nlevels-1; level++ ) //对每层图像上分配相应角点数
{
nfeaturesPerLevel[level] = cvRound(ndesiredFeaturesPerScale);
sumFeatures += nfeaturesPerLevel[level];
ndesiredFeaturesPerScale *= factor;
}
nfeaturesPerLevel[nlevels-1] = std::max(nfeatures - sumFeatures, 0);//剩下角点数,由最上层图像提取
// Make sure we forget about what is too close to the boundary
//edge_threshold_ = std::max(edge_threshold_, patch_size_/2 + kKernelWidth / 2 + 2);
// pre-compute the end of a row in a circular patch
int halfPatchSize = patchSize / 2; //计算每个特征点圆邻域的位置信息
vector<int> umax(halfPatchSize + 2);
int v, v0, vmax = cvFloor(halfPatchSize * sqrt(2.f) / 2 + 1);
int vmin = cvCeil(halfPatchSize * sqrt(2.f) / 2);
for (v = 0; v <= vmax; ++v) //
umax[v] = cvRound(sqrt((double)halfPatchSize * halfPatchSize - v * v));
// Make sure we are symmetric
for (v = halfPatchSize, v0 = 0; v >= vmin; --v)
{
while (umax[v0] == umax[v0 + 1])
++v0;
umax[v] = v0;
++v0;
}
allKeypoints.resize(nlevels);
for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level)
{
int featuresNum = nfeaturesPerLevel[level];
allKeypoints[level].reserve(featuresNum*2);
vector<KeyPoint> & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
// Detect FAST features, 20 is a good threshold
FastFeatureDetector fd(20, true);
fd.detect(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, maskPyramid[level]);//Fast角点检测
// Remove keypoints very close to the border
KeyPointsFilter::runByImageBorder(keypoints, imagePyramid[level].size(), edgeThreshold);//去除邻近边界的点
if( scoreType == ORB::HARRIS_SCORE )
{
// Keep more points than necessary as FAST does not give amazing corners
KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, 2 * featuresNum);//按Fast强度排序,保留前2*featuresNum个特征点
// Compute the Harris cornerness (better scoring than FAST)
HarrisResponses(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, 7, HARRIS_K); //计算每个角点的Harris强度响应
}
//cull to the final desired level, using the new Harris scores or the original FAST scores.
KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, featuresNum);//按Harris强度排序,保留前featuresNum个
float sf = getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
// Set the level of the coordinates
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
{
keypoint->octave = level; //层信息
keypoint->size = patchSize*sf; //
}
computeOrientation(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, halfPatchSize, umax); //计算角点的方向,(2)分析
}
}
2.4.2 质心法计算角点主方向
static void computeOrientation(const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,
int halfPatchSize, const vector<int>& umax)
{
// Process each keypoint
for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(), //为每个角点计算主方向
keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
{
keypoint->angle = IC_Angle(image, halfPatchSize, keypoint->pt, umax);//计算质心方向
}
}
static float IC_Angle(const Mat& image, const int half_k, Point2f pt,
const vector<int> & u_max)
{
int m_01 = 0, m_10 = 0;
const uchar* center = &image.at<uchar> (cvRound(pt.y), cvRound(pt.x));
// Treat the center line differently, v=0
for (int u = -half_k; u <= half_k; ++u)
m_10 += u * center[u];
// Go line by line in the circular patch
int step = (int)image.step1();
for (int v = 1; v <= half_k; ++v) //每次处理对称的两行v
{
// Proceed over the two lines
int v_sum = 0;
int d = u_max[v];
for (int u = -d; u <= d; ++u)
{
int val_plus = center[u + v*step], val_minus = center[u - v*step];
v_sum += (val_plus - val_minus); //计算m_01时,位置上差一个符号
m_10 += u * (val_plus + val_minus);
}
m_01 += v * v_sum;//计算上下两行的m_01
}
return fastAtan2((float)m_01, (float)m_10);//计算角度
}
2.4.3 计算特征点描述子
static void computeDescriptors(const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, Mat& descriptors,
const vector<Point>& pattern, int dsize, int WTA_K)
{
//convert to grayscale if more than one color
CV_Assert(image.type() == CV_8UC1);
//create the descriptor mat, keypoints.size() rows, BYTES cols
descriptors = Mat::zeros((int)keypoints.size(), dsize, CV_8UC1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints.size(); i++)
computeOrbDescriptor(keypoints[i], image, &pattern[0], descriptors.ptr((int)i), dsize, WTA_K);
}
static void computeOrbDescriptor(const KeyPoint& kpt,
const Mat& img, const Point* pattern,
uchar* desc, int dsize, int WTA_K)
{
float angle = kpt.angle;
//angle = cvFloor(angle/12)*12.f;
angle *= (float)(CV_PI/180.f);
float a = (float)cos(angle), b = (float)sin(angle);
const uchar* center = &img.at<uchar>(cvRound(kpt.pt.y), cvRound(kpt.pt.x));
int step = (int)img.step;
#if 1
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点的值
center[cvRound(pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a)*step + \
cvRound(pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b)]
#else
float x, y;
int ix, iy;
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点,插值法
(x = pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b, \
y = pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a, \
ix = cvFloor(x), iy = cvFloor(y), \
x -= ix, y -= iy, \
cvRound(center[iy*step + ix]*(1-x)*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix]*(1-x)*y + \
center[iy*step + ix+1]*x*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix+1]*x*y))
#endif
if( WTA_K == 2 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)//每个特征描述子长度为32个字节
{
int t0, t1, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
val = t0 < t1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(2); t1 = GET_VALUE(3);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 3;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(10); t1 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 5;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 6;
t0 = GET_VALUE(14); t1 = GET_VALUE(15);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 7;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else if( WTA_K == 3 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 12)
{
int t0, t1, t2, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1); t2 = GET_VALUE(2);
val = t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0);
t0 = GET_VALUE(3); t1 = GET_VALUE(4); t2 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7); t2 = GET_VALUE(8);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(9); t1 = GET_VALUE(10); t2 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 6;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else if( WTA_K == 4 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)
{
int t0, t1, t2, t3, u, v, k, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
t2 = GET_VALUE(2); t3 = GET_VALUE(3);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val = k;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
t2 = GET_VALUE(6); t3 = GET_VALUE(7);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
t2 = GET_VALUE(10); t3 = GET_VALUE(11);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
t2 = GET_VALUE(14); t3 = GET_VALUE(15);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 6;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "Wrong WTA_K. It can be only 2, 3 or 4." );
#undef GET_VALUE
}
3. ORB特征匹配
#include 参考:
1. ORB原理与Opencv源码解析
2. ORBSLAM2学习(一):ORB算法原理