C# 学习笔记
此笔记极水~ ,来自两年前的库存。
是来自 B站 刘铁猛大佬 的视频,因为 好奇学了学。
其他
c# 变量的 内联赋值 vs. 构造函数内赋值
(引用自:https://www.iteye.com/blog/roomfourteen224-2208838)
上下文:c#中变量的内联赋值其实是在构造函数中完成的,JIT会把变量的赋值语句放入每个构造函数开始的位置,因此,当类中有很多变量使用内联赋值,同时类也有多个构造函数的时候,实际编译生成的代码量会以乘法的方式叠加。比如一个类中有3个变量使用内联赋值,有4个构造函数,那么实际生成的赋值语句的数量将达到3x4=12句。
结论:尽量避免使用内联赋值,优先使用构造函数内赋值
两种程序
VS 中可以创建两种 C# 程序,无论是 控制台(Console)还是窗口(Form),还是 ASP。都分为 .NET FrameWork 和 .NET Core 两种版本。前者只适用于 Windows,且被微软商业化;后者开源,且支持跨平台。但要论方便 还是 .NET FrameWork 。
类库的引用:
- DLL 引用 (黑盒引用)
- 项目引用 (白盒引用)
- 需要包含到当前 solution 下。一个项目可以被多个解决方案包含。
=> 依赖关系 ! <-> 软件质量
assembly :程序集,装配件
NuGet:引用包,相比于一个库一个库的引用更快更好。
强依赖:没有这个类无法工作!这个类出错,全都不能用。
UML 通用建模语言,类图。
编程建议:
- 改错一定要找到 根本错误,不要打补丁。
- 程序尽量:
- 类之间低耦合,高内聚(内聚:该放哪放哪)
- 库之间弱依赖,高内聚。
输出格式化字符串
string str = "hello"; int i = 10;
Console.Write($"{str}, {i}");
原始字符串
@"D:\BiShe\TestPic\faces6.jpg"
// \不会被转义
winform程序中使用控制台
在Qt中,经常使用qDebug()<<“Hello World”;的方式往控制台打印一些输出,以便观察程序的运行情况。
在Java中(eclipse、myeclipse中),经常使用的是System.out.println(“Hello World”);的方式。
在Android中,经常使用的是Log.d(“Hello World”);
. . .
在C#的时候,使用的是Console.WriteLine(“Hello World”);
开发winform的时候,需要先往主函数所在的源文件中加入以下内容。
引入库:
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
在Main()前,添加:
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern bool AllocConsole();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
static extern bool FreeConsole();
在Main()中,第一行添加:
AllocConsole();
在Main()中,最后一行添加:
FreeConsole();
示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
// 控制台输出,需加入此库
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace HelloWorld_WindowsForm
{
static class Program
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern bool AllocConsole();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
static extern bool FreeConsole();
///
/// 应用程序的主入口点。
///
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
// 允许调用控制台输出
AllocConsole();
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.Run(new LoginPage());
// 释放
FreeConsole();
}
}
}
初见类 class
类 —— 现实世界事物抽象所得到的结果
抽象 -> 建模(去伪存真,由表及里)
—— 辩证唯物主义 ~
获取对象
获取对象 = 实例化 <- 使用 new 操作符。
Form MyForm = new Form();
MyForm.Text = "My Form";
MyForm.ShowDialog();
区别于 Form MyForm; ->该语句未引用任何实例。
多个变量可以引用同一个实例。
个人:C#中变量分为值类型与引用类型,其内存存储方式另有特点,不完全是C/C++,也不完全是Python的形式。 可见 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ma4y1E7LD?p=7,后面记的笔记
类的三大成员
类声明中使用成员时,可以this.member,也可以直接member
- 属性 Property
- 存储数据,表示状态
- 方法 Method
- 能做什么
- 事件 Event
- 类或对象通知其他类或对象的机制,为C#所特有。
- 善用事件机制非常重要。(别滥用)
特殊类或对象在成员方面侧重点不同。
- 模型类或对象重在属性,如Entity Framework
- 工具类或对象重在方法,如Math , Console
- 通知类或对象重在事件,如各种Timer
timer例程:
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Threading;
namespace Timer
{
///
/// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑
///
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
DispatcherTimer timer = new DispatcherTimer();
timer.Interval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1);
timer.Tick += Timer_Tick;// += 用于挂接事件
timer.Start();
}
private void Timer_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
this.timerTextBox.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
静态成员与实例成员
- 静态(static)成员表示是 类的成员
- 实例(非静态)成员表示是 对象的成员
绑定(Binding)指的是编译器如何把一个成员与类或对象关联起来。
访问成员操作符: .
基本元素
构成C#语言的基本元素:
- 标记(Token):
- 关键字(Keyword)
- 操作符(Operator)
- 标识符(Indentifier)
- 若想使用关键字作为标识符,可采用
@做前缀。 - 标识符甚至可以用中文
- 其他与 C++类似。
- 建议:方法用动词,变量用名词。=>总之,标识符要有意义。
- 建议:类名用 Pascal法(每个单词首字母都大写),变量名用驼峰法。
- 若想使用关键字作为标识符,可采用
- 标点符号
- 文本
- 注释与空白
- 注释同 C/C++
变量类型
int ,long(字面值后缀 L)
double(字面值后缀 D,默认),float(字面值后缀F)
char(字面值单引号,单字符),string(字面值双引号,多字符)
bool (false/true)
空值null
var 变量类型自动推断
C#中任何对象都可以用
GetType().Name来获取类型字名符串。single表示单精度浮点型(float)
注意(强类型):var的类型一旦确定,该变量就只能是这个类型。
方法
类内定义,要想类外访问,需要函数顶以前加 public。
插曲 —— 递归之汉诺塔问题
对递归的理解的要点主要在于放弃!
放弃你对于理解和跟踪递归全程的企图,只理解递归两层之间的交接,以及递归终结的条件。
类型
C# 强类型编程语言,比 C/C++强,不会进行类型自动转换!
模仿弱类型的机制:dynamic
反射机制:运行时知道类型的成员。
Type myType = typeof(Form);//类型也是类型
Console.WriteLine(mytype.Name);
//Form
Console.WriteLine(mytype.FullName);
//System.Windows.Forms.Form
Console.WriteLine(mytype.BaseType.FullName);
//System.Windows.Forms.ContainerControl
System.Reflection.PropertyInfo[] pInfo = myType.GetProperties();
foreach (var i in pInfo)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.Name);
}
Console.WriteLine(" ------------- ");
System.Reflection.MethodInfo[] mInfo = myType.GetMethods();
foreach (var i in mInfo)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.Name);
}
存储方式:
- 栈:小、快 —— 函数调用
- 常见错误:栈溢出
- 堆:大、慢 —— 存放对象实例
- 常见错误:内存泄露
C#中是有指针的,但是不能随便用,要用 unsafe 关键字声明 并 在项目 build 属性中指明
public unsafe void func()
{
int* p = stackalloc int[1024];
...
}
或者
public void func()
{
unsafe
{
int* p = stackalloc int[1024];
...
}
}
可利用 windows自带的 performer moniter 检测程序内存 win+r -> 输入 perfmon
类型在C#语言中的作用
一个C#类型中所包含的信息有:
-
存储此类型变量所需的内存空间大小
-
此类型的值可表示的最大、最小值范围
-
此类型所包含的成员(如方法、属性、事件等).此类型由何基类派生而来
-
程序运行的时候,此类型的变量在分配在内存的什么位置
- Stack简介
- Stack overflow. Heap简介
- 使用Performance Monitor查看进程的堆内存使用量
- 关于内存泄漏
-
此类型所允许的操作(运算)
C# 五大数据类型
- 类 Classes
- 结构体 Structures
- 枚举 Enumerations
- 接口 Interfaces
- 委托 Delegates
C#类型的派生谱系
Object
- 引用类型
- 类
- 接口
- 委托
- 值类型
- 结构体
- 枚举
蓝色字体是真正的数据类型,黑色只是关键字。它们都是关键字,部分类型(蓝色字体)太过常用而被C#吸收为关键字,同时它们又是C#的最基本类型/内建类型。
int,double,short等是结构体?! <- 值类型
.isClass() :返回数据类型是否是类
int --- Int32
short --- Int16
long --- Int64
char --- 16位
Byte --- 8位
枚举 举例:
Form f = new Form();
f.WindowState = FormWindowState.Normal;//Normal是一枚举类型。
重要:
个人:C#中变量分为值类型与引用类型,其内存存储方式另有特点,不完全是C/C++,也不完全是Python的形式。 可见 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ma4y1E7LD?p=7,后面记的笔记
引用参数变量 / 输出参数变量
参数类型前加 ref 引用参数变量
参数类型前加 out 输出参数变量
public double Add(ref double a,ref double b){...}
public void Add(double a,double b,out double c){...}
变量声明/定义
有效的修饰符组合(opt可选) 类型 变量名 初始化器(opt可选)
变量定义
变量=以变量名所对应的内存地址为起点、以其数据类型所要求的存储空间为长度的一块内存区域
有符号整数的负数用补码的形式存储。
地址从低往高走,存储用高位低位 / 高低字节
类型转换
short s = 1000;
string str = Convert.ToString(s,2);//转换成二进制形式
引用变量
引用类型声明给 4字节 空白内存
实例化才给内存+地址,以及此时才计算需要多大内存,并把地址放到变量名中
类实例会有默认值,内存统统刷为0.
C# 中本地变量在使用前必须有显式初始化/赋值。
常量
- 类型前关键字
const - 声明时必须初始化。
装箱/拆箱
装箱
使用 Object(引用类型)等于一个本地变量(值类型),会在堆上再复制本地变量(值类型)的值并将其地址赋给 Object(引用类型)
拆箱
将 Object(引用类型)转换为值类型赋给本地变量(值类型):将堆上内存的值赋给这个本地变量(值类型)
数组
二维数组
真正的二维数组,而不是 c++ / java 那样的数组的数组。但类似矩阵,要求每行都一样长。
int [,] a = new int [3,4] {
{0, 1, 2, 3} , /* 初始化索引号为 0 的行 */
{4, 5, 6, 7} , /* 初始化索引号为 1 的行 */
{8, 9, 10, 11} /* 初始化索引号为 2 的行 */
};
// 访问数组
a[1,2]
交错数组
即 数组的数组,内部的数组可以有不同长度 ,java 可以,但 c++ 不行
int [][] a = new int[][]{new int[]{1,2,3},new int[]{4,5} };
//访问
a[1][2]
方法 method
C# 是纯面向对象的语言,所有方法都是基于类的。
方法命名:
- pascal 首字母大小
- 动词/短语
parameter 形式参数
augument 实际参数
直接在 Program类中写函数并调用,需要加static关键字。
构造器 constructor
狭义的构造器指 实例构造器
不声明编译器提供默认构造器
类似 C++,有参构造会阻止编译器生成默认构造器
快捷键 ctor + 两次tab键 ,
方法的重载
方法名一样,方法签名不能一样
声明带有重载的方法(类似 C++)
- 方法签名(method signature )由方法的名称、类型形参的个数和它的每一个形参(按从左到右的顺序)的类型和种类(值、引用或输出)组成。方法签名不包含返回类型。
- 实例构造函数签名由它的每一个形参(按从左到右的顺序)的类型和种类(值、引用或输出)组成。
- 重载决策(到底调用哪一个重载)︰用于在给定了参数列表和一组候选函数成员的情况下,选择一个最佳函数成员来实施调用。
类型形参 << 泛型
参数种类:默认值传递, ref 引用传递,out 输出传递
stack frame
caller 主调者
callee 被调者
压入栈的变量归主调者管,参数从左往右的顺序压入栈
返回的变量存储在 CPU 的寄存器中。
操作符
- 优先级从高往低由大变小
- 大多数从左往右,除了最后一行
=是先算等号右边。 - 后置++/-- 比 前置++/–优先级高
- default 运算符,内存块刷0
default(Form),注意容易出错!可能并不能用0。 ->是指针用的,类似C++,需要 unsafe上下文&取地址。*x取对象await异步 ;- 逻辑 与/或 有短路效应。
- (T)x 类型转换
- new 也是个操作符 / 关键字
- ?条件操作符可以单用?!。
初始化器:
Form myForm = new Form(){Text = "Hello"};
myForm.ShowDialog();
基类类型是可以直接用 = 进行初始化
string str = "Hello";
int[] nums = {1,2,3,4,5};
为匿名类型创造对象:
var person = new {Name = "Mr.Okay",Age = 34};
Console.WriteLine(person.GetType().Name);
注意:一旦一个类中使用了 new 操作符时,就会与其他类构成了很强的耦合。
存在一个“依赖注入”的设计模式,可以使变成弱耦合。
var 声明隐式变量
继承中的 new
可以在派生类中作为修饰符声明重载基类的方法。
注意其与 override 的区别,new 是隐藏,override是重载,后者可以用于泛型。
checked / unchecked
检测溢出。引发异常
uint x = uint.MaxValue;
Console.WriteLine(x);
string binString = Convert.ToString(x, 2);
Console.WriteLine(binString);
try
{
uint y = checked(x + 1);
//uint y = unchecked(x + 1);
//uncheck 默认,不检测溢出
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is Overflow");
//throw;
}
delegate
- 声明委托
- 当作操作符,已经被 lambda表达式技术代替。声明匿名方法
查文档去!
sizeof
获取结构体类型所占的字节数
获取自定义类型使需要 unsafe 上下文(关键字+设置)。
数组
int[] myIntArray1 = new int[10];
int[] myIntArray2 = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
Console.WriteLine(myIntArray2[myIntArray2.Length - 1])
字典(Dictionary) -泛型类
操作符重载
class Person
{
public static operator +(Person p1,Persob p2){...}
}
operator + 中间有个空格
委托!
Action act = new Action(Func);
act();// = Func()
类型转换
强制类型转换 (T)x
-
隐式(implicit)类型转换
-
不丢失精度的转换
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/language-specification/conversions -
子类向父类的转换
-
装箱
-
-
显式(explicit)类型转换
-
有可能丢失精度(甚至发生错误)的转换,即cast(译"铸造")
- 直接丢去数据位,可能导致数据出错。
-
拆箱
-
使用Convert类
- ToFloat X ,ToSingle √
-
ToString方法与各数据类型的Parse/TryParse方法
using System; namespace TypeConvert { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("Input num1: "); string str1 = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("Input num2: "); string str2 = Console.ReadLine(); // double num1 = Convert.ToDouble(str1); // double num2 = Convert.ToDouble(str2); double num1 = double.Parse(str1); // Parse 只能转换正确格式的字符串 double num2 = double.Parse(str2); Console.Write("Result: "); Console.WriteLine(num1 + num2); Console.ReadKey(true); } } }- 格式不正确Parse会发出异常,可以使用 TryParse(返回bool),
-
-
自定义类型转换操作符
- 示例
//类的自定义转换
using System;
namespace TypeConvert
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stone stone = new Stone();
stone.Age = 5000;
Monkey wukongSun = (Monkey)stone;
Console.WriteLine(wukongSun.Age);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
class Stone
{
public int Age;
}
class Monkey
{
public int Age;
//将 explicit转换成implicit即为隐式转换。
public static explicit operator Monkey(Stone stone)
{
Monkey monkey = new Monkey();
monkey.Age = stone.Age / 500;
return monkey;
}
}
}
- 注意“类型提升”。
浮点除法中,除数可以是 0 .结果是 +/-Infinity
通过double.PositiveInfinity/double.NegativeInfinity 来获取正负无穷大。它们相除得到NaN
左移/右移
注意 左移只补0,右移 正数补0负数补1.
is / as 类型比较操作符
is 是否是某类型(包括父类,一定继承自 object),返回 bool
var res = teacher is Form;
as 判断是否对象是某类型,不是返回 null;是则返回对象引用。可以用于派生类向基类的类型转换
object o = new Teacher();
Teacher t = o as Teacher;
if (t != null)
{
t.Func();
}
Nullable 可空类型
正常 int等类型不可赋值为 null,C#引入可空类型:
Nullable x = null;
Console.WriteLine(x.HasValue);
// false
x = 100;
//等价于
int? x = null;
Console.WriteLine(x.HasValue);
// false
x = 100
其他
int? x = null;
int y =x??0;
// ??:x是null吗?是则y为0.
- 可空类型的真正的值 ——
.Value属性 - 是否有真正的值 ——
.HasValue属性
表达式
语句
- 语句只能出现在函数体中。
ildasm VS prompt中提供的C#反编译工具。
!分号结束不一定是语句。 using是指令,类中变量声明也不是语句。
if / else
if (3>2)
System.Console.WriteLine("Hello");
建议:
一个函数最好只有一个功能
else if语句是一种逐级筛选。
块语句 block
- 总会被编译器当作一条语句。
- 被当作一条完整的语句(不用加
;了)
VS中,使用快捷键:
ctrl + }键可以在两个大括号之间跳转光标。
标签语句
配合 goto 等使用。
hello:Console.WriteLine("Hello");
goto hello;
try/catch/finally/throw
目的:捕获异常,输出易于理解的错误信息,防止程序崩溃。
finally:try后总会被执行
throw:抛出异常,可以指出异常/不指出。
例程,
using System;
namespace Study_Try
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Caculator c = new Caculator();
int r = c.Add("abc","0");
Console.WriteLine(r);
System.Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Caculator
{
public int Add(string str1,string str2)
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
bool hasError = false;
try
{
a = int.Parse(str1);
b = int.Parse(str2);
}
catch(ArgumentNullException ane)
{
Console.WriteLine(ane.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch(FormatException fe)
{
Console.WriteLine(fe.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch(OverflowException oe)
{
Console.WriteLine(oe.Message);
hasError = true;
}
finally
{
if (hasError)
{
Console.WriteLine("Execution has error!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Done!");
}
}
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
}
建议:平时就养成习惯:一定要尽可能的捕获所有可能出现的异常。异常崩溃是最严重的BUG。
for循环
三个都不写,即for(;;) 相当于 while(true).
建议:多写算法题,每个算法题做完之后写总结!归类,便于运用/面试时快速想出来。
foreach 循环
foreach( var i in nums){...}
- 数组都是基于 array 类。
- 可以被遍历的类都有
IEnumerable的接口。
迭代器
using System.Collections;
...
int[] intArray = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6};
IEnumerator enumerator = intArray.GetEnumerator();//故事-指月
while(enumerator.MoveNext())
{ Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
IEnumerator类的 Reset方法可以重置索引
return
原则:
1.尽早return,在函数中先判断特殊情况是否return。避免头重脚轻,出现if语句中出现大量代码的情况。
- 确保任何情况都可以 return!
字段
-
什么是字段
- 字段(field)是一种表示与对象或类型(类与结构体)关联的变量
- 字段是类型的成员,旧称“成员变量”
- 与对象关联的字段亦称“实例字段”
- 与类型关联的字段称为“静态字段”,由static修饰
-
字段的声明
- 参见C#语言定义文档
- 尽管字段声明带有分号,但它不是语句
- 字段的名字一定是名词
-
字段的初始值
- 无显式初始化时,字段获得其类型的默认值,所以字段"永远都不会未被初始化"
- 显式初始化相当于在构造函数中初始化。推荐显式初始化,这样可以不受构造函数变化影响。
- 实例字段初始化的时机——对象创建时
-
静态字段初始化的时机——类型被加载(load)时
-
只读字段 ,
readonly关键字- 只能在构造对象时初始化,之后不能改。注意每个对象都可以初始化自己的只读字段。
- 实例只读字段
- 可以在定义对象时初始化
- 静态只读字段
- 只能在定义时/static构造函数中初始化。
static构造函数
- 会在数据类型被加载时执行,永远只执行一次。
class Student
{
...
static Student()
{
...
}
}
属性 property
C# 特有,为了替代 C++/JAVA 中 私有变量 + Set/Get成员函数 的组合。
-
什么是属性
-
属性( property)是一种用于访问对象或类型的特征的成员,特征反映了状态
-
属性是字段的自然扩展
- 从命名上看,字段(field)更偏向于实例对象在内存中的布局,property更偏向于反映现实世界对象的特征
- 对外:暴露数据,数据可以是存储在字段里的,也可以是动态计算出来的
- 对内:保护字段不被非法值"污染”
-
属性由Get/Set方法对进化而来
-
属性是又一个“语法糖"(属性背后的秘密)
-
-
属性的声明
-
完整声明——后台(back)成员变量与访问器(注意使用code snippet和refactor工具)
propfull + 两次tab键 -
简略声明——只有访问器(查看L代码)
prop + 两次tab键,set和get方法都是空的,直接分号。 -
动态计算值的属性
-
注意实例属性和静态属性属性的名字一定是名词
-
只读属性——只有getter没有setter(只有get块)
-
可以在 get/set关键字前加 private声明私有
- 尽管语法上正确,几乎没有人使用"只写属性”,因为属性的主要目的是通过向外暴露数据而表示对象/类型的状态
-
-
属性与字段的关系
- 一般情况下,它们都用于表示实体(对象或类型)的状态
- 属性大多数情况下是字段的包装器(wrapper)
- 建议:永远使用属性(而不是字段)来暴露数据,即字段永远都是private或protected的
建议:是动态计算还是存储,根据访问是否频繁决定!
完整声明属性要先有私有字段,再声明访问器。
- 在 set 上下文中,
value关键字代表传进来的值。 - 命名采用 Pascal法,首字母大写。
- 静态属性要求私有字段也是静态的。
- 属性初始化:
stu = new Student(){Name = "Ben"};
using System;
namespace FieldToProperty
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.Age = 20;
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.Age = 20;
Student student3 = new Student();
student3.Age = 200;
int AvgAge = student1.Age + student2.Age + student3.Age;
AvgAge /= 3;
Console.WriteLine(AvgAge);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
if (value >=0 && value<=120)
{
this.age = value;
}
else
throw new Exception("value of Age has error");
}
}
}
}
索引器
-
什么是索引器
- 索引器(indexer) 是这样一种成员:它使对象能够用与数组相同的方式(即使用下标)进行索引
-
索引器的声明
- 参见C#语言定义文档
- 注意:没有静态索引器
需要System.Contains.Generic名称空间
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Study_Indexer
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu["Math"] = 100;
Console.WriteLine(stu["Math"]);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary scoreDictionary = new Dictionary();
public int? this[string subject]
{
get
{
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
return this.scoreDictionary[subject];
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
set
{
if (value.HasValue == false)
{
throw new Exception("score has error");
}
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value;
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject,value.Value);
}
}
}
}
}
常量
常量更快,效率更高。其他只是变量
什么是常量
- 常量(constant)是表示常量值(即,可以在编译时计算的值)的类成员
- 常量隶属于类型而不是对象,即没有"实例常量”
- “实例常量”的角色由只读(readonly)实例字段来担当
- 注意区分成员常量与局部常量
- 常量的声明
- 各种"只读”的应用场景
- 为了提高程序可读性和执行效率一一 常量
- 为了防止对象的值被改变——只读字段
- 向外暴露不允许修改的数据一一只读属性(静态或非静态 ),功能与常量有一些重叠
- 当希望成为常量的值其类型不能被常量声明接受时(类/自定义结构体)—— 静态只读字段
参数
- 传值参数 — 最常用(不带修饰符)
- 值类型参数
- 引用类型参数(C#中引用代表地址,传入函数的引用类型与实参地址相同,但是可以 new一个新对象并赋予新地址)
- 注意避免“副作用”:改变实参
- 输出参数
- 前加
out关键字。不分配副本,就是原对象。 - 默认实参与刚传入的形参都是未赋值的。
- 为了解决只有返回不够输出的问题!
- 前加
- 引用参数
- 前加
ref关键字。不分配副本,就是原对象。 - 注意调用函数传入实参时,实参前面也要加关键字
ref - 引用类型参数:地址都没复制,就是引用。函数中给参数赋值就是给实参赋值
- 前加
- 数组参数
func(int[] intArray){...}- 数组参数作为最后一个参数时,可以加
params关键字,可以把输出初始化列表直接作为参数调用函数。
- 具名参数
- 不再受限于位置
- 调用时:形参:实参
- 可选参数
- 定义函数时:形参 = 默认值
- 扩展方法( this参数)
- 可以给某个类型添加方法(扩展方法)
- 方法必须是公有、静态的,即被public static所修饰
- 必须是形参列表中的第一个,由this修饰
- 必须由一个静态类(一般类名为SomeTypeExtension)来统一收纳对SomeType类型的扩展方法
- 举例:LiNQ方法
注:out、ref等关键字都是在函数定义与函数调用时都要加在实参/形参前面。
传值参数之引用类型示例
C#中引用代表地址,传入函数的引用类型与实参地址相同,因而操作参数就是改变传入的实参。但是可以 new一个新对象并赋予新地址.
using System;
namespace Study_parameter
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Name = "Mr.Okay";
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
Console.WriteLine("ID of old stu is {0}", stu.GetHashCode());
ShowStudentID(stu);
Console.WriteLine("After func , ID of old stu is {0}", stu.GetHashCode());
}
static void ShowStudentID(Student stu)
{
Console.WriteLine("In function , ID of old stu is {0}", stu.GetHashCode());
stu = new Student() {Name = "Ben"};
Console.WriteLine("In function , ID of new stu is {0}",stu.GetHashCode());
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
扩展方法示例
using System;
namespace Study_thisFunc
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double pi = 3.14159;
double y = pi.Round(4);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
static class DoubleExtension
{
public static double Round(this double x, int digit)
{
double result = Math.Round(x, digit);
return result;
}
}
}
LINQ初见
LINQ:.NET Language Integrated Query:语言集成查询
其实是数据库的本事
建议学SQL!
using System.Linq;
List myList = new List(){1,2,3};
bool res = myList.All(i=>i>10);
它为数组等类型追加了一些扩展方法。
本质是泛型委托,注意这些方法需要的参数,第一个是需要函数传入的类型,之后是需要函数输出的类型。
.select(p=>p.FirstName+""+p.LastName),批量获取对象属性/字段.Where(p=>p.FirstName=="Peter")找出所有姓都是 Peter的人.All(p=>p.FirstName=="Peter")是否所有人的姓都是 Peter.Any(p=>p.FirstName=="Peter")是否有人的姓都是 Peter.GroupBy(p=>p.FirstName)按照姓分组,“组”有Key和Count属性.Count(p=>p.FirstName=="Peter")一共有多少个姓Peter的- …
获取对象唯一值
C#中所有引用类型都是继承自 Object对象,都有一个方法:
object.GetHashCode()
委托
委托( delegate )是函数指针的“升级版”,委托是一种“类”!
- 实例: C/C+ +中的函数指针
- 一切皆地址
- 变量(数据)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的值
- 函数(算法)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的一组机器语言指令
- 直接调用与间接调用
- 直接调用:通过函数名来调用函数, CPU通过函数名直接获得函数所在地址并开始执行>返回
- 间接调用:通过函数指针来调用函数,CPU通过读取函数指针存储的值获得函数所在地址并开始执行>返回
- Java中没有与委托相对应的功能实体
- 委托的简单使用
- Action委托,无返回
- Func委托,有返回
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
Action action = new Action(cal.Report);
cal.Report();
action.Invoke();
action();
Func func1 = new Func(cal.add);
Func func2 = new Func(cal.sub);
int x = 100;
int y = 200;
int z = 0;
z = func1.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = func2(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public void Report()
{
Console.WriteLine("I have 3 method");
}
public int add(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
}
public int sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
}
自定义委托
委托是一种类,即在类声明的层次声明委托!在名称空间体中声明。
public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);
完整示例
namespace MyDelegate
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
Calc cal1 = new Calc(cal.Add);
Calc cal2 = new Calc(cal.Sub);
Calc cal3 = new Calc(cal.Div);
Calc cal4 = new Calc(cal.Mul);
double x = 1.0;
double y = 0.5;
double z = cal1.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = cal2.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = cal3(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = cal4(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
}
}
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y);
class Calculator
{
public double Add(double a,double b)
{
return a + b;
}
public double Sub(double a, double b)
{
return a - b;
}
public double Mul(double a, double b)
{
return a * b;
}
public double Div(double a, double b)
{
return a / b;
}
}
}
委托的一般使用
委托的赋值操作符:+=
- 实例:把方法当作参数传给另一个方法
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用"指定的外部方法来产生结果
- 相当于“填空题”
- 常位于代码中部
- 委托有返回值
- 正确使用2:回调( callback)方法,调用指定的外部方法
- 相当于“流水线”
- 常位于代码末尾
- 委托无返回值
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用"指定的外部方法来产生结果
- 注意:难精通+易使用+功能强大东西,一旦被滥用则后果非常严重
- 缺点1:这是一种方法级别的紧耦合,现实工作中要慎之又慎
- 缺点2:使可读性下降、debug的难度增加
- 缺点3∶把委托回调、异步调用和多线程纠缠在一起,会让代码变得难以阅读和维护
- 缺点4:委托使用不当有可能造成内存泄漏和程序性能下降
模板方法与回调函数示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace TemplateAndCallback
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func func1 = new Func(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func func2 = new Func(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Logger logger = new Logger();
Action action = new Action(logger.Log);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1, action);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2, action);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Products.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Products.Name);
}
}
class Logger
{
public void Log(Product product)
{
Console.WriteLine("Profuct '{0}' created at {1}.Price is {2}.",product.Name,DateTime.UtcNow,product.Price);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public Product Products { get; set; }
}
class WrapFactory
{
public Box WrapProduct(Func getProduct,Action logCallBack)
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
if (product.Price >= 10)
logCallBack(product);
box.Products = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product() { Name="Pizza",Price = 15};
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product() { Name = "ToyCar", Price = 5};
return product;
}
}
}
委托的高级使用
- 多播( multicast )委托
- 一个委托使用多个方法:
action1 += action2; - 还可以多次使用同一个方法
- 一个委托使用多个方法:
- 隐式异步调用
- 同步与异步的简介
- 中英文的语言差异 ↓
- 同步:你做完了我(在你的基础上)接着做
- 异步:咱们两个同时做(相当于汉语中的“同步进行")
- 同步调用与异步调用的对比
- 每一个运行的程序是一个进程( process )
- 每个进程可以有一个或者多个线程(thread )
- 同步调用是在同一线程内
- 异步调用的底层机理是多线程
- 串行同步单线程,并行异步多线程
- 隐式多线程v.s.显式多线程
- 直接同步调用:使用方法名
- 间接同步调用:使用单播/多播委托的Invoke方法
- 隐式异步调用:使用委托的BeginInvoke
- 显式异步调用:使用Thread或 Task
- 同步与异步的简介
- 应该适时地使用接口(interface)取代一些对委托的使用
- Java完全地使用接口取代了委托的功能,即Java没有与C#中委托相对应的功能实体。
事件
一种类型成员
事件不是委托!
初步了解事件
定义:单词Event,译为“事件”
- 《牛葳津词典》中的解释是"a thing that happens, especially something important"
- 通顺的解释就是"能够发生的什么事情”
角色:使对象或类具备通知能力的成员
- (中译)事件(event)是一种使对象或类能够提供通知的成员
- (原文)An event is a member that enables an object or class
to provide notifications. - “对象O拥有一个事件E"想表达的思想是:当事件E发生的时候,O有能力通知别的对象
使用:用于对象或类间的动作协调与信息传递(消息推送)
原理:事件模型(event model)中的两个“5”
- “发生→响应“中的5个部分——闹钟响了你起床、孩子饿了你做饭…这里隐含着"订阅"关系(A 发生了->订阅->B 做什么)
- “发生→响应"中的5个动作——(1)我有一个事件→(2)一个人或者一群人关心我的这个事件→(3)我的这个事件发生了→(4)关心这个事件的人会被依次通知到→(5)被通知到的人根据拿到的事件信息(又称"事件数据"、“事件参数"、"通知”)对事件进行响应(又称“处理事件”)。
提示:
- 事件多用于桌面、手机等开发的客户端编程,因为这些程序经常是用户通过事件来"驱动"的
- 各种编程语言对这个机制的实现方法不尽相同
- Java语言里没有事件这种成员,也没有委托这种数据类型。Java的“事件"是使用接口来实现的
- MVC、MVP、MVVM等模式,是事件模式更高级、更有效的“玩法”。
- 日常开发的时候,使用已有事件的机会比较多,自己声明事件的机会比较少,所以先学使用。
事件的功能 = 通知 + 详细信息(可选)
术语统一:
- 事件的订阅者 = 事件消息的接收者 = 事件的响应者 = 事件的处理者 = 被事件所通知的对象
- 事件参数 = 事件信息 = 事件消息 = 时间数据
事件的应用
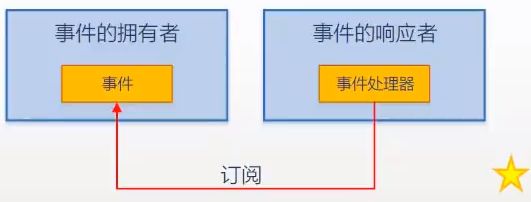
事件模型的五个组成部分
-
- 事件的拥有者( event source,对象)
- 2.事件成员( event,成员)
- 3.事件的响应者( event subscriber,对象)
- 4.事件处理器(event handler,成员)——本质上是一个回调方法
- 5.事件订阅——把事件处理器与事件关联在一起,本质上是一种以委托类型为基础的“约定”
注意
- 事件处理器是方法成员
- 挂接事件处理器的时候,可以使用委托实例,也可以直接使用方法名,这是个”语法糖”
- 事件处理器对事件的订阅不是随意的,匹配与否由声明事件时所使用的委托类型来检测
- 事件可以同步调用也可以异步调用
注意事件与事件处理器 的 约定!利用 VS来自动生成约定的东西!
事件拥有者与事件处理者之间的关系
- 两者是两个不同对象
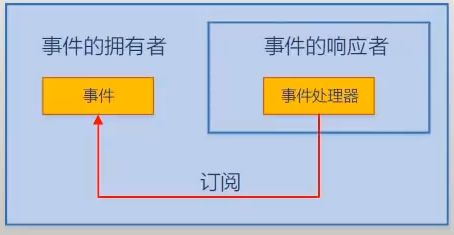
例子
timer.Elapsed += boy.Action;
事件拥有者与响应者是两个对象
using System;
using System.Timers;
//省略了名称空间声明
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.Interval = 1000; //1s
Boy boy = new Boy();
timer.Elapsed += boy.Action;
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
Console.WriteLine("Jump!");
}
}
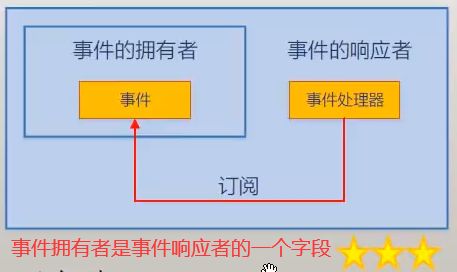
事件拥有者是事件响应者的一个字段
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Study_Event2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form form = new Form();
Controller ctr = new Controller(form);
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class Controller
{
private Form form;
public Controller(Form form)
{
if (form!=null)
{
this.form = form;
this.form.Click += this.FormClickDo;
}
}
private void FormClickDo(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
this.form.Text = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString();
}
}
}
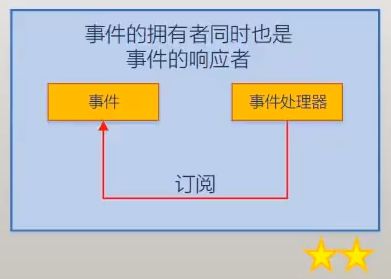
两者一体
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Study_Event3
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyFrom myForm = new MyFrom();
myForm.Click += myForm.MyDoClick;
myForm.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyFrom : Form
{
internal void MyDoClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString();
}
}
}
事件的声明
-
事件的声明
- 完整声明
- 简略声明(字段式声明,field-like )
-
有了委托字段/属性,为什么还需要事件?
- 为了程序的逻辑更加“有道理”、更加安全,防止“借刀杀人”(如果只用公有委托字段,则可能会被乱用。尽管它们都能实现一样的功能,但是事件约束更多,更安全)
-
所以事件的本质是委托字段的一个包装器
- 这个包装器对委托字段的访问起限制作用,相当于一个“蒙板"
- 封装(encapsulation)的一个重要功能就是隐藏
- 事件对外界隐藏了委托实例的大部分功能,仅暴露添加/移除事件处理器的功能
- 添加/移除事件处理器的时候可以直接使用方法名,这是委托实例所不具备的功能
-
用于声明事件的委托类型的命名约定
- 用于声明Foo事件的委托,一般命名为FooEventHandler(除非是一个非常通用的事件约束)
- FooEventHandler委托的参数一般有两个(由Win32 API演化而来,历史悠久)
- 第一个是object类型,名字为sender,实际上就是事件的拥有者、事件的source,
- 第二个是EventArgs类的派生类,类名一般为FooEventArgs,参数名为e。也就是前面讲过的事件参数
- 虽然没有官方的说法,但我们可以把委托的参数列表看做是事件发生后发送给事件响应者的"事件消息”
- 触发Foo事件的方法一般命名为OnFoo,即"因何引发”、“事出有因"
- 访问级别应该为protected,不能为public,不然又成了可以“借刀杀人"了.
- 注意:一个方法做一件事,OnFoo方法单独写出来
-
事件的命名约定
- 带有时态的动词或者动词短语
- 事件拥有者“正在做”什么事情,用进行时;事件拥有者“做完了“什么事情,用完成时
事件完整声明
关键部分
//事件参数类声明
//注 1.要继承自 EventArgs
//注 5.命名习惯:以 EventArgs 结尾
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
// 事件处理器声明
//注 1.它其实是个委托
//注 2.委托是个类,与类声明同级,都在名称空间中
//注 3.注意参数列表:事件拥有者,事件参数
//注 4.返回值为 void
//注 5. 命名习惯:以 EventHandler 结尾
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
// 事件声明(在事件拥有者类的定义中)
//注 1.两部分:私有委托字段 + 事件完整声明
private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;
public event OrderEventHandler Order
{
add
{
this.orderEventHandler += value;
}
remove
{
this.orderEventHandler -= value;
}
}
//事件触发
if(this.orderEventHandler != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "GongPaoChicken";
e.Size = "large";
this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
}
完整部分
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace Study_Event5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName { get; set; }
public string Size { get; set; }
}
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
public class Customer
{
private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;
public event OrderEventHandler Order
{
add
{
this.orderEventHandler += value;
}
remove
{
this.orderEventHandler -= value;
}
}
public double Bill { get; set; }
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("I will pay {0}.", this.Bill);
}
public void WalkIn()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walking into the restaurant");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sitting down ...");
}
public void Think()
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think ...");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
if(this.orderEventHandler != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "GongPaoChicken";
e.Size = "large";
this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadLine(); ;
this.WalkIn();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
public class Waiter
{
internal void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish: {0}.",e.DishName);
double price = 10.0;
switch(e.Size)
{
case "small":
price *= 0.5;
break;
case "medium":
price *= 1.0;
break;
case "large":
price *= 1.5;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill += price;
}
}
}
事件简略声明
//事件声明
public event OrderEventHandler Order;
//事件触发
if (this.Order != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = "GongPaoChicken";
e.Size = "large";
this.Order.Invoke(this, e);
}
- 其实在反编译器中发现,它们(EventHandler等)都是被隐藏了。
- 在Customer类内部能够使用Order事件去做非空比较以及调用Order.Invoke方法纯属不得已而为之,因为使用事件的简化声明时,我们没有手动声明一个委托类型的字段。这是微软编译器语法糖所造成的语法冲突和前后不一致。
- 其实可以直接用自带的
EventHandler.
事件与委托的关系
-
事件真的是“以特殊方式声明的委托字段/实例"吗?
- 不是!只是声明的时候"看起来像”(对比委托字段与事件的简化声明,field-like )
- 事件声明的时候使用了委托类型,简化声明造成事件看上去像一个委托的字段(实例),而 event关键字则更像是一个修饰符——这就是错觉的来源之一
- 订阅事件的时候+=操作符后面可以是一个委托实例,这与委托实例的赋值方法语法相同,这也让事件看起来像是一个委托字段——这是错觉的又一来源
- 重申:事件的本质是加装在委托字段上的一个"蒙板" (mask ),是个起掩蔽作用的包装器。这个用于阻挡非法操作的"蒙板"绝不是委托字段本身
-
为什么要使用委托类型来声明事件?
- 站在source的角度来看,是为了表明source能对外传递哪些消息
- 站在subscriber的角度来看,它是一种约定,是为了约束能够使用什么样签名的方法来处理(响应)事件
- 委托类型的实例将用于存储(引用)事件处理器
-
对比事件与属性
- 属性不是字段——很多时候属性是字段的包装器,这个包装器用来保护字段不被滥用
- 事件不是委托字段——它是委托字段的包装器,这个包装器用来保护委托字段不被滥用
- 包装器永远都不可能是被包装的东西
类 class
其他
析构
~Student()
{
...
}
静态构造
class Student
{
public static int Amount{get;set;}
static Student()
{
Amount = 0;
}
public Student()
{
Amount++;
}
}
初见-反射
Type t = typedef(Student);
object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t,42,"Ben");
Student stu = o as Student;
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
dynamic
Type t = typedef(Student);
dynamic d = Activator.CreateInstance(t,42,"Ben");
Console.WriteLine(d.Name);
成员类
class Student
{
class aabb
{
...
}
...
}
类声明
C#/JAVA :声明即定义。
访问权限
-
public
表示可以被其他项目的程序通过依赖+名称空间所见
-
internal(在名称空间中是默认)
表示不可以被其他项目(Assembly)的程序所见,但可以被同项目不同名称空间的程序所见
注:一个项目编译结果是一个程序集/装配集(Assembly)
一个名称空间中如果没有任何类暴露,则名称空间也不会暴露。
- private,(在类中是默认)限制于当前类体中,派生类也无权访问。命名建议
_foo,即在前加一个下划线,表示是私有的实例字段 - protected,派生类可访问,可以跨程序集
- internal 与 proteced 可以一起使用,是 或 的关系。即可被程序集中其他类或派生类访问。
继承
- 类前面加
sealed,则不可再被继承 - 一个类只能继承自一个基类,但可以继承有多个基接口
- 派生类的访问级别不能超过基类的访问级别
横向扩展:增加成员
纵向扩展:重写
构造的调用顺序:同C++,从基类到派生类
关键字 base,派生类可以以此访问上一层一类的对象。但是也只能访问上一级,不能 base.base
!!!构造器是不会被继承的!!!只会有编译器提供的默认构造器(前提还是基类可以默认构造)
C#也有初始化列表,但只能是this / base
class Vehicle
{
public string Owner { get; set; }
public Vehicle(string owner)
{
Owner = owner;
}
public Vehicle():this("N/A"){}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public Car():base("N/A")
{
}
}
重写
- 重写与隐藏(后面讲)的发生条件:函数成员,可见,签名一致。
- 属性,方法都可被重写!
多态,基类可以引用派生类对象,并调用派生类重写的方法。
class Vehicle
{
public virtual void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running. ---In Vehicle");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running. ---In Car");
}
}
对于如下代码:
Vehicle vc = new Car();
vc.Run();
输出
I'm running. ---In Car
隐藏
几乎不用!
如果不用重写,也就是不用 virtual 和 override,则不会产生多态的效果。声明类型是啥就用哪个版本
可选:用于隐藏的函数可以加 new关键字。
class Vehicle
{
public virtual void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running. ---In Vehicle");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm running. ---In Car");
}
}
对于如下代码:
Vehicle vc = new Car();
vc.Run();
输出
I'm running. ---In Vehicle
接口
为做基类而生的“抽象类”与“开放/关闭原则”
“开放/关闭原则”:除非修Bug和添加功能,否则不应该修改一个类的代码!
抽象类
有未实现的函数成员,即被 abstract修饰,且不是private。此时这个类就是抽象类,其类声明前要加关键字abstract。
abstract class Vehicle
{
...
public abstract void Run();
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
...
public override void Run(){...}
}
其派生类需要实现这些函数成员才能摆脱抽象类的身份。注意,派生类在实现时也需要在前面加关键字override.
接口
一个抽象类中全都是 abstract 的函数,则可把abstract class,直接替换为 关键字interface —— 接口,此时需要再把类中函数声明前的public abstract,以及派生类中的override也全部去掉!
所以接口都是 public的!是要提供的一种服务!
interface IVehicleBase
{
...
void Run();
void Stop();
}
abstract class Vehicle:IVehicleBase
{
...
public abstract void Run();
public void Stop(){...}
}
什么是接口和抽象类
- 接口和抽象类都是“软件工程产物"
- 具体类→抽象类→接口:越来越抽象。内部实现的东西越来越少
- 抽象类是未完全实现逻辑的类(可以有字段和非public成员。它们代表了"具体逻辑"。
- 抽象类为复用而生:专门作为基类来使用。也具有解耦功能
- 封装确定的。开放不确定。推迟到合适的子类(派生类)中去实现
- 接口是完全未实现逻辑的“类”(““纯虚类”﹔只有函数成员;成员全部public)。接口为解耦而生:“高内聚。低耦合”。方便单元测试
- 接口是一个"协约”,早已为工业生产所熟知(有分工必有协作。有协作必有协约)。
- **接口也可被作为一种函数参数类型,或者类成员类型!**或者可以直接理解为接口就是一种纯抽象类,不实例化就行
- 它们都不能实例化。只能用来声明变量。引用具体类(concrete class)的实例
依赖反转原则
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-tu50CRUW-1692105515282)(C:%5CUsers%5CLiyi%5CAppData%5CRoaming%5CTypora%5Ctypora-user-images%5C1626612001693.png)]
接口隔离原则
接口设置要合理,调用者绝不多要!即不能设计不会被使用的接口。
即也是一种单一职责原则。
做法:把功能本质不同的接口分开
注意:把握一个度,也不能切的太碎!
接口的显式实现
interface IGentleman
{
void Love();
}
interface IKiller
{
void Kill();
}
class WarmKiller:IGentleman,IKiller
{
public void Love(){...}
//↓ 只有我们将这个实例作为IKiller,时才会看见Kill接口!
void IKiller.Kill(){...}
}
...
var wk = new WarmKiller();
//wk 看不到Kill方法
IKiller killer = wk;
//killer 此时就能看见Kill,但看不见Love
//or
IKiller killer = new WarmKiller();
var wk1 = killer as WarmKiller;
//wk1 看不到Kill方法;能看见Love
接口继承
- 接口继承可以继承多个。
interface ITank:IVehicle,IWeapon{}
测试
…
NuGet包管理器:Moq —— 帮助测试省去重复定义类的过程
反射
.NET框架的功能,并不是语言的功能!.NET Framework与Core也不同,但是API不同
反射:reflect
反射与依赖注入
- 反射:以不变应万变(更松的耦合)。
- 反射与接口的结合
- 反射与特性的结合
- 依赖注入:此DI(Dependency Injection)非彼DI(依赖反转DIP)。但没有彼DI就没有此Dl…
//直接使用
Student stu = new Student();
var t = stu.GetType();//获取类型信息
object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);
MethodInfo studyMi = t.GetMethod("study");
studyMi.Invoke(o,null);
NuGet中找 DependencyInjection。微软的
泛型 generic
解决类型膨胀,成员膨胀的问题。
- 泛型会类型推断
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Apple apple = new Apple() { Color = "Red" };
Book book = new Book() {Name = "MyBook"};
Box box1 = new Box(apple);
Box box2 = new Box(book);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Cargo.Color);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Cargo.Name);
}
}
class Apple
{
public string Color { get; set; }
}
class Book
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Box
{
public TCargo Cargo { get; set; }
public Box(TCargo Cargo)
{
this.Cargo = Cargo;
}
}
泛型接口
interface IUnique
{
TId ID{get;set;}
}
class Student:IUnique
{
public TId ID {get;set;}
public string Name {get;set;}
}
//另一种方式
class Student:IUnique
{
public ulong ID {get;set;}
public string Name {get;set;}
}
- C# 提供的泛型数据结构与算法:
System.Collections.Generic
泛型委托
C#提供:
- Action 无返回
- Func 有返回
还可以根据输入的类型找到正确的重载函数
Lambda
Func func1 = (double a, double b)=>{return a+b;}
//因为委托中已经确定输入类型了,所以此时Lambda的输入类型可以去掉
- Lambda 是 inline 方法、匿名方法
- 返回委托,可以直接赋给委托变量
- 委托定义时也可直接等于 方法/Lambda
- return 也能省略?!
partial类
- 减少派生类
- partial写在 在类修饰符后面,class关键字前面
- 可以类的不同部分用不同速度更新(一个类写在两个地方)
- 甚至一个类两个语言
枚举,结构体
枚举类型
- 人为限定取值范围的整数
- 整数值的对应
- 比特位式用法
结构体(struct)
- 值类型。可装/拆箱
- 可实现接口。不能派生自类/结构体。
- 不能有显式无参构造器
枚举
- 打印枚举值时,会把枚举的字符串(标识符名)打印出来
- 可利用二进制位或运算来让一个枚举变量获得多个枚举值,并通过位与运算得知该变量是否有相应呃枚举值
结构体
- 结构体是值类型(内存即存储的实例,栈)