Nginx的安装及负载均衡搭建
一.Nginx的安装
1)准备安装环境
yum install -y make gcc gcc-c++ pcre-devel pcre zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel
- PERE
PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions)是一个Perl库,包括 perl 兼容的正则表达式库。
nginx的http模块使用pcre来解析正则表达式,所以需要在linux上安装pcre库。
注:pcre-devel是使用pcre开发的一个二次开发库。nginx也需要此库。
- zlib
zlib库提供了很多种压缩和解压缩的方式,nginx使用zlib对http包的内容进行gzip,所以需要在linux上安装zlib库。
- openssl
OpenSSL 是一个强大的安全套接字层密码库,囊括主要的密码算法、常用的密钥和证书封装管理功能及SSL协议,
并提供丰富的应用程序供测试或其它目的使用。
nginx不仅支持http协议,还支持https(即在ssl协议上传输http),所以需要在linux安装openssl库。
2)下载安装包
下载地址:nginx: download
Nginx官网提供了三个类型的版本
- Mainline version:是 Nginx 目前主力在做的版本,可以说是开发版
- Stable version:最新稳定版,生产环境上建议使用的版本
- Legacy versions:遗留的老版本的稳定版
3)上传安装包并解压
tar xvf nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local/设置软链接
ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.24.0/ /usr/local/nginx4)创建用户和组
groupadd -r nginx
useradd nginx -u 666 -r -g nginx -c "nginx user"-
groupadd -r nginx: 这个命令用于创建一个名为“nginx”的用户组,并将其添加到系统中。选项-r表示创建系统组。 -
useradd nginx -u 666 -r -g nginx -c "nginx user": 这个命令用于创建一个名为“nginx”的用户,并将其添加到组“nginx”中。选项-u 666表示将用户的UID设置为666。选项-r表示创建系统账户。选项-g nginx表示将用户添加到组“nginx”中。选项-c "nginx user"表示为用户指定一个自定义的描述信息,这里是“nginx user”。
5)编译安装
./configure \
> --user=nginx --group=nginx \
> --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
> --with-http_stub_status_module \
> --with-http_ssl_module- ./confire 用于对将安装的软件进行配置,检查当前的环境是否满足安装软件( Nginx )的依赖关系 。
- --prefix 选项用于设置 Nginx 安装目录,默认值是 usr / local/ nginx ,因而也可以省略此选项或指定到其位置,
- --with-http_ssl_module 选项用于设置在 Nginx 中允许使用 http_ss modu 模块的相关功能。
- 行尾的 '\'表示未结束需要换到下一行书写。
- "--with-"选项用于添加模块,Nginx中有很多模块,需要安装时只需要重新编译在通过选项添加模块即可
make && make install"&&"符号根据前一个命令的返回值决定是否执行后一个命令,前一个成功执行就会执行后面这个命令,这样可以减少手动操作,当然也可以一次执行命令。
6)启动Nginx:
进入Nginx的目录的sbin下
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
./nginx
执行成功不会有任何信息返还,使用ps命令查看
ps aux | grep nginx
7)停止Nginx:
1.立即停止服务:
./nginx -s stop注意:这种停止方法不管当前工作进程是否在处理工作,立即停止工作,使用这种需注意。
2.从容停止服务:
./nginx -s quit这种停止方法会在进程处理完后再停止服务
3.使用kill命令关闭进程
通过ps命令获取Nginx进程的PID,使用kill命令关闭进程或使用killall命令
kill nginx PID
killall nginx
注意:nginx启动后会自动监听80端口,如80端口被占用则会启动失败。
netstat -tlnp查看端口占用
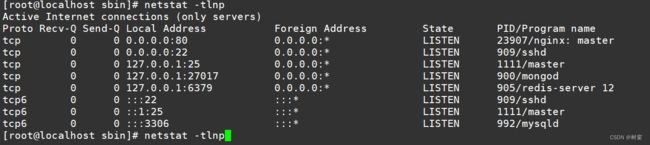 Nginx 的主进程正在监听 TCP 协议 80 端口 ,说明 Nginx目前已经启动。另外,netstat 命令的四个选项:t、l、n、p分别表示查看tcp协议、查看监听服务、不解析名称以及显示进程名和 PID。
Nginx 的主进程正在监听 TCP 协议 80 端口 ,说明 Nginx目前已经启动。另外,netstat 命令的四个选项:t、l、n、p分别表示查看tcp协议、查看监听服务、不解析名称以及显示进程名和 PID。
8)添加服务脚本:
由于每次启动nginx都需要到安装目录下启动,十分麻烦所以添加服务脚本可以大大的减少这种操作。
在CentOS 7中,服务的systemctl脚本被存放在/usr/lib/systemd/目录下。这个目录下有system和user两个子目录,分别存放系统服务和用户服务的相关脚本。
如果你想要开机就能运行的程序,即:不需要登录即可运行的服务。最好将其作为系统服务来管理。对于系统服务,你可以将相关的脚本文件放置在/usr/lib/systemd/system目录下。
每一个服务脚本一般包含三个部分:[Unit]、[Service]和[Install]。这些部分分别定义了服务的单位(Unit)、服务本身的配置(Service)以及服务的安装相关设置(Install)。
- [Unit]部分包含关于服务的元数据,例如服务的描述、依赖关系等信息。
- [Service]部分定义了服务的具体配置,包括服务的运行命令、工作目录、环境变量等。
- [Install]部分定义了服务的安装设置,例如服务的启动级别、所属用户等。
脚本如下:
[root@localhost sbin]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
description=nginx - high performance web server
Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/
After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
注意:添加完毕后需运行"systemctl daemon-reload "
"systemctl daemon-reload "是用于重新加载systemd的配置文件和单位文件的命令
[Unit]:服务的说明
Description:描述服务
After:描述服务类别
[Service]服务运行参数的设置
Type=forking是后台运行的形式
ExecStart为服务的具体运行命令
ExecReload为重启命令
ExecStop为停止命令
PrivateTmp=True表示给服务分配独立的临时空间
注意:启动、重启、停止命令全部要求使用绝对路径
[Install]服务安装的相关设置,可设置为多用户
报错:
[root@localhost sbin]# ./nginx
nginx: [alert] could not open error log file: open() "/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log" failed (2: No such file or directory)
2023/08/15 19:23:23 [emerg] 22354#0: open() "/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log" failed (2: No such file or directory)
原因分析:Nginx目录下无logs文件
解决办法:创建logs文件
#创建logs目录
mkdir logs
#赋予权限
chmod 700 logs/验证:
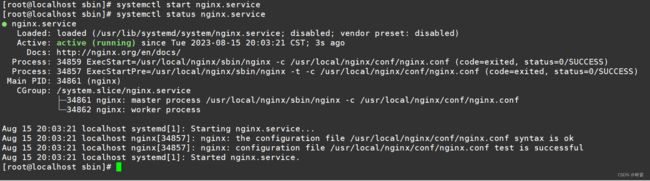
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t正常情况会输出一下信息:
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
二.nginx的负载均衡搭建
1)准备服务器
准备三台虚拟机,一台安装了nginx,两台web服务器
2)修改配置文件
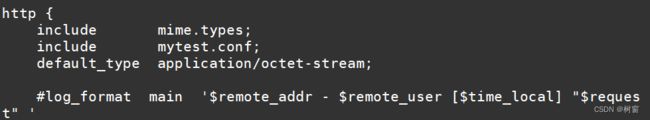
引入文件
编写配置文件
more mytest.conf
upstream backend {
server 192.168.136.135:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.136.134:80 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.myname.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
[root@localhost conf]#