Go 程序设计语言学习笔记
前几天刚把 Go 入门指南看了一下,所以趁热打铁,再来加深一下印象。
go 中 Printf 函数常用转义字符表:
verb 描述
%d 十进制整数
%x 十六进制
%o 八进制
%b 二进制
%f 浮点数:如 3.141593
%g 浮点数:如 3.141592653589793
%e 浮点数:如 3.141593e+00
%t 布尔型:true 或 false
%c 字符
%s 字符串
%q 带引号的字符串(如 "abc")或者字符(如 'c')
%v 内置格式的任何值
%T 任何值的类型
%% 百分号本身示例程序
先来个Go语言实战的示例程序(这个示例程序包含了 go 中常见的大部分知识,也展示了 go 代码的组织风格),目录结构如下:
.
├── data
│ └── data.json
├── go.mod
├── main.go
├── matchers
│ └── rss.go
└── search
├── default.go
├── feed.go
├── match.go
└── search.gomain.go
package main
import (
"log"
"os"
_ "github.com/goinaction/code/chapter2/sample/matchers"
"github.com/goinaction/code/chapter2/sample/search"
)
// init is called prior to main.
func init() {
// Change the device for logging to stdout.
log.SetOutput(os.Stdout)
}
// main is the entry point for the program.
func main() {
// Perform the search for the specified term.
search.Run("president")
}
go.mod
module github.com/goinaction/code/chapter2/sample
replace github.com/goinaction/code/chapter2/sample => ./
go 1.17
matchers
matchers/rss.go
package matchers
import (
"encoding/xml"
"errors"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"regexp"
"github.com/goinaction/code/chapter2/sample/search"
)
type (
// item defines the fields associated with the item tag
// in the rss document.
item struct {
XMLName xml.Name `xml:"item"`
PubDate string `xml:"pubDate"`
Title string `xml:"title"`
Description string `xml:"description"`
Link string `xml:"link"`
GUID string `xml:"guid"`
GeoRssPoint string `xml:"georss:point"`
}
// image defines the fields associated with the image tag
// in the rss document.
image struct {
XMLName xml.Name `xml:"image"`
URL string `xml:"url"`
Title string `xml:"title"`
Link string `xml:"link"`
}
// channel defines the fields associated with the channel tag
// in the rss document.
channel struct {
XMLName xml.Name `xml:"channel"`
Title string `xml:"title"`
Description string `xml:"description"`
Link string `xml:"link"`
PubDate string `xml:"pubDate"`
LastBuildDate string `xml:"lastBuildDate"`
TTL string `xml:"ttl"`
Language string `xml:"language"`
ManagingEditor string `xml:"managingEditor"`
WebMaster string `xml:"webMaster"`
Image image `xml:"image"`
Item []item `xml:"item"`
}
// rssDocument defines the fields associated with the rss document.
rssDocument struct {
XMLName xml.Name `xml:"rss"`
Channel channel `xml:"channel"`
}
)
// rssMatcher implements the Matcher interface.
type rssMatcher struct{}
// init registers the matcher with the program.
func init() {
var matcher rssMatcher
search.Register("rss", matcher)
}
// Search looks at the document for the specified search term.
func (m rssMatcher) Search(feed *search.Feed, searchTerm string) ([]*search.Result, error) {
var results []*search.Result
log.Printf("Search Feed Type[%s] Site[%s] For URI[%s]\n", feed.Type, feed.Name, feed.URI)
// Retrieve the data to search.
document, err := m.retrieve(feed)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
for _, channelItem := range document.Channel.Item {
// Check the title for the search term.
matched, err := regexp.MatchString(searchTerm, channelItem.Title)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// If we found a match save the result.
if matched {
results = append(results, &search.Result{
Field: "Title",
Content: channelItem.Title,
})
}
// Check the description for the search term.
matched, err = regexp.MatchString(searchTerm, channelItem.Description)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// If we found a match save the result.
if matched {
results = append(results, &search.Result{
Field: "Description",
Content: channelItem.Description,
})
}
}
return results, nil
}
// retrieve performs a HTTP Get request for the rss feed and decodes the results.
func (m rssMatcher) retrieve(feed *search.Feed) (*rssDocument, error) {
if feed.URI == "" {
return nil, errors.New("No rss feed uri provided")
}
// Retrieve the rss feed document from the web.
resp, err := http.Get(feed.URI)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Close the response once we return from the function.
defer resp.Body.Close()
// Check the status code for a 200 so we know we have received a
// proper response.
if resp.StatusCode != 200 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("HTTP Response Error %d\n", resp.StatusCode)
}
// Decode the rss feed document into our struct type.
// We don't need to check for errors, the caller can do this.
var document rssDocument
err = xml.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&document)
return &document, err
}
search
search/default.go
package search
// defaultMatcher implements the default matcher.
type defaultMatcher struct{}
// init registers the default matcher with the program.
func init() {
var matcher defaultMatcher
Register("default", matcher)
}
// Search implements the behavior for the default matcher.
func (m defaultMatcher) Search(feed *Feed, searchTerm string) ([]*Result, error) {
return nil, nil
}
search/feed.go
package search
import (
"encoding/json"
"os"
)
const dataFile = "data/data.json"
// Feed contains information we need to process a feed.
type Feed struct {
Name string `json:"site"`
URI string `json:"link"`
Type string `json:"type"`
}
// RetrieveFeeds reads and unmarshals the feed data file.
func RetrieveFeeds() ([]*Feed, error) {
// Open the file.
file, err := os.Open(dataFile)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Schedule the file to be closed once
// the function returns.
defer file.Close()
// Decode the file into a slice of pointers
// to Feed values.
var feeds []*Feed
err = json.NewDecoder(file).Decode(&feeds)
// We don't need to check for errors, the caller can do this.
return feeds, err
}
search/match.go
package search
import (
"log"
)
// Result contains the result of a search.
type Result struct {
Field string
Content string
}
// Matcher defines the behavior required by types that want
// to implement a new search type.
type Matcher interface {
Search(feed *Feed, searchTerm string) ([]*Result, error)
}
// Match is launched as a goroutine for each individual feed to run
// searches concurrently.
func Match(matcher Matcher, feed *Feed, searchTerm string, results chan<- *Result) {
// Perform the search against the specified matcher.
searchResults, err := matcher.Search(feed, searchTerm)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
// Write the results to the channel.
for _, result := range searchResults {
results <- result
}
}
// Display writes results to the console window as they
// are received by the individual goroutines.
func Display(results chan *Result) {
// The channel blocks until a result is written to the channel.
// Once the channel is closed the for loop terminates.
for result := range results {
log.Printf("%s:\n%s\n\n", result.Field, result.Content)
}
}
search/search.go
package search
import (
"log"
"sync"
)
// A map of registered matchers for searching.
var matchers = make(map[string]Matcher)
// Run performs the search logic.
func Run(searchTerm string) {
// Retrieve the list of feeds to search through.
feeds, err := RetrieveFeeds()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create an unbuffered channel to receive match results to display.
results := make(chan *Result)
// Setup a wait group so we can process all the feeds.
var waitGroup sync.WaitGroup
// Set the number of goroutines we need to wait for while
// they process the individual feeds.
waitGroup.Add(len(feeds))
// Launch a goroutine for each feed to find the results.
for _, feed := range feeds {
// Retrieve a matcher for the search.
matcher, exists := matchers[feed.Type]
if !exists {
matcher = matchers["default"]
}
// Launch the goroutine to perform the search.
go func(matcher Matcher, feed *Feed) {
Match(matcher, feed, searchTerm, results)
waitGroup.Done()
}(matcher, feed)
}
// Launch a goroutine to monitor when all the work is done.
go func() {
// Wait for everything to be processed.
waitGroup.Wait()
// Close the channel to signal to the Display
// function that we can exit the program.
close(results)
}()
// Start displaying results as they are available and
// return after the final result is displayed.
Display(results)
}
// Register is called to register a matcher for use by the program.
func Register(feedType string, matcher Matcher) {
if _, exists := matchers[feedType]; exists {
log.Fatalln(feedType, "Matcher already registered")
}
log.Println("Register", feedType, "matcher")
matchers[feedType] = matcher
}
data
data/data.json
[
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1001",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1008",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1006",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1007",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1057",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1021",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1012",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=1003",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=2",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=3",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=5",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=13",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=46",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=7",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=10",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=39",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "npr",
"link" : "http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=43",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "bbci",
"link" : "http://feeds.bbci.co.uk/news/rss.xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "bbci",
"link" : "http://feeds.bbci.co.uk/news/business/rss.xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "bbci",
"link" : "http://feeds.bbci.co.uk/news/world/us_and_canada/rss.xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_topstories.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_world.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_us.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_allpolitics.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_crime.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_tech.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_health.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "cnn",
"link" : "http://rss.cnn.com/rss/cnn_topstories.rss",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "foxnews",
"link" : "http://feeds.foxnews.com/foxnews/opinion?format=xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "foxnews",
"link" : "http://feeds.foxnews.com/foxnews/politics?format=xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "foxnews",
"link" : "http://feeds.foxnews.com/foxnews/national?format=xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "foxnews",
"link" : "http://feeds.foxnews.com/foxnews/world?format=xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "nbcnews",
"link" : "http://feeds.nbcnews.com/feeds/topstories",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "nbcnews",
"link" : "http://feeds.nbcnews.com/feeds/usnews",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "nbcnews",
"link" : "http://rss.msnbc.msn.com/id/21491043/device/rss/rss.xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "nbcnews",
"link" : "http://rss.msnbc.msn.com/id/21491571/device/rss/rss.xml",
"type" : "rss"
},
{
"site" : "nbcnews",
"link" : "http://rss.msnbc.msn.com/id/28180066/device/rss/rss.xml",
"type" : "rss"
}
]入门
找重复行
test.txt
hello
hello
world
world
worldpackage main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
counts := make(map[string]int)
f, err := os.Open("test.txt")
if err == nil {
input := bufio.NewScanner(f)
for input.Scan() {
counts[input.Text()]++
}
}
f.Close()
for line, n := range counts {
if n > 1 {
fmt.Printf("line:%s\tcount:%d\n", line, n)
}
}
}
//line:hello count:2
//line:world count:3package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"strings"
)
func main() {
counts := make(map[string]int)
data, err := ioutil.ReadFile("test.txt")
if err != nil {
return
}
for _, line := range strings.Split(string(data), "\r\n"){
counts[line]++
}
for line, n := range counts {
if n > 1 {
fmt.Printf("line:%s\tcount:%d\n", line, n)
}
}
}
//line:hello count:2
//line:world count:3GIF动画
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"image/gif"
"io"
"log"
"math"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
)
var palette = []color.Color{color.White, color.Black}
const (
whiteIndex = 0
blackIndex = 1
)
func main() {
// go run main.go >out.gif
rand.Seed(time.Now().UTC().UnixNano())
if len(os.Args) > 1 && os.Args[1] == "web" {
handler := func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
lissajous(w)
}
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
}
lissajous(os.Stdout)
}
func lissajous(out io.Writer) {
const (
cycles = 5
res = 0.001
size = 100
nframes = 64
delay = 8
)
freq := rand.Float64() * 3.0
anim := gif.GIF{LoopCount: nframes}
phase := 0.0
for i := 0; i < nframes; i++ {
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, 2*size+1, 2*size+1)
img := image.NewPaletted(rect, palette)
for t := 0.0; t < cycles*2*math.Pi; t += res {
x := math.Sin(t)
y := math.Sin(t*freq + phase)
img.SetColorIndex(size+int(x*size+0.5), size+int(y*size+0.5), blackIndex)
}
phase += 0.1
anim.Delay = append(anim.Delay, delay)
anim.Image = append(anim.Image, img)
}
gif.EncodeAll(out, &anim)
}
并发获取多个URL
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
)
func main() {
start := time.Now()
ch := make(chan string)
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
go fetch(url, ch)
}
for range os.Args[1:] {
fmt.Println(<-ch)
}
fmt.Printf("%.2fs elapsed\n", time.Since(start).Seconds())
}
func fetch(url string, ch chan <- string) {
start := time.Now()
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
ch <- fmt.Sprint(err)
return
}
nbytes, err := io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, resp.Body)
resp.Body.Close()
if err != nil {
ch <- fmt.Sprintf("while reading %s: %v", url, err)
return
}
secs := time.Since(start).Seconds()
ch <- fmt.Sprintf("%.2fs %7d %s", secs, nbytes, url)
}
//E:\Project\test_go>go build main.go
//E:\Project\test_go>main.exe http://gopl.io https://godoc.org
//1.50s 30539 https://godoc.org
//1.84s 4154 http://gopl.io
//1.84s elapsed
一个Web服务器
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/hello", handler)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
}
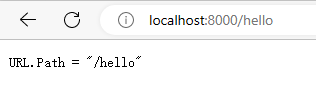
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "URL.Path = %q\n", r.URL.Path)
}
添加访问计数功能
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"sync"
)
var mu sync.Mutex
var count int
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
http.HandleFunc("/count", counter)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
}
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
mu.Lock()
count++
mu.Unlock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "URL.Path = %q\n", r.URL.Path)
}
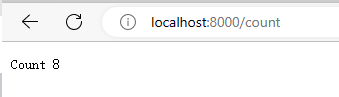
func counter(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
mu.Lock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Count %d\n", count)
mu.Unlock()
}打印消息头
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"sync"
)
var mu sync.Mutex
var count int
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
http.HandleFunc("/count", counter)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
}
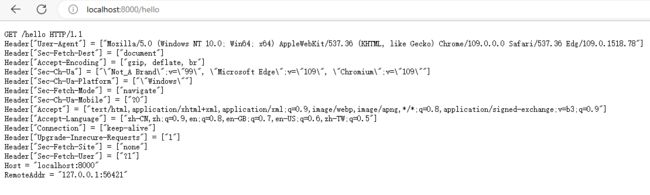
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
mu.Lock()
count++
mu.Unlock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s %s\n", r.Method, r.URL, r.Proto)
for k, v := range r.Header {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Header[%q] = %q\n", k, v)
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Host = %q\n", r.Host)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "RemoteAddr = %q\n", r.RemoteAddr)
if err := r.ParseForm(); err != nil {
log.Print(err)
}
for k, v := range r.Form {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Form[%q] = %q\n", k, v)
}
}
func counter(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
mu.Lock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Count %d\n", count)
mu.Unlock()
}
整合gif到web
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"image/gif"
"io"
"log"
"math"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
)
var palette = []color.Color{color.White, color.Black}
const (
whiteIndex = 0
blackIndex = 1
)
func main() {
handler := func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
lissajous(w)
}
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
}
func lissajous(out io.Writer) {
const (
cycles = 5
res = 0.001
size = 100
nframes = 64
delay = 8
)
freq := rand.Float64() * 3.0
anim := gif.GIF{LoopCount: nframes}
phase := 0.0
for i := 0; i < nframes; i++ {
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, 2*size+1, 2*size+1)
img := image.NewPaletted(rect, palette)
for t := 0.0; t < cycles*2*math.Pi; t += res {
x := math.Sin(t)
y := math.Sin(t*freq + phase)
img.SetColorIndex(size+int(x*size+0.5), size+int(y*size+0.5), blackIndex)
}
phase += 0.1
anim.Delay = append(anim.Delay, delay)
anim.Image = append(anim.Image, img)
}
gif.EncodeAll(out, &anim)
}
程序结构
变量
类型和表达式部分可以省略一个,但是不能都省略
var name type = expression
var i, j, k int
var b, f, s = true, 2.3, "four"
var f, err = os.Open(name)短变量声明
短变量声明可以用来声明和初始化局部变量。
name := expression
i, j := 0, 1
i, j := j, i
f, err := os.Open(name)短变量声明最少声明一个新变量,否则,代码无法编译通过(这个还是比较好理解,因为短变量声明本意就是为新的局部变量准备的,如果没有新变量,直接使用普通赋值岂不是更好)。
.\main.go:7:4: no new variables on left side of :=指针
指针的值是一个变量的地址,用以指示值所保存的位置。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
x := 1
p := &x
fmt.Println(*p) // 1
*p = 2
fmt.Println(x) // 2
var y, z int
fmt.Println(&y == &y, &y == &z, &y == nil) // true false false
}函数返回局部变量的地址
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(f() == f()) // false
v := 1
incr(&v) // 2
fmt.Println(incr(&v)) // 3
}
func f() *int {
v := 1
return &v
}
func incr(p *int) int {
*p ++
return *p
}
指针对于 flag 包很关键,使用程序的命令行参数来设置整个程序内变量的值。
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
var name string
var age int
var married bool
flag.StringVar(&name, "name", "everyone", "The greeting object.")
flag.IntVar(&age, "age", 18, "The greeting object's age.")
flag.BoolVar(&married, "married", false, "Is the greeting object married?")
flag.Parse() //更新标识变量的默认值
fmt.Println("name:", name)
fmt.Println("age:", age)
fmt.Println("married:", married)
}D:\MyProject\Go\test>main -name="Looking" -age=30 -married
name: Looking
age: 30
married: true
D:\MyProject\Go\test>main --help
flag provided but not defined: -marrie
Usage of main:
-age int
The greeting object's age. (default 18)
-married
Is the greeting object married?
-name string
The greeting object. (default "everyone")new函数
可以使用内置预声明的 new 函数创建变量,只是不需要引入一个虚拟的名字。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
p := new(int)
fmt.Println(*p) // 0
*p = 2
fmt.Println(*p) // 2
}
// new 是一个预声明的函数,可以重定义为其他类型
func delta(old, new int) int { // 在 delta 函数内,内置的 new 函数暂时不可用
return new - old
}
类型声明
package main
import "fmt"
type Celsius float64
type Fahrenheit float64
const (
AbsoluteZeroC Celsius = -273.15
FreezingC Celsius = 0
BollingC Celsius = 0
)
func main() {
var c Celsius
var f Fahrenheit
fmt.Println(c == 0) // true
fmt.Println(f == 0) // true
//fmt.Println(c == f) // 不同命名类型的值不能直接比较
fmt.Println(c == Celsius(f)) // true 强制类型转换后可以进行比较
c = 100
fmt.Println(c.String())
}
func (c Celsius) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%g C", c)
}
包和文件
包的导入
目录结构
.
├── main.go
└── tempconv
├── conv.go
└── tempconv.gotempconv/conv.go
package tempconv
func CToF(c Celsius) Fahrenheit {
return Fahrenheit(c*9/5 + 32)
}
func FToC(f Fahrenheit) Celsius {
return Celsius(f-32) * 5 / 9
}tempconv/tempconv.go
package tempconv
import "fmt"
type Celsius float64
type Fahrenheit float64
const (
AbsoluteZeroC Celsius = -273.15
FreezingC Celsius = 0
BollingC Celsius = 100
)
func (c Celsius) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%g C", c)
}
func (f Fahrenheit) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%g F", f)
}./main.go
package main
import "fmt"
import "./tempconv"
func main() {
f := tempconv.CToF(tempconv.BollingC)
fmt.Println(f) // 212 F
}结果调用的时候报错了
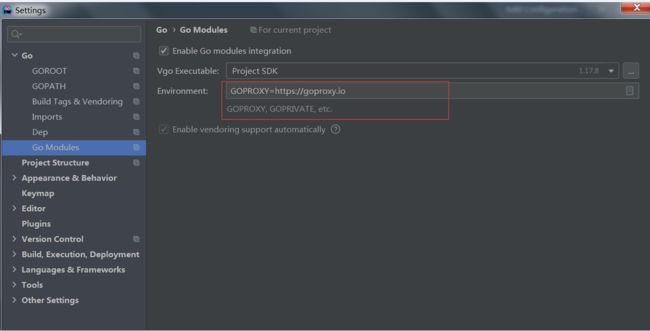
build command-line-arguments: cannot find module for path XXXXXX然后设置一下环境变量就好了(目前还是新手,暂且不去追究具体原理)
go env -w GO111MODULE=auto还有就是我同步依赖的时候,一直同步失败,后来按照网上的方案配置了一下公共代理才搞定
包初始化
包的初始化按照声明顺序初始化,在依赖已解析的情况下,根据依赖顺序进行初始化。init 函数可以用来初始化,这个函数不能被调用和引用。
func init(){ /*...*/ }作用域
在包级别(就是在任何函数外)的声明,可以被同一个包的任何文件引用,比如conv.go不用显式导入,就可以引用同包里边tempconv.go 里声明的变量。
同其他语言一样,如果内外语法块都有声明,内部声明(局部声明)的优先级更高,会覆盖外部声明。
局部变量让外部变量失效
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
)
var cwd string
func init(){
cwd, err := os.Getwd() // := 将变量变成了局部声明
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("os.Getwd failed: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("init", cwd)
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("main", cwd)
}
不使用 := ,声明变量 err,
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
)
var cwd string
func init(){
var err error
cwd, err = os.Getwd()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("os.Getwd failed: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("init", cwd)
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("main", cwd)
}基本数据
整数
Go 具备有符号整数和无符号整数,有符号分别为 int8,int16,int32,int64,对应的无符号整数为 uint8, uint16,uint32,uint64,还有两种类型 int 和 uint。
rune 同义于 int32,byte 同义于 uint8,使用 rune 和 byte 时,强调值是原始数据,而非量值。
int, uint, uintptr 和其他大小明确的相似类型的区别,比如 int 天然大小是 32 位,但 int 若要当做 int32使用,必须显示转换,反之亦然。有符号位的最高位作为符号位。int8可以从 -128到127取值,uint8 从0到255取值。
二元运算符优先级:
* / % << >> & &^
+ - | ^
== != < <= > >=
&&
||Go中取模运算符的正负号始终与被除数保持一致:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(5 % -3) // 2
fmt.Println(-5 % -3) // -2
}无论是有符号还是无符号数,超出类型范围高位会毫无提示丢失:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var u uint8 = 255
fmt.Println(u, u+1, u*u) // 255 0 1; 255*255=65025 "1111111000000001"
var i int8 = 127
fmt.Println(i, i+1, i*i) // 127, -128 1; 127*127=16129 "11111100000001"
}全部基本类型(布尔值,数值,字符串)的值都可以比较,位清空 x&^y 也可简单理解成 x&(^y),也即 y 取反以后和 x 按位与。
Go也支持基本位运算,
& 按位与
| 按位或
^ 按位异或
&^ 位清空(z = x&^y,若 y 的某位是1,则 z 的对应位为0,否则为 x 的对应位)
<< 左移
>> 右移package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x uint8 = 1<<1 | 1<<5
var y uint8 = 1<<1 | 1<<2
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", x) // "00100010"
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", y) // "00100010"
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", x&y) // "00100010"
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", x|y) // "00100110"
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", x^y) // "00100110"
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", x&^y) // "00100000"
fmt.Printf("%08b\n", x&(^y)) // "00100000"
for i := uint(0); i < 8; i++ {
if x&(1<>1) // "00010001"
} Go的无符号整形往往只用于位运算和特定算术运算符,例如实现位集,解析二进制文件,散列或加密,无符号整数很少用于表示非负值。对于算术和逻辑的二元运算符,操作数的类型必须相同。
很多整型到整型的相互转换并不会引起值的变化,仅仅告知编译器应该如何解读该值。不过缩减大小的整型转换可能改变值或者损失精度。
fmt 格式化输出技巧:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
i := 438
// [1]告知 Printf 重复使用第一个操作数,%b %o %x 告知输出的进制,#告知输出相应的表示进制的前缀
fmt.Printf("%d %[1]b %#[1]o %#[1]x %[1]X", i) // 438 110110110 0666 0x1b6 1B6
}浮点数
Go支持两种大小的浮点数 float32和float64,math 包给出了浮点值的极限。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(math.MaxFloat32) // 3.4028234663852886e+38
fmt.Println(math.MaxFloat64) // 1.7976931348623157e+308
fmt.Println(math.E) // 2.718281828459045
fmt.Println(math.Pi) // 3.141592653589793
var f float32 = 16777216
fmt.Println(f == f+1) // true, float32能精确表示的正整数范围有限
for i := 0; i < 8; i++ {
fmt.Printf("i = %d e^x = %8.3f\n", i, math.Exp(float64(i))) // 这种表示倒是和 python 的 format 比较像
}
// >>> "pi = {:8.2f}".format(3.1415926)
//'pi = 3.14'
//
//i = 0 e^x = 1.000
//i = 1 e^x = 2.718
//i = 2 e^x = 7.389
//i = 3 e^x = 20.086
//i = 4 e^x = 54.598
//i = 5 e^x = 148.413
//i = 6 e^x = 403.429
//i = 7 e^x = 1096.633
}复数
布尔值
bool值只有 真(true)和假(false)两种可能,且无法隐式转换成数值,反之也不行。如果转换中常常用到,就需要专门写个函数。
func btoi(b bool) int {
if b {
return 1
}
return 0
}
func itob(i int) bool {
return i != 0
}字符串
内置的len函数返回字符串的字节数(不是字符数):
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s := "hello, world"
fmt.Println(s[0:5]) // hello
fmt.Println(s[7:]) // world
fmt.Println(s[:]) // hello, world
fmt.Println("goodbye" + s[5:]) // goodbye, world
s = "left foot"
t := s
s += ", right foot"
fmt.Println(s)
fmt.Println(t) // 字符串值本身无法改变,无法被修改
}字符串字面量
字符串的值可以直接写成字符串字面量。其中转义序列使用 \ 开始,原生的字符串字面量使用反引号而不是双引号括起来。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"unicode/utf8"
)
func main() {
s := "hello, 世界"
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 13 字节数
fmt.Println(utf8.RuneCountInString(s)) // 9 字符数
for i := 0; i < len(s); {
r, size := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(s[i:])
fmt.Printf("%d\t%c\n", i, r)
i += size
}
//0 h
//1 e
//2 l
//3 l
//4 o
//5 ,
// 6
//7 世
//10 界
}package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s := "hello, 世界"
n := 0
for _, c := range s { // 对字符串每个字符进行遍历
fmt.Printf("%c\n", c)
n++
}
fmt.Printf("% x\n", s)
}fmt.Printf 的谓词 % x(中间有空格)以16进制形式输出,并在两个数位间插入空格。
字符串和字节切片
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(string("65")) // 65
fmt.Println(string(65)) // A
fmt.Println(string(0x4eac)) // 京
fmt.Println(string(1234567)) // �
}4个标准库对字符串的操作特别重要:bytes, strings, strconv 和 unicode。
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(comma("123456789"))
}
// 整数字符串递归添加逗号
func comma(s string) string {
n := len(s)
if n <= 3 {
return s
}
return comma(s[:n-3]) + "," + s[n-3:]
}为了避免转换和不必要的内存分配,bytes 和 strings 都预备了很多对应的实用函数,唯一不同的是操作对象由字符串变成了字节数组:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
s := "aa bc"
b := []byte(s)
fmt.Println(strings.Contains(s, "a")) // true
fmt.Println(bytes.Contains(b, []byte("a"))) // true
fmt.Println(strings.Count(s, "a")) // 2
fmt.Println(bytes.Count(b, []byte("a"))) // 2
fmt.Println(strings.Fields(s)) // [aa bc]
fmt.Println(bytes.Fields(b)) // [[97 97] [98 99]]
fmt.Println(strings.HasPrefix(s, "a")) // true
fmt.Println(bytes.HasPrefix(b, []byte("a"))) // true
fmt.Println(strings.Index(s, "b")) // 3
fmt.Println(bytes.Index(b, []byte("b"))) // 3
fmt.Println(strings.Join([]string{"a", "b", "cd"}, "")) // abcd
fmt.Println(bytes.Join([][]byte{[]byte("a"), []byte("b"), []byte("cd")}, []byte(""))) // [97 98 99 100]
}bytes.Buffer
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(intsToString([]int{1, 2, 3})) // [1,2,3]
}
func intsToString(values []int) string {
var buf bytes.Buffer
buf.WriteByte('[')
for i, v := range values {
if i > 0 {
buf.WriteString(",")
}
fmt.Fprintf(&buf, "%d", v)
}
buf.WriteByte(']')
return buf.String()
}如果要追加非 ASCII 字符,需要使用 but.WriteRune,否则可能出现溢出报错比如: constant 22909 overflows byte
字符串和数字的相互转换
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
x := 123
y := fmt.Sprintf("%d", x)
fmt.Println(y, strconv.Itoa(x)) // 123 123
fmt.Println(strconv.FormatInt(int64(x), 2)) // 111011
s := fmt.Sprintf("x=%b", x) // x=1111011
fmt.Println(s)
fmt.Printf("x=%b", x) // x=1111011
fmt.Println()
a, _ := strconv.Atoi("1234")
b, _ := strconv.ParseInt("1111", 2, 8) // 二进制,最长8位,若超过最大位数,显示能表示的最大值
fmt.Println(a) // 1234
fmt.Println(b) // 15
}
常量
常量是一种表达式,其在编译阶段就计算出表达式的值,本质上都属于基本类型:布尔型,字符串或数字。常量操作数的数学运算、逻辑运算和比较运算依然是常量。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
const noDelay time.Duration = 0
const timeout = 5 * time.Minute
fmt.Printf("%T %[1]v\n", noDelay) // time.Duration 0s
fmt.Printf("%T %[1]v\n", timeout) // time.Duration 5m0s
fmt.Printf("%T %[1]v\n", time.Minute) // time.Duration 1m0s
const (
a = 1
b
c = 2
d
)
fmt.Println(a, b, c, d) // 1 1 2 2
}常量生成器 iota
package main
import "fmt"
type WeekDay int
const (
Sunday WeekDay = iota
Monday
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Friday
Saturday
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(Wednesday) // 3
fmt.Println(Friday) // 5
}
无类型常量
只有常量才是无类型的,若将无类型常量声明为变量或者赋值给变量,则会隐式转换成该变量的类型。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var f float64 = 212
fmt.Println((f - 32) * 5 / 9) // 100
fmt.Println(5 / 9 * (f - 32)) // 0
fmt.Println(5.0 / 9.0 * (f - 32)) // 100
}Go中只有大小不明确的 int 类型,却没有大小不明确的 float 和 complex 类型。
复合数据类型
数组
数组是拥有相同数据类型元素的固定长度序列,因其长度固定,Go中很少直接使用。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var a [3]int // [0 0 0]
var q [3]int = [3]int{1, 2, 3} // [1 2 3]
var r [3]int = [3]int{1, 2} // [1 2 0]
fmt.Println(a, q, r)
}
数组字面量中,... 如果出现在数组长度的位置,那么数组长度由其初始长度决定,数组的长度必须是常量表达式,因此 [3]int 和 [4]int 是不同的数组类型。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
q := [...]int{1, 2, 3}
fmt.Printf("%T\n", q) // [3]int
q = [4]int{1, 2, 3} // cannot use [4]int{...} (type [4]int) as type [3]int in assignment
}
如果一个数组的元素可比较,那么这个数组也可比较。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := [2]int{1, 2}
b := [...]int{1, 2}
c := [2]int{1, 3}
fmt.Println(a == b, a == c, b == c) // true false false
d := [3]int{1, 2}
fmt.Println(a == d) // invalid operation: a == d (mismatched types [2]int and [3]int)
}package main
import (
"crypto/sha256"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
c1 := sha256.Sum256([]byte("x"))
c2 := sha256.Sum256([]byte("X"))
fmt.Printf("%x\n%x\n%t\n%T\n", c1, c2, c1 == c2, c1)
//
//2d711642b726b04401627ca9fbac32f5c8530fb1903cc4db02258717921a4881
//4b68ab3847feda7d6c62c1fbcbeebfa35eab7351ed5e78f4ddadea5df64b8015
//false
//[32]uint8
}
slice
切片可以理解为是可变长度的数组
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
months := [...]string{1: "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June",
"July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"}
Q2 := months[4:7]
summer := months[6:9]
fmt.Println(Q2) // [April May June]
fmt.Println(summer) // [June July August]
endlessSummer := summer[:5] // [June July August September October]
fmt.Println(endlessSummer)
}slice就地修改
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
data := []string{"one", "", "three"}
fmt.Printf("%q\n", nonempty(data)) // ["one" "three"]
fmt.Printf("%q\n", data) // ["one" "three" "three"]
}
func nonempty(strings []string) []string {
i := 0
for _, s := range strings {
if s != "" {
strings[i] = s
i++
}
}
return strings[:i]
}实现堆栈
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
stack := []string{"one", "two", "three"} // ["one" "three" "three"]
fmt.Println(stack)
top := stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
fmt.Println(stack) // [one two]
fmt.Println(top) // three
}
移除元素
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
stack := []int{1, 2, 3, 4}
fmt.Println(remove(stack, 1)) // [1 3 4]
}
func remove(s []int, i int) []int {
copy(s[i:], s[i+1:])
return s[:len(s)-1]
}map
map初始化以前是零值
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func main() {
//ages := map[string]int{"alice": 34, "charlie":31}
var ages map[string]int // map 的零值是 nil
fmt.Println(ages == nil) // true
ages["charlie"] = 31 // panic: assignment to entry in nil map
ages = map[string]int{}
fmt.Println(ages == nil) // false
ages["charlie"] = 31
ages["alice"] = 34
fmt.Println(ages) // map[alice:34 charlie:31]
delete(ages, "alice") // 即使 alice 不存在,delete 操作也不会报错
fmt.Println(ages) // map[charlie:31]
ages["alice"] = 31
for name, age := range ages {
fmt.Printf("%s\t%d\n", name, age)
}
// 排序输出
var names []string = make([]string, 0, len(ages)) // 提前知道names的长度,
for name := range ages {
names = append(names, name)
}
fmt.Println(names) // [charlie alice]
sort.Strings(names)
fmt.Println(names) // [alice charlie]
for _, name := range names {
fmt.Printf("%s\t%d\n", name, ages[name])
}
age, ok := ages["bob"]
if !ok {
fmt.Printf("bob not in ages, get default age %d", age) // bob not in ages, get default age 0
}
}Go读取输入串并处理
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
input := bufio.NewScanner(os.Stdin)
for input.Scan() {
line := input.Text()
fmt.Println("line:", line)
}
}延迟初始化
package main
import "fmt"
var graph = make(map[string]map[string]bool)
func main() {
addEdge("hello", "world")
fmt.Println(graph)
fmt.Println(hasEdge("hello", "world")) // true
fmt.Println(hasEdge("hello", "World")) // false
}
func addEdge(from, to string) {
edges := graph[from]
if edges == nil {
edges = make(map[string]bool)
graph[from] = edges
}
edges[to] = true
}
func hasEdge(from, to string) bool {
return graph[from][to]
}结构体
结构体比较
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
type Employee struct {
ID int
Name string
Address string
DoB time.Time
Position string
Salary int
ManagerID int
}
type Point struct {
X, Y int
}
type address struct {
hostname string
port int
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(Scale(Point{1, 2}, 5)) // {5 10}
p := Point{1, 2}
q := Point{2, 1}
fmt.Println(p.X == q.Y && p.Y == q.X) // true
fmt.Println(p == q) // false
hits := make(map[address]int)
hits[address{"golang.org", 443}]++
fmt.Println(hits) // map[{golang.org 443}:1]
}
func Scale(p Point, factor int) Point {
return Point{p.X * factor, p.Y * factor}
}结构体嵌套和匿名成员
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
type Employee struct {
ID int
Name string
Address string
DoB time.Time
Position string
Salary int
ManagerID int
}
type Point struct {
X, Y int
}
type Circle struct {
Point // 匿名成员
Radius int
}
type Wheel struct {
Circle // 匿名成员
Spokes int
}
func main() {
var w Wheel
w.X = 8 // 等价于w.Circle.Point.X = 8
w.Y = 8 // 匿名成员的名字就是对应类型的名字
w.Radius = 5
w.Spokes = 20
fmt.Println(w) // {{{8 8} 5} 20}
}# 使得 Printf 的格式化符号 %v 以类似 Go 语法的方式输出对象
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
type Employee struct {
ID int
Name string
Address string
DoB time.Time
Position string
Salary int
ManagerID int
}
type Point struct {
X, Y int
}
type Circle struct {
Point // 匿名成员
Radius int
}
type Wheel struct {
Circle // 匿名成员
Spokes int
}
func main() {
var w Wheel
//w = Wheel{Circle{Point{8, 8}, 5}, 20}
w = Wheel{
Circle: Circle{
Point: Point{
X: 8,
Y: 8,
},
Radius: 5,
},
Spokes: 20,
}
// main.Wheel{Circle:main.Circle{Point:main.Point{X:8, Y:8}, Radius:5}, Spokes:20}
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", w) // # 使得 Printf 的格式化符号 %v 以类似 Go 语法的方式输出对象
}
JSON
marshal
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
)
type Movie struct {
Title string
Year int `json:"released"`
Color bool `json:"color,omitempty"` // omitempty 表示如果这个成员的值为空或零值,则不输出成员到 json
Actors []string
}
func main() {
var movies = []Movie{
{
Title: "Casablanca",
Year: 1942,
Color: false,
Actors: []string{"Humphrey Bogart", "Ingrid Bergman"},
},
{
Title: "Cool Hand Luke",
Year: 1967,
Color: true,
Actors: []string{"Paul Newman"},
},
{
Title: "Bullitt",
Year: 1968,
Color: true,
Actors: []string{"Steve McQueen", "Jacqueline Bisset"},
},
}
fmt.Println(movies) // [{Casablanca 1942 false [Humphrey Bogart Ingrid Bergman]} {Cool Hand Luke 1967 true [Paul Newman]} {Bullitt 1968 true [Steve McQueen Jacqueline Bisset]}]
//data, err := json.Marshal(movies) // [{"Title":"Casablanca","released":1942,"Actors":["Humphrey Bogart","Ingrid Bergman"]},{"Title":"Cool Hand Luke","released":1967,"color":true,"Actors":["Paul Newman"]},{"Title":"Bullitt","released":1968,"color":true,"Actors":["Steve McQueen","Jacqueline Bisset"]}]
data, err := json.MarshalIndent(movies, "", " ") // 比 json.Marshal 多了两个参数,一个前缀字符串和缩进字符串
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("JSON marshaling failed: %s", err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s\n", data)
//[
// {
// "Title": "Casablanca",
// "released": 1942,
// "Actors": [
// "Humphrey Bogart",
// "Ingrid Bergman"
// ]
// },
// {
// "Title": "Cool Hand Luke",
// "released": 1967,
// "color": true,
// "Actors": [
// "Paul Newman"
// ]
// },
// {
// "Title": "Bullitt",
// "released": 1968,
// "color": true,
// "Actors": [
// "Steve McQueen",
// "Jacqueline Bisset"
// ]
// }
//]
}
unmarshal
通过合理定义数据结构,我们可以选择将哪部分 JSON 数据解码到结构体对象中,如下,就将 JSON 中 Title 和 Year 的其他字段丢弃了。
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
)
type Movie struct {
Title string
Year int `json:"released"` // Year 对应到 json 的 released
Color bool `json:"color,omitempty"` // omitempty 表示如果这个成员的值为空或零值,则不输出成员到 json
Actors []string
}
func main() {
var movies = []Movie{
{
Title: "Casablanca",
Year: 1942,
Color: false,
Actors: []string{"Humphrey Bogart", "Ingrid Bergman"},
},
{
Title: "Cool Hand Luke",
Year: 1967,
Color: true,
Actors: []string{"Paul Newman"},
},
{
Title: "Bullitt",
Year: 1968,
Color: true,
Actors: []string{"Steve McQueen", "Jacqueline Bisset"},
},
}
data, err := json.MarshalIndent(movies, "", " ") // 比 json.Marshal 多了两个参数,一个前缀字符串和缩进字符串
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("JSON marshaling failed: %s", err)
}
var titles []struct {
Title string
Year int `json:"released"`
}
if err := json.Unmarshal(data, &titles); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("JSON unmarshaling failed: %s", err)
}
fmt.Println(titles) // [{Casablanca 1942} {Cool Hand Luke 1967} {Bullitt 1968}]
}
即使JSON的首字母不是大写,结构体成员的名称也必须首字母大写。
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"net/url"
"os"
"strings"
"time"
)
const IssuesURL = "https://api.github.com/search/issues"
type IssuesSearchResult struct {
TotalCount int `json:"total_count"`
Items []*Issues
}
type Issues struct {
Number int
HTMLURL string `json:"html_url"`
Title string
State string
User *User
CreatedAt time.Time `json:"created_at"`
Body string
}
type User struct {
Login string
HTMLURL string `json:"html_url"`
}
func SearchIssues(terms []string) (*IssuesSearchResult, error) {
q := url.QueryEscape(strings.Join(terms, " "))
resp, err := http.Get(IssuesURL + "?q=" + q)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
resp.Body.Close()
return nil, fmt.Errorf("search query failed: %s", resp.Status)
}
var result IssuesSearchResult
if err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil {
resp.Body.Close()
return nil, err
}
resp.Body.Close()
return &result, nil
}
func main() {
result, err := SearchIssues(os.Args[:1])
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%d issues:\n", result.TotalCount)
for _, item := range result.Items {
fmt.Printf("#%-5d %9.9s %.55s\n", item.Number, item.User.Login, item.Title)
}
}文本和HTML模板
package main
import (
"html/template"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
const templ = `A: {{.A}}
B: {{.B}}
`
t := template.Must(template.New("escape").Parse(templ))
var data struct {
A string
B template.HTML
}
data.A = "Hello!"
data.B = "Hello!"
if err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data); err != nil { // A: <b>Hello!</b>
B: Hello!
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
函数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(hypot(3, 4))
fmt.Printf("%T\n", hypot) // func(float64, float64) float64
}
func hypot(x, y float64) (z float64) { // 返回列表有变量时,需要括号括起来
z = math.Sqrt(x*x + y*y)
return
}函数如果有命名的返回值,可以省略return 语句的操作数,也称为裸返回。也即将每个命名返回结果按照顺序返回的快捷方法。
错误处理策略
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
//log.SetPrefix("wait: ") // 可以自定义错误前缀
//log.SetFlags(0)
url := "xxx"
if err := WaitForServer(url); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Site is down: %v\n", err) // 会将时间和日期作为前缀添加到错误消息前
//fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Site is down: %v\n", err)
//os.Exit(1)
}
//2023/06/13 18:45:31 server not responding (Head "xxx": unsupported protocol scheme ""); retrying...
//2023/06/13 18:45:32 server not responding (Head "xxx": unsupported protocol scheme ""); retrying...
//2023/06/13 18:45:34 server not responding (Head "xxx": unsupported protocol scheme ""); retrying...
//2023/06/13 18:45:38 server not responding (Head "xxx": unsupported protocol scheme ""); retrying...
//2023/06/13 18:45:46 server not responding (Head "xxx": unsupported protocol scheme ""); retrying...
//2023/06/13 18:46:02 server not responding (Head "xxx": unsupported protocol scheme ""); retrying...
//2023/06/13 18:49:17 Site is down: server xxx failed to respond after 1m0s
}
func WaitForServer(url string) error {
const timeout = 30 * time.Second
deadline := time.Now().Add(timeout)
for tries := 0; time.Now().Before(deadline); tries++ { // 截止日期之前,指数时间间隔重试
_, err := http.Head(url)
if err == nil {
return nil
}
log.Printf("server not responding (%s); retrying...", err)
time.Sleep(time.Second << uint(tries)) // 指数退避政策
}
return fmt.Errorf("server %s failed to respond after %s", url, timeout)
}Go的错误处理规律,先进行错误检查,成功的逻辑(实际的函数体)在外层作用域。
文件结束标识符
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
in := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
for {
r, _, err := in.ReadRune()
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("read failed: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println(r)
}
}
函数变量
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
f := square
fmt.Printf("%T\n", f)
f = negative
fmt.Printf("%T\n", f)
//f = product // cannot use product (type func(int, int) int) as type func(int) int in assignment
var t func(int) int
fmt.Println(t == nil) // true。函数类型的零值(空函数)是 nil
// strings.Map 对 字符串的每个字符都调用 func
fmt.Println(strings.Map(add1, "HAL9000")) // IBM:111
fmt.Println(strings.Map(add1, "VMS")) // WNT
fmt.Println(strings.Map(add1, "Admin")) // Benjo
fmt.Printf("%*s\n", 4, "he")
}
func add1(r rune) rune {
return r + 1
}
func square(n int) int {
return n * n
}
func negative(n int) int {
return -n
}
func product(m, n int) int {
return m * n
}
匿名函数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// strings.Map 对 字符串的每个字符都调用 func
fmt.Println(strings.Map(func(r rune) rune {return r + 1 }, "HAL9000")) // IBM:111 匿名函数
f := squares()
fmt.Println(f()) // 1
fmt.Println(f()) // 4
fmt.Println(f()) // 9
fmt.Println(squares()()) // 1
fmt.Println(squares()()) // 1
fmt.Println(squares()()) // 1
}
func squares() func() int {
var i int
return func() int { // 里层匿名函数可以获取并更新外层函数的局部变量,因此函数是引用类型,且无法进行比较
i++ // 变量的生命周期不是由它的作用域决定的,x 隐藏在函数变量 f 中
return i * i
}
}匿名函数进行递归调用时,必须先声明变量,再将匿名函数赋值给这个变量。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
var prereqs = map[string][]string{
"algorithms": {"data structures"},
"calculus": {"linear algebra"},
"compilers": {
"data structures",
"formal languages",
"computer organization",
},
"data structures": {"discrete math"},
"databases": {"data structures"},
"discrete math": {"intro to programming"},
"networks": {"operating systems"},
"operating systems": {"data structures", "computer organization"},
"programming languages": {"data structures", "computer organization"},
}
func main() {
for _, item := range topoSort(prereqs){
fmt.Println(item)
}
}
func topoSort(m map[string][]string) []string {
var order []string
seen := make(map[string]bool)
var visitAll func(items []string) // 内部声明匿名函数
visitAll = func(items []string) {
for _, item := range items {
if !seen[item] {
seen[item] = true
visitAll(m[item]) // 递归调用, 优先学习先行课
order = append(order, item) // 将 item 的先行课学完以后,再学当前这门课程
}
}
}
var keys []string
for key := range m {
keys = append(keys, key)
}
sort.Strings(keys)
visitAll(keys)
fmt.Println(seen)
return order
}变长函数
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(sum()) // 0
fmt.Println(sum(3)) // 3
fmt.Println(sum(1, 2, 3, 4)) // 10
values := []int{1, 2, 3, 4}
fmt.Println(sum(values...)) // 10
fmt.Printf("%T\n", f) // func([]int)
fmt.Printf("%T\n", g) // func(...int) int
}
func f([]int) {}
func g(...int) {}
func sum(vals ...int) int {
total := 0
for _, val := range vals {
total += val
}
return total
}延迟函数调用
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"time"
)
func main() {
bigSlowOperation() // defer 会把最外一层函数放到最后调用
//2023/06/15 21:59:16 enter bigSlowOperation
//2023/06/15 21:59:26 exit bigSlowOperation (10.0080289s)
double(4) // double(4) = 8
}
func bigSlowOperation() {
defer trace("bigSlowOperation")()
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
}
func trace(msg string) func() {
start := time.Now()
log.Printf("enter %s", msg)
return func() {
log.Printf("exit %s (%s)", msg, time.Since(start))
}
}
func double(x int) (result int) {
defer func() {fmt.Printf("double(%d) = %d\n", x, result)}() //
return x + x
}宕机
发生宕机时,所有的延迟函数以倒序执行。
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
f(3)
//f(3)
//f(2)
//f(1)
//defer 1
//defer 2
//defer 3
}
func f(x int) {
fmt.Printf("f(%d)\n", x+0/x)
defer fmt.Printf("defer %d\n", x)
f(x -1)
}Go的宕机机制让延迟执行的函数在栈清理之前调用。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"runtime"
)
func main() {
defer printStack()
f(3)
}
func printStack() {
var buf[4096]byte
n := runtime.Stack(buf[:], false)
os.Stdout.Write(buf[:n]) // 将堆栈信息写入到标准输出
}
func f(x int) {
fmt.Printf("f(%d)\n", x+0/x)
defer fmt.Printf("defer %d\n", x)
f(x -1)
}方法
方法的声明
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
type Point struct{ X, Y float64 }
// 普通函数
func Distance(p, q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(q.X-p.X, q.Y-p.Y)
}
// 方法, p 称为方法的接收者,由于其会频繁使用,最好简短且始终保持一致
func (p Point) Distance(q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(q.X-p.X, q.Y-p.Y)
}
func main() {
p := Point{1, 2}
q := Point{4, 6}
fmt.Println(Distance(p, q)) // 5
fmt.Println(p.Distance(q)) // 5
}每一个类型有他自己命名空间,编译器会根据方法名和接受者类型来决定调用哪一个方法。相同类型拥有的方法名必须唯一,不同类型可以使用相同的方法名。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
type Point struct{ X, Y float64 }
type Path []Point
// 普通函数
func Distance(p, q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(q.X-p.X, q.Y-p.Y)
}
// 方法, p 称为方法的接收者,由于其会频繁使用,最好简短且始终保持一致
func (p Point) Distance(q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(q.X-p.X, q.Y-p.Y)
}
// 方法,针对 Point 数组的 Distance 方法
func (path Path) Distance() float64 {
sum := 0.0
for i := range path{
if i > 0 {
sum += path[i-1].Distance(path[i])
}
}
return sum
}
func main() {
p := Point{1, 2}
q := Point{4, 6}
fmt.Println(Distance(p, q)) // 5
fmt.Println(p.Distance(q)) // 5
perim := Path{
{1, 1},
{5, 1},
{5, 4},
{1, 1},
}
fmt.Println(perim.Distance()) // 12
}
指针接受者的方法
习惯上,如果Point的任何一个方法使用指针接收者,那么所有的 Point 方法都应该使用指针接受者。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
type Point struct{ X, Y float64 }
func (p *Point) ScaleBy(factor float64) {
p.X *= factor
p.Y *= factor
}
// 方法, p 称为方法的接收者,由于其会频繁使用,最好简短且始终保持一致
func (p Point) Distance(q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(q.X-p.X, q.Y-p.Y)
}
func main() {
p := &Point{1, 2}
p.ScaleBy(2)
fmt.Println(*p) // {2 4}
q := Point{1, 2}
qptr := &q
qptr.ScaleBy(3)
fmt.Println(q) // {3 6}
fmt.Println(qptr.Distance(q)) // 0 ,编译器隐式解引用接收者,获取实际地址。
r := Point{1, 2}
(&r).ScaleBy(4)
fmt.Println(r) // {4 8}
//Point{1, 2}.ScaleBy(5) // 编译错误,不能获取字面量的地址
fmt.Println(Point{1, 2}.Distance(q))
}
nil是合法的接受者
package main
import "fmt"
// *IntList的类型nil代表空列表
type IntList struct {
Value int
Tail *IntList
}
func (list *IntList) Sum() int {
if list == nil {
return 0
}
return list.Value + list.Tail.Sum()
}
func main() {
a := IntList{
Value: 1,
Tail: &IntList{
Value: 2,
Tail: &IntList{
Value: 3,
Tail: &IntList{
Value: 4,
Tail: nil,
},
},
},
}
fmt.Println((&a).Sum()) // 10
}package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/url"
)
func main() {
m := url.Values{"lang": {"en"}}
m.Add("item", "1")
m.Add("item", "2")
fmt.Println(m.Get("item"))
m = nil
fmt.Println(m.Get("item"))
m.Add("item", "3") // 宕机
}
结构体内嵌组成类型
package main
import (
"fmt"
"image/color"
"math"
)
type Point struct {
X, Y float64
}
type ColoredPoint struct {
Point
Color color.RGBA
}
func (p Point) Distance(q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(p.X-q.X, p.Y-q.Y)
}
func main() {
var cp ColoredPoint
cp.X = 1
fmt.Println(cp.Point.X) // 1
cp.Point.Y = 2
fmt.Println(cp.Y) // 2
red := color.RGBA{255, 0, 0, 255}
blue := color.RGBA{0, 0, 255, 255}
p := ColoredPoint{Point{1, 2}, red}
q := ColoredPoint{Point{4, 6}, blue}
// Point 实现了 Distance 方法,Point 作为内嵌结构体,所以 ColoredPoint 也可以调用这个方法
fmt.Println(p.Distance(q)) // 报错
fmt.Println(p.Distance(q.Point)) // 5
fmt.Println(p.Point.Distance(q.Point)) // 5
q.Point = p.Point
fmt.Println(p, q) // {{1 2} {255 0 0 255}} {{1 2} {0 0 255 255}}
}结构体可以声明多个匿名字段,这个类型的值可以拥有 Point 所有方法和 RGBA 所有方法,以及任何其他在 ColoredPoint 类型中声明的方法。
type ColoredPoint struct {
Point
color.RGBA
}package main
import "sync"
// 将两个相关变量放到了一个包级别的变量中
var cache = struct {
sync.Mutex
mapping map[string]string
}{mapping: make(map[string]string),}
func Lookup(key string) string {
cache.Lock()
v := cache.mapping[key]
cache.Unlock()
return v
}方法变量与表达式
和调用普通函数不同,调用方法必须提供接受者。方法表达式写成T.f,其中 T 是类型,把原来的方法接收者替换成函数的第一个形参,且可以像平常的函数一样调用。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
type Point struct {
X, Y float64
}
func (p Point) Distance(q Point) float64 {
return math.Hypot(p.X-q.X, p.Y-q.Y)
}
func (p *Point) scaleBy(factor float64) {
p.X *= factor
p.Y *= factor
}
func main() {
p := Point{1, 2}
q := Point{4, 6}
distance := Point.Distance
fmt.Println(distance(p, q)) // 5
fmt.Printf("%T\n", distance) // func(main.Point, main.Point) float64
scale := (*Point).scaleBy
scale(&p, 2)
fmt.Println(p) // {2 4}
fmt.Printf("%T\n", scale) // func(*main.Point, float64)
}通过方法向量对点集合进行位移操作
package main
import "fmt"
type Point struct {
X, Y float64
}
func (p Point) Add(q Point) Point {
return Point{p.X + q.X, p.Y + q.Y}
}
func (p Point) Sub(q Point) Point {
return Point{p.X - q.X, p.Y - q.Y}
}
type Path []Point
func (path Path) TranslateBy(offset Point, add bool) Path {
var op func(p, q Point) Point
if add {
op = Point.Add
} else {
op = Point.Sub
}
for i := range path {
path[i] = op(path[i], offset)
}
return path
}
func main() {
p := Point{1, 2}
q := Point{4, 6}
r := Point{1, 1}
translate := Path.TranslateBy
path := translate([]Point{p, q}, r, true) // [{2 3} {5 7}]
fmt.Println(path)
path = translate([]Point{p, q}, r, false) // [{0 1} {3 5}]
fmt.Println(path)
}封装
package main
import "fmt"
type Counter struct {
n int
}
func (c *Counter) N() int {
return c.n
}
func (c *Counter) Incr() {
c.n++
}
func (c *Counter) Reset() {
c.n = 0
}
func main() {
a := &Counter{5}
fmt.Println(a.N()) // 5
a.Incr()
fmt.Println(a.N()) // 6
a.Reset()
fmt.Println(a.N()) // 0
a.n = 7
fmt.Println(a.N()) // 7
}
接口
接口类型
一个接口类型定义了一套方法,如果一个具体类型要实现该接口,则必须实现接口类型定义的所有方法。
空接口对实现类型没有任何要求,可以把任何值赋值给接口类型。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var any interface{}
any = true
fmt.Println(any) // true
any = 12.34
fmt.Println(any) // 12.34
any = "hello"
fmt.Println(any) // hello
}
实现接口
如果一个类型实现了接口的所有方法,那么这个类型实现了这个接口。
接口值
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
)
func main() {
var w io.Writer
fmt.Printf("%T\n", w) //
w = os.Stdout
fmt.Printf("%T\n", w) // *os.File
w = new(bytes.Buffer)
fmt.Printf("%T\n", w) // *bytes.Buffer
}
当main调用f时,他把一个类型为 *bytes.Buffer 的空指针给了 out 参数,所以 out 的动态值确实是 空,但是他的动态类型是 *bytes.Buffer(也即值为nil,但是类型不为 nil),所以 out 是包含空指针的非空接口,防御性检查 out != nil 仍然为 true。
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"io"
)
func main() {
var buf *bytes.Buffer
var debug bool
debug = false
if debug {
buf = new(bytes.Buffer)
}
f(buf)
if debug {
fmt.Println(buf)
}
}
func f(out io.Writer) {
if out != nil {
out.Write([]byte("done!\n")) // panic: runtime error: invalid memory address or nil pointer dereference
}
}sort.Interface
按照艺术家进行排序和逆排序输出
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"sort"
"text/tabwriter"
"time"
)
type Track struct {
Title string
Artist string
Album string
Year int
Length time.Duration
}
func length(s string) time.Duration {
d, err := time.ParseDuration(s)
if err != nil {
panic(s)
}
return d
}
var tracks = []*Track{
{"Go", "Delilah", "From the Roots Up", 2012, length("3m38s")},
{"Go", "Moby", "Moby", 1992, length("3m37s")},
{"Go Ahead", "Alicia Keys", "As I Am", 2007, length("4m36s")},
{"Ready to Go", "Martin Solveig", "Smash", 2011, length("4m24s")},
}
func printTracks(tracks []*Track) {
const format = "%v\t%v\t%v\t%v\t%v\t\n"
tw := new(tabwriter.Writer).Init(os.Stdout, 0, 8, 2, ' ', 0)
fmt.Fprintf(tw, format, "Title", "Artist", "Album", "Year", "Length")
fmt.Fprintf(tw, format, "-----", "------", "-----", "----", "------")
for _, t := range tracks {
fmt.Fprintf(tw, format, t.Title, t.Artist, t.Album, t.Year, t.Length)
}
tw.Flush()
}
type byArtist []*Track
func (x byArtist) Len() int {
return len(x)
}
func (x byArtist) Less(i, j int) bool {
return x[i].Artist < x[j].Artist
}
func (x byArtist) Swap(i, j int) {
x[i], x[j] = x[j], x[i]
}
func main() {
printTracks(tracks)
fmt.Println()
sort.Sort(byArtist(tracks)) // 排序
printTracks(tracks)
fmt.Println()
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(byArtist(tracks))) // 逆排序
printTracks(tracks)
fmt.Println()
}
Title Artist Album Year Length
----- ------ ----- ---- ------
Go Delilah From the Roots Up 2012 3m38s
Go Moby Moby 1992 3m37s
Go Ahead Alicia Keys As I Am 2007 4m36s
Ready to Go Martin Solveig Smash 2011 4m24s
Title Artist Album Year Length
----- ------ ----- ---- ------
Go Ahead Alicia Keys As I Am 2007 4m36s
Go Delilah From the Roots Up 2012 3m38s
Ready to Go Martin Solveig Smash 2011 4m24s
Go Moby Moby 1992 3m37s
Title Artist Album Year Length
----- ------ ----- ---- ------
Go Moby Moby 1992 3m37s
Ready to Go Martin Solveig Smash 2011 4m24s
Go Delilah From the Roots Up 2012 3m38s
Go Ahead Alicia Keys As I Am 2007 4m36s自定义多层比较函数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"sort"
"text/tabwriter"
"time"
)
type Track struct {
Title string
Artist string
Album string
Year int
Length time.Duration
}
func length(s string) time.Duration {
d, err := time.ParseDuration(s)
if err != nil {
panic(s)
}
return d
}
var tracks = []*Track{
{"Go", "Delilah", "From the Roots Up", 2012, length("3m38s")},
{"Go", "Moby", "Moby", 1992, length("3m37s")},
{"Go Ahead", "Alicia Keys", "As I Am", 2007, length("4m36s")},
{"Ready to Go", "Martin Solveig", "Smash", 2011, length("4m24s")},
}
func printTracks(tracks []*Track) {
const format = "%v\t%v\t%v\t%v\t%v\t\n"
tw := new(tabwriter.Writer).Init(os.Stdout, 0, 8, 2, ' ', 0)
fmt.Fprintf(tw, format, "Title", "Artist", "Album", "Year", "Length")
fmt.Fprintf(tw, format, "-----", "------", "-----", "----", "------")
for _, t := range tracks {
fmt.Fprintf(tw, format, t.Title, t.Artist, t.Album, t.Year, t.Length)
}
tw.Flush()
}
type customSort struct {
t []*Track
less func(x, y *Track) bool
}
func (x customSort) Len() int {
return len(x.t)
}
func (x customSort) Less(i, j int) bool {
return x.less(x.t[i], x.t[j])
}
func (x customSort) Swap(i, j int) {
x.t[i], x.t[j] = x.t[j], x.t[i]
}
func main() {
sort.Sort(customSort{tracks, func(x, y *Track) bool {
if x.Title != y.Title {
return x.Title < y.Title
}
if x.Year != y.Year {
return x.Year < y.Year
}
if x.Length != y.Length {
return x.Length < y.Length
}
return false
}})
printTracks(tracks)
}
Title Artist Album Year Length
----- ------ ----- ---- ------
Go Moby Moby 1992 3m37s
Go Delilah From the Roots Up 2012 3m38s
Go Ahead Alicia Keys As I Am 2007 4m36s
Ready to Go Martin Solveig Smash 2011 4m24s package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func main() {
values := []int{3, 1, 4, 1}
fmt.Println(sort.IntsAreSorted(values)) // false
sort.Ints(values)
fmt.Println(values) // [1 1 3 4]
fmt.Println(sort.IntsAreSorted(values)) // true
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(values)))
fmt.Println(values) // [4 3 1 1]
fmt.Println(sort.IntsAreSorted(values)) // false
}
可识别联合体
尽管 sqlQuote 支持任意类型的实参,但仅当实参类型能够符合类型分支中的一个时才能正常运行到结束,其他类型会抛错,表面上x的类型是 interface{},实际上我们把他当作 int, uint, bool, string 和 nil 的一个可识别联合体。
package main
import "fmt"
func sqlQuote(x interface{}) string {
switch x := x.(type) {
case nil:
return "NULL"
case int, uint:
return fmt.Sprintf("%d", x)
case bool:
if x {
return "TRUe"
}
case string:
return sqlQuote(x)
default:
panic(fmt.Sprintf("unexpected type %T: %v", x, x))
}
return ""
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(sqlQuote(nil))
}基于标记的 XML 解析
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"strings"
)
import "encoding/xml"
func containsAll(x, y []string) bool {
for len(y) <= len(x) {
if len(y) == 0 {
return true
}
if x[0] == y[0] {
y = y[1:]
}
x = x[1:]
}
return false
}
func main() {
dec := xml.NewDecoder(os.Stdin)
var stack []string
for {
tok, err := dec.Token()
if err == io.EOF {
break
}else if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "xmlselect:%v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
switch tok := tok.(type) {
case xml.StartElement:
stack = append(stack, tok.Name.Local)
case xml.EndElement:
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
case xml.CharData:
if containsAll(stack, os.Args[1:]) {
fmt.Printf("%s: %s\n", strings.Join(stack, " "), tok)
}
}
}
}
goroutine和通道
goroutine
main函数返回时,所有的goroutine都暴力直接终结,然后程序退出。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
go spinner(100 * time.Millisecond)
const n = 45
fibN := fib(n)
fmt.Printf("\rFibonacci(%d) = %d\n", n, fibN) // Fibonacci(45) = 1134903170
}
func spinner(delay time.Duration) {
for {
for _, r := range `-\|/` {
fmt.Printf("\r%c", r)
time.Sleep(delay)
}
}
}
func fib(x int) int {
if x < 2 {
return x
}
return fib(x-1) + fib(x-2)
}
并发时钟服务器
server
package main
import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
"time"
)
func main() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Print(err)
continue
}
handleConn(conn)
}
}
func handleConn(c net.Conn) {
defer c.Close()
for {
_, err := io.WriteString(c, time.Now().Format("15:04:05\n"))
if err != nil {
return
}
time.Sleep(1*time.Second)
}
}client
client从server 读取,然后写入到标准输出
package main
import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
"os"
)
func main() {
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
mustCopy(os.Stdout, conn)
}
func mustCopy(dst io.Writer, src io.Reader) {
if _, err := io.Copy(dst, src); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}若有多个客户端进行请求,则第二个客户端必须等第一个客户端结束才能正常工作,可以使用 goroutine 并发处理请求。
package main
import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
"time"
)
func main() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Print(err)
continue
}
go handleConn(conn) // 并发处理连接
}
}
func handleConn(c net.Conn) {
defer c.Close()
for {
_, err := io.WriteString(c, time.Now().Format("15:04:05\n"))
if err != nil {
return
}
time.Sleep(1*time.Second)
}
}并发回声服务器
server
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"strings"
"time"
)
func main() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Print(err)
continue
}
go handleConn(conn) // 并发处理连接
}
}
func handleConn(c net.Conn) {
input := bufio.NewScanner(c)
for input.Scan() {
go echo(c, input.Text(), 1*time.Second) // 并发处理同一个连接的多个呼叫
}
c.Close()
}
func echo(c net.Conn, shout string, delay time.Duration) {
fmt.Fprintln(c, "\t", strings.ToUpper(shout)) // 将呼叫转换后回写给客户端
time.Sleep(delay)
fmt.Fprintln(c, "\t", shout)
time.Sleep(delay)
fmt.Fprintln(c, "\t", strings.ToLower(shout))
}client
package main
import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
"os"
)
func main() {
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
go mustCopy(os.Stdout, conn) // 并发将服务器的回声写到标准输出
mustCopy(conn, os.Stdin) // 通过标准输入进行呼叫
}
func mustCopy(dst io.Writer, src io.Reader) {
if _, err := io.Copy(dst, src); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}Hello
HELLO
Hello
hello通道
ch <- x // 发送语句
x = <-ch // 接收赋值
<-ch // 丢弃赋值可以使用内置的 close 来关闭通道
无缓冲通道
无缓冲通道也称为同步通道,发送操作会阻塞,直到另一个 goroutine 在对应通道执行接收操作。
管道
结束时,只有在通知接收方 goroutine所有数据都已发送完毕时才需要关闭管道。关闭 naturals 通道导致计算平方的循环快速运转,并将 0 传递给 printer
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
naturals := make(chan int)
squares := make(chan int)
// counter
go func() {
for x := 0; x < 10; x++ {
naturals <- x
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
close(naturals)
}()
// squarer
go func() {
for {
x, ok := <-naturals
if !ok {
break // 通道关闭且读完
}
squares <- x * x
}
close(squares)
}()
// printer
for {
fmt.Println(<-squares)
}
}
单向通道
双向通道可以隐式转换成单向通道,比如 可以把 chan int 转换成输入通道 chan<- int 或者输出通道 <-chan int
package main
import "fmt"
// chan<- 发送(输入)管道,只允许往管道发送,不允许从管道接收
// <-chan 接收(输出)管道,只允许从管道接收,不允许从管道发送
func counter(out chan<- int) {
for x := 0; x <= 10; x++ {
out <- x
}
close(out)
}
func squarer(out chan<- int, in <-chan int) {
for v := range in {
out <- v * v
}
close(out)
}
func printer(in <-chan int) {
for v := range in {
fmt.Println(v)
}
}
func main() {
naturals := make(chan int)
squares := make(chan int)
go counter(naturals)
go squarer(squares, naturals)
printer(squares)
}
缓冲通道
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
ch := make(chan string, 3)
ch <- "A"
ch <- "B"
ch <- "C"
//ch <- "D" // 超过缓冲长度,阻塞
fmt.Println(<-ch) // A
fmt.Println(cap(ch)) // 缓冲区长度 3
fmt.Println(len(ch)) // 通道元素的长度 2
fmt.Println(<-ch) // B
ch <- "D"
ch <- "E"
}
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(mirroredQuery())
}
func mirroredQuery() string {
responses := make(chan string, 3)
go func() { responses <- request("asia.gopl.io") }()
go func() { responses <- request("europe.gopl.io") }()
go func() { responses <- request("americas.gopl.io") }()
return <-responses
}
func request(hostname string) (response string) {
return hostname
}
select多路复用
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
ch := make(chan int, 1)
// 偶数只能往通道写,奇数只能从通道读取
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
fmt.Println("index", i)
select {
case x := <-ch:
fmt.Println(x) // 0 2 4 6 8
case ch <- i:
}
}
//index 0
//index 1
//0
//index 2
//index 3
//2
//index 4
//index 5
//4
//index 6
//index 7
//6
//index 8
//index 9
//8
}select 的默认情况,用来指定没有其它通信时可以立即执行的操作(如果没有 default,有没有其它通信,接收操作将被阻塞)。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"time"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Commencing countdown.")
tick := time.Tick(time.Second)
abort := make(chan struct{})
go func() {
os.Stdin.Read(make([]byte, 1))
abort <- struct{}{}
}()
for countdown := 10; countdown > 0; countdown-- {
fmt.Println(countdown)
select {
case <-tick:
case <-abort:
fmt.Println("Launch aborted!")
return
default:
// nothing to do
}
}
print("Launch starting...")
}并发目录遍历
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
func main() {
roots := []string{"."}
fileSizes := make(chan int64)
go func() {
for _, root := range roots {
walkDir(root, fileSizes)
}
close(fileSizes)
}()
var nfiles, nbytes int64
for size := range fileSizes {
nfiles++
nbytes += size
}
fmt.Printf("%d files %.1f KB\n", nfiles, float64(nbytes)/1e6)
}
func walkDir(dir string, fileSizes chan<- int64) {
for _, entry := range dirents(dir) {
if entry.IsDir() {
subdir := filepath.Join(dir, entry.Name())
walkDir(subdir, fileSizes)
} else {
fileSizes <- entry.Size()
}
}
}
func dirents(dir string) []os.FileInfo {
entries, err := ioutil.ReadDir(dir)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "du1: %v\n", err)
return nil
}
return entries
}
聊天服务器
server
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
)
type client chan<- string
var (
entering = make(chan client)
leaving = make(chan client)
messages = make(chan string)
)
func main() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
go broadcaster()
for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Print(err)
continue
}
go handleConn(conn)
}
}
func broadcaster() {
clients := make(map[client]bool)
for {
select {
case msg := <-messages:
for cli := range clients {
cli <- msg
}
case cli := <-entering:
clients[cli] = true
case cli := <-leaving:
delete(clients, cli)
close(cli)
}
}
}
func handleConn(conn net.Conn) {
ch := make(chan string)
go clientWriter(conn, ch)
who := conn.RemoteAddr().String()
ch <- "You are " + who
messages <- who + " has arrived"
entering <- ch
input := bufio.NewScanner(conn)
for input.Scan() {
messages <- who + ": " + input.Text()
}
leaving <- ch
messages <- who + " has left"
conn.Close()
}
func clientWriter(conn net.Conn, ch <-chan string) {
for msg := range ch {
fmt.Fprintln(conn, msg)
}
}
cli1、cli2、cli3...
package main
import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
"os"
)
func main() {
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", "localhost:8000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
mustCopy(os.Stdout, conn) // 将服务端的消息打印到标准输出
}
func mustCopy(dst io.Writer, src io.Reader) {
if _, err := io.Copy(dst, src); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}You are 127.0.0.1:51853
127.0.0.1:51855 has arrived
127.0.0.1:51855 has left使用共享变量实现并发
互斥锁
使用容量为1的通道来实现计数信号量
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
var (
sema = make(chan struct{}, 1)
balance int
)
func Deposit(wg *sync.WaitGroup, amount int) {
defer wg.Done()
sema <- struct{}{} // 因为容量为1,若有其他 goroutine 进行写操作,将被阻塞
balance += amount
<-sema
}
func Balance() int {
sema <- struct{}{}
b := balance
<-sema
return b
}
func main() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go Deposit(&wg, 5)
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println(Balance()) // 50
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
var (
mu sync.Mutex
balance int
)
func Deposit(amount int) {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
deposit(amount)
}
func deposit(amount int) {
balance += amount
}
func Balance() int {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
return balance
}
func Withdraw(amount int) bool {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
Deposit(-amount)
if balance < 0 {
Deposit(amount)
return false
}
return true
}
func main() {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go Deposit(5)
}
fmt.Println(Balance())
}
读写互斥锁
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
var (
mu sync.Mutex
rmu sync.RWMutex
balance int
)
func Deposit(amount int) {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
deposit(amount)
}
func deposit(amount int) {
balance += amount
}
func Balance() int {
// 共享锁,读取的时候可以同时运行
rmu.RLock()
defer rmu.RUnlock()
return balance
}
func Withdraw(amount int) bool {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
Deposit(-amount)
if balance < 0 {
Deposit(amount)
return false
}
return true
}
func main() {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go Deposit(5)
}
fmt.Println(Balance())
}
内存同步
像通道通信和互斥锁操作的同步原语都会导致处理器把累积的写操作刷回内存并提交。因为赋值和 Print 对应不同的变量,所以编译器会认为这两个语句的执行顺序不会影响结果。这些并发问题可以采用成熟的模式来避免,即尽量把变量限制到单个的 goroutine 中,其他使用互斥锁。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
var x, y int
go func() {
x = 1
fmt.Print("y:", y, " ")
}()
go func() {
y = 1
fmt.Print("x:", x, " ")
}()
// x:1 y:0
// x:0 y:1
// y:0 x:1
// ...
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
延迟初始化
延迟一个昂贵的初始化步骤到实际需要时是一个很好的实践(比如Ruby的单例,调用 .instance 时才实例化一个对象)。
package main
import "image"
var icons map[string]image.Image
func loadIcons() {
icons = map[string]image.Image{
"spades.png": loadIcon("spades.png"),
"hearts.png": loadIcon("heats.png"),
"diamonds.png": loadIcon("diamonds.png"),
"clubs.png": loadIcon("clubs.png"),
}
}
func loadIcon(icon string) image.Image { return nil }
func Icon(name string) image.Image {
if icons == nil {
loadIcons()
}
return icons[name]
}
func main() {
}
因此,一个 goroutine 发现 icons 不是 nil 并不意味着变量的初始化已经完成(有可能才完成内存分配)。
package main
import (
"image"
"sync"
)
var mu sync.RWMutex
var icons map[string]image.Image
func loadIcons() {
icons = map[string]image.Image{
"spades.png": loadIcon("spades.png"),
"hearts.png": loadIcon("heats.png"),
"diamonds.png": loadIcon("diamonds.png"),
"clubs.png": loadIcon("clubs.png"),
}
}
func loadIcon(icon string) image.Image { return nil }
// 并发安全
func Icon(name string) image.Image {
// 为了避免不能并发访问变量,可以使用共享锁改进这个问题
mu.RLock()
if icons != nil {
icon := icons[name]
mu.RUnlock()
return icon
}
mu.RUnlock()
// 获取互斥锁
mu.Lock()
if icons != nil {
loadIcons()
}
icon := icons[name]
mu.Unlock()
return icon
}
func main() {
}
反射
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
t := reflect.TypeOf(3)
fmt.Println(t) // int
fmt.Println(t.String()) // int
fmt.Printf("%T\n", 3) // int
var w io.Writer = os.Stdout
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(w)) // *os.File
fmt.Println("--------")
v := reflect.ValueOf(3)
fmt.Println(v) // 3
x := v.Interface()
fmt.Println(x) // 3
i := x.(int)
fmt.Println(i) // 3
fmt.Printf("%v\n", v) // 3
fmt.Println(v.String()) // ,value 的 String() 方法仅仅暴露了类型
fmt.Println(v.Type()) // int
}
使用 reflect.Value 设置值
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
x := 2
a := reflect.ValueOf(2) // 2
b := reflect.ValueOf(x) // 2
c := reflect.ValueOf(&x) // &x
d := c.Elem() // 2
fmt.Println(a.CanAddr()) // false
fmt.Println(b.CanAddr()) // false
fmt.Println(c.CanAddr()) // false
fmt.Println(d.CanAddr()) // true
px := d.Addr().Interface().(*int)
*px = 3
fmt.Println(x) // 3
d.Set(reflect.ValueOf(4))
fmt.Println(x) // 4
// d.SetString("hello") // panic
var y interface{}
ry := reflect.ValueOf(&y).Elem()
ry.Set(reflect.ValueOf(5))
// ry.SetInt(6) // panic
fmt.Println(y) // 5
stdout := reflect.ValueOf(os.Stdout).Elem()
fmt.Println(stdout.Type()) // os.File
fd := stdout.FieldByName("fd")
fmt.Println(fd.CanAddr(), fd.CanSet()) // false false
}
低级编程
unsafe
package main
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
var x struct {
a bool
b int16
c []int
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(x), unsafe.Alignof(x)) // 32 8
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(x.a), unsafe.Alignof(x.a), unsafe.Offsetof(x.a)) // 1 1 0
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(x.b), unsafe.Alignof(x.b), unsafe.Offsetof(x.b)) // 2 2 2
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(x.c), unsafe.Alignof(x.c), unsafe.Offsetof(x.c)) // 24 8 8
}