## 前言
sparrow-js 提供两个重要提升研发效率的设计:一个是编辑区块,一个是搜索组件,本次主要介绍编辑区块部分的设计思路;采用自问自答的方式说明编辑区块的由来。
## 编辑区块是什么?
特定场景功能的代码片段,通过基础组件和有特定功能的逻辑组件组合而成,可增删改;可生成可读性强的源代码。
## 为什么会有编辑区块?
编辑区块是为sparrow-js的核心目标提效量身定做的,sparrow本身有基本可视化搭建的能力,但是通用的可视化方案提效能力有限,可能只是基础组件的拼接,操作繁杂,输出的代码更侧重UI层面的代码。前端开发由UI部分和逻辑部分组成,UI部分通过基础组件的可视化搭建就可以完成,逻辑部分比如表单上面的删除、编辑、上下线等操作,这些带有特定功能逻辑的代码需找到个介质来承载,编辑区块就是为了承载基础UI和特定逻辑功能的容器。
## 编辑区块是怎样使用的?
先来张图片:
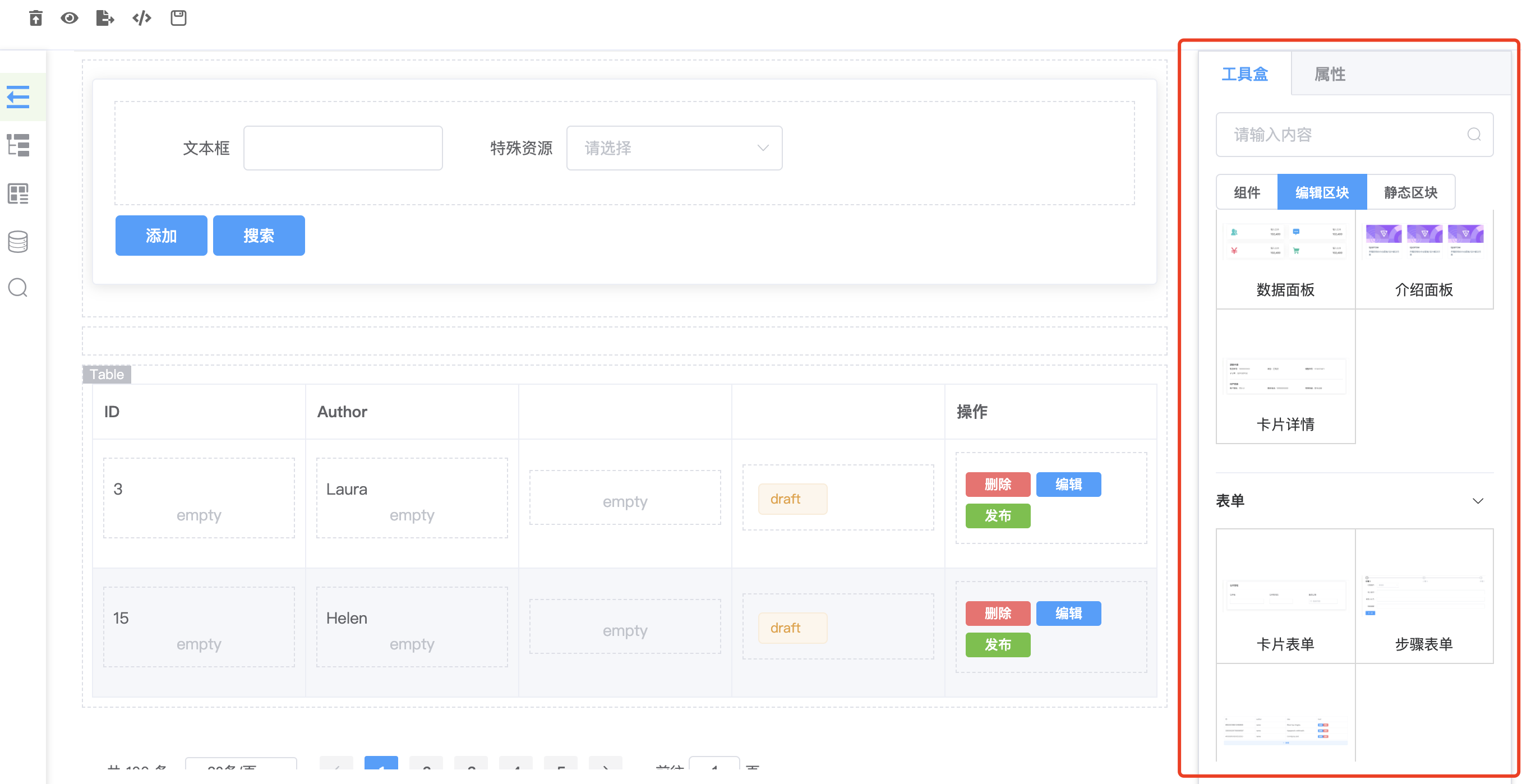
选择界面右边的工具盒-》编辑区块,点击或者拖拽需要的区块即可,点击视图区域即可以配置,删除,新增等操作。
## 编辑区块是怎样制作出来的?
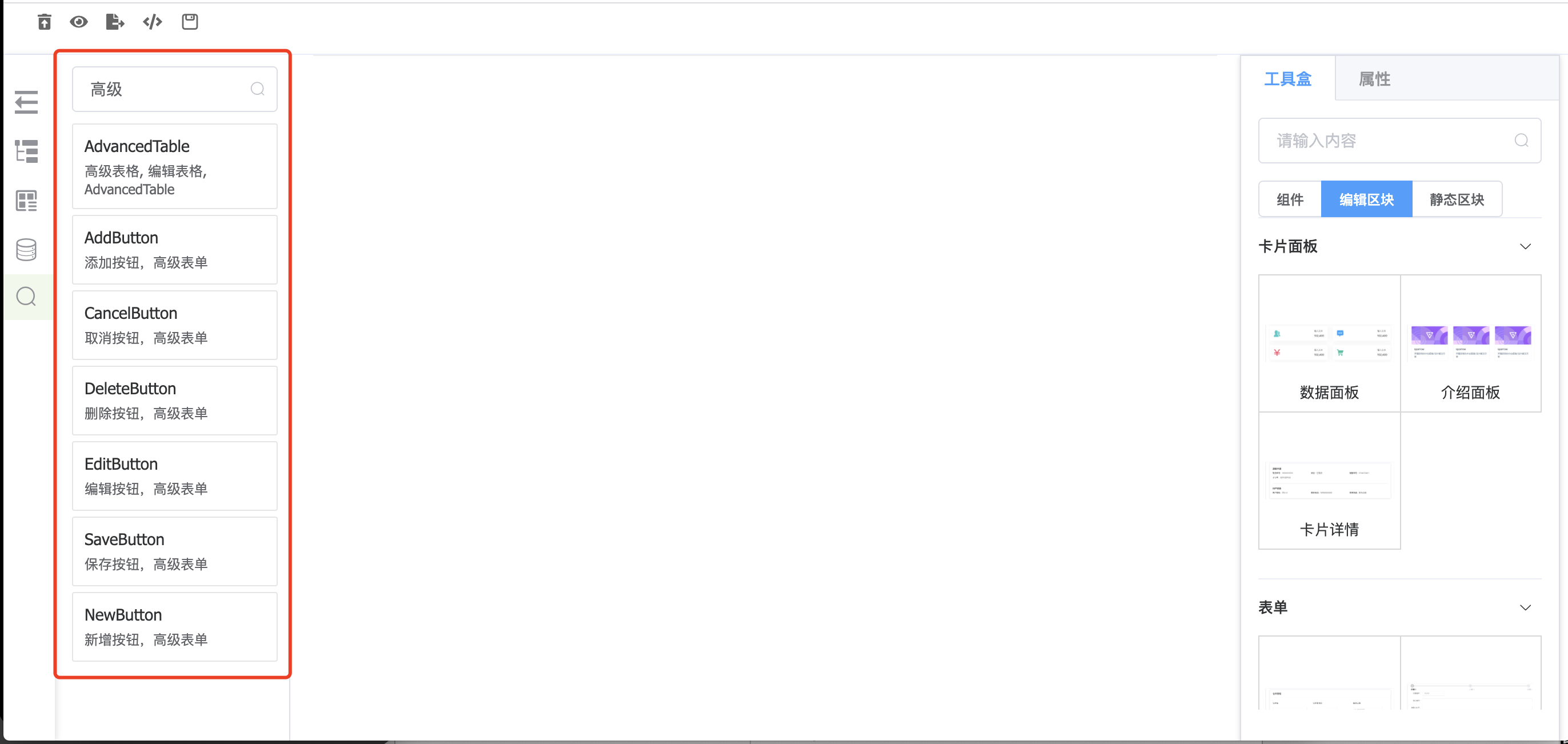
编辑区块,已高级表单为例:
文件结构
```bash
├── AdvancedTable
│ ├── AddButton
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── index.vue
│ ├── CancelButton
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── index.vue
│ ├── DeleteButton
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── index.vue
│ ├── EditButton
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── index.vue
│ ├── NewButton
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── index.vue
│ ├── SaveButton
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── index.vue
│ ├── index.ts
│ └── init.ts
```
1.首先需要先写出完整的静态功能区块,如下简化代码
```bash
```
2. 将1代码拆解成如上目录结构,
如编辑按钮,继承基础按钮,定制化配置,在从vue文件取出方法、数据、引用等内容,为后续组装提供信息。
```bash
// 动态化按钮
export default class EditButton extends Button{
name: string = 'EditButton';
vueParse: any;
constructor (params: any) {
super(params)
this.config.model.custom.label = '编辑';
this.config.model.attr.size = 'mini';
this.config.model.attr.type = 'primary';
this.config.model.attr['@click'] = 'toggle(row.id)';
this.setAttrsToStr();
this.init();
}
private init () {
const fileStr = fsExtra.readFileSync(path.join(Config.templatePath, 'EditBlock/AdvancedTable/EditButton', 'index.vue'), 'utf8');
this.vueParse = new VueParse(this.uuid, fileStr);
}
}
// 按钮VUE 文件,存放逻辑
新增
```
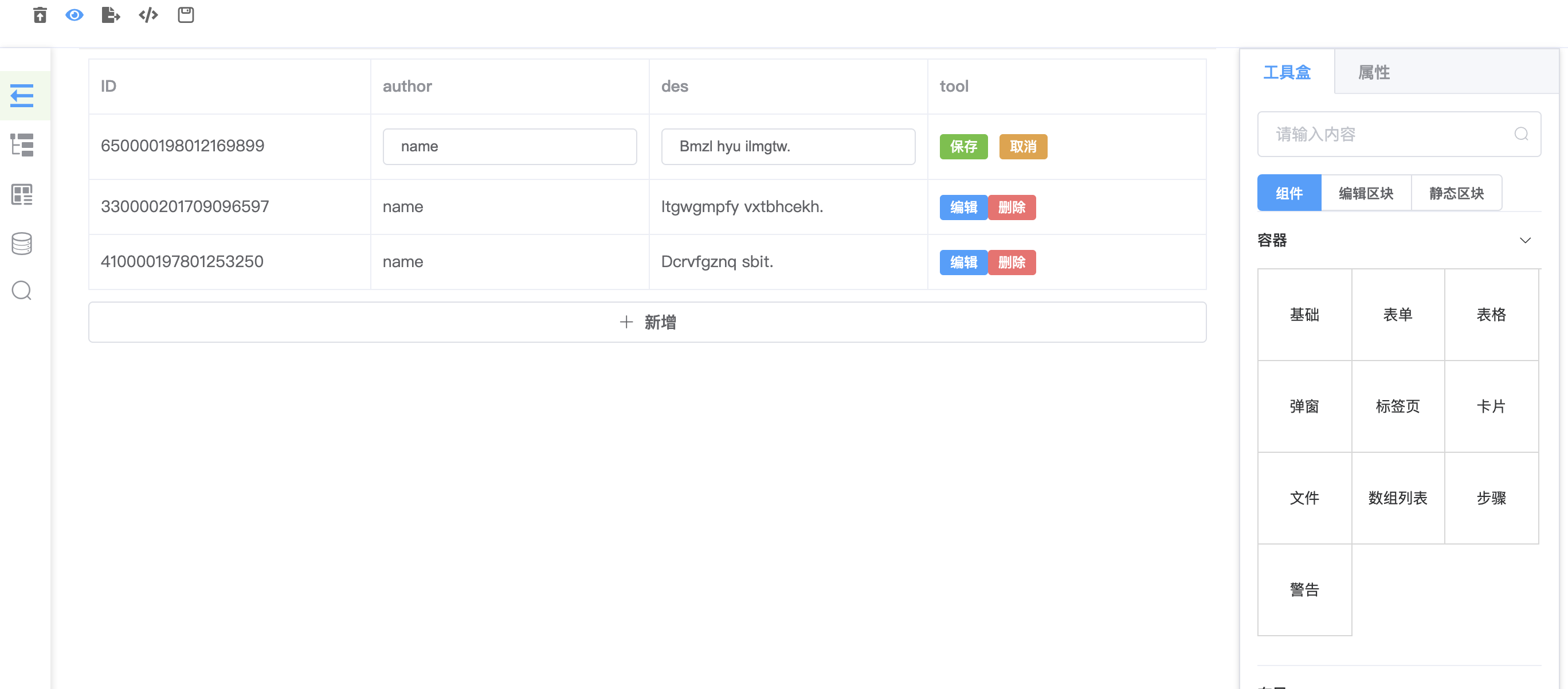
3. 将数据注册到搜索组件,搜索结果如下图:
通过点击、拖拽放到想放的位置即可。
4. 视图区的操作数据传回server
server先生成组件对象树,对2中的template部分、script部分、style部分进行组装,script部分通过babel ast对相应组件进行拆解,最后根据对象树重新组装成想要的代码。拆解代码如下:
```bash
import * as cheerio from 'cheerio';
import * as parser from '@babel/parser';
import traverse from '@babel/traverse';
import generate from '@babel/generator';
import * as _ from 'lodash';
export default class VueParse{
template: string = '';
data: any = [];
methods: any = [];
components: any = [];
importDeclarations: any = [];
uuid: string = '';
vueStr: string = '';
vueScript: string = '';
$: any;
scriptAst: any;
style: string = '';
created: any;
constructor (uuid: string, vueStr: string) {
this.uuid = uuid;
this.vueStr = vueStr.replace(/_unique/g, this.uuid);
this.init();
}
private init () {
const template = this.vueStr.match(/([\s\S])*<\/template>/g)[0];
const style = this.vueStr.match(/(?<=
if (style) {
this.style = style[0];
}
this.$ = cheerio.load(template, {
xmlMode: true,
decodeEntities: false
});
this.template = this.$('.root').html();
this.vueScript = this.vueStr.match(/(?<=