死锁及死锁检测
一、什么是死锁
线程a占有资源1,线程b占有资源2,现在线程a想要访问资源2,线程b想要访问资源1;
这样两个线程都访问不到自己想要的资源,并且互相僵持在这,我们将这总现象称之为死锁。
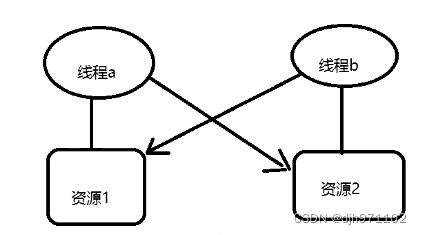
这只是两个线程的例子,如果是多个线程,死锁是什么样子呢?
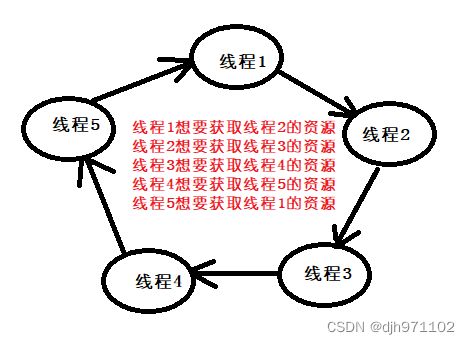
多个线程之间依次想要访问其他线程的资源,这样相互僵持形成的一个访问闭环。
二、死锁产生的条件
1.条件互斥:进程/线程要求对所分配的资源进行排它性控制,即在一段时间内某资源仅为一进程/线程所占用。
2.请求和保持:当进程/线程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放。
3.不剥夺:进程/线程已获得的资源在未使用完之前,不能剥夺,只能在使用完时由自己释放。
4.环路等待:在发生死锁时,必然存在一个进程/线程——资源的环形链。
三、如何检测死锁
资源获取环可以采用图来存储,使用有向图来存储。
线程 A 获取线程 B 已占用的锁,则为线程 A 指向线程 B。
运行过程中线程 B 获取成功的锁即为线程 B 已占用的锁(可以使用hook方法得到)。
检测的原理采用另一个线程定时对图进程检测是否有环的存在。
四、死锁检测组件的实现
1、先构建出有向图的数据结构,然后hook住标准的加解锁api(pthread_mutex_lock);
hook类似于c++语法中的重写
2、在hook方法中把线程与锁的关系构建成一个有向图(线程为图的顶点,线程与线程之间因为锁的关系确定为边),最后我们需要在程序的运行期间时刻监控线程与锁之间的关系,通过线程在加锁前、加锁后以及释放锁之后的3个阶段来维护有向图的正确性(通过有向图的状态我们就可以判断是否有死锁)。
(1)加锁之前:当前线程需要加的锁是否被其他线程占用,如果是,就让当前线程指向占有锁的线程(构成一条边)。
举例:线程A需要对线程B已经lock的锁lock的话,需要在线程A到线程B之间加一个边,线程A指向线程B。
(2)加锁之后:需要将锁和线程建立起一对一的关系(说明该锁目前被哪个线程使用),存在2种情况:
a.该锁之前没有被其他线程lock过,直接建立起线程id和锁id的关系-这种情况很明了,就是使用一个结构体变量来表示对应的线程id和锁id。
b.该锁之前被其他线程lock过,但是后来被该线程unlock了,这时候需要判断当前线程和该线程之间是否存在边,如果存在,需要先删除边,然后再将锁id和当前线程建立起一对一关系。
举例:对于b来说,按照步骤(1)的例子来说,如果线程A与线程B之间有线程A指向线程B的边,并且B在lock锁之后又unlock了该锁,这时候A就能够对该锁lock了,但是lock之前需要将A到B的边进行删除,因为该锁已经从B转移到了A。
(3)释放锁之后:查询锁id的下标,然后将其锁id和线程id设置为0(清除步骤二建立的对应关系)。
3、对每一个节点都进行深度遍历,半段路径中是否存在闭环现象,若存在则就有死锁。
五、c实现代码
#define _GNU_SOURCE //此宏可以开启dlfcn库里的一些开关
#include