Vite介绍和原理解析
Vite号称是 下一代的前端开发和构建工具 ,目前已经在前端社区里逐步开始流行起来了。它采用了全新的unbundle思想来提升整体的前端开发体验。比起传统的webpack构建,在性能速度上都有了质的提高。那么接下来这篇文章,将主要介绍其使用方法和工作原理。
是什么
Vite名字来源于法语, 意思为rapid,quickly。正好反映了其核心卖点—— "快速" 。在整体功能上实现了类似于预配置的webpack加dev server的功能, 用于提高前端项目的整体构建速度。根据测试,服务器启动速度和HMR基本上都可以达到毫秒级别。
使用方法
vite的使用方式十分简单,目前官方提供了脚手架来快速启动一个新项目:
npm init @vitejs/app
// yarn
yarn create @vitejs/app
接着就会进入交互式模式,让你选择对应的模板,输入项目名等操作。如果需要手动指定模板和项目名,可以使用如下命令:
npm init @vitejs/app my-vite-demo --template react
这里指定的所有相关项目模板都可以在 https://github.com/vitejs/awesome-vite#templates 仓库中找到。项目启动后,就可以直接使用如下命令进行启动和预览了
# 安装依赖
yarn install
# 开发环境下使用
yarn dev
# 打包
yarn run build
# 用来预览打包后的效果
yarn run serve
插件机制
vite主要使用插件进行扩展功能,可以看到上述最简单的初始化项目启动后,在其配置文件 vite.config.ts 文件下,有如下代码:
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import reactRefresh from '@vitejs/plugin-react-refresh'
// [https:](https://vitejs.dev/config/)[//vitejs.dev/config/](https://vitejs.dev/config/)
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [reactRefresh()]
})
可以看到这里引用了一个名为 reactRefresh 的插件, 这个插件可以在修改react组件的时候,不丢失其状态。同样的,如果有需要实现其他额外的功能,都可以借助vite的插件机制进行扩展。这些第三方插件模块可以通过 https://github.com/vitejs/awesome-vite#plugins 这个仓库找到。同时,由于vite插件扩展了rollup的接口,所以要实现一个自己的vite插件跟写rollup插件是类似的。此处,可以参考 插件 API | Vite 官方中文文档 。
工作原理
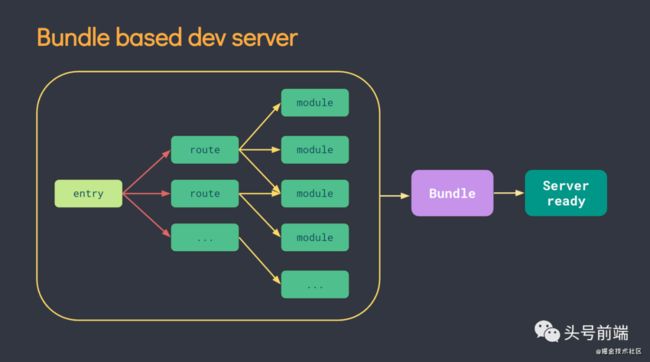
上面介绍了这么多,那么Vite是如何实现超快速的开发体验的呢? https://github.com/vitejs/vite/tree/main/packages 我们都知道,传统打包构建工具,在服务器启动之前,需要从入口文件完整解析构建整个应用。因此,有大量的时间都花在了依赖生成,构建编译上。
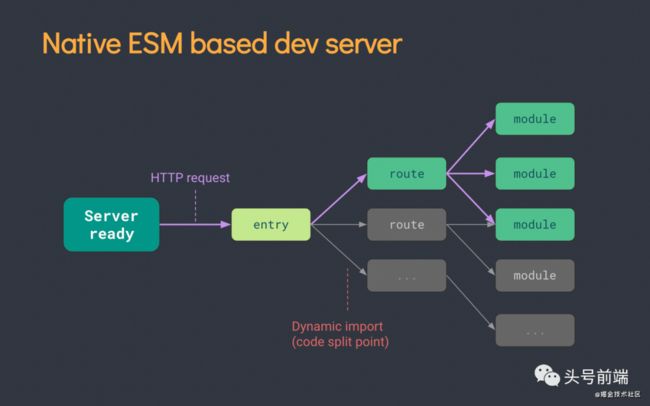
而vite主要遵循的是使用ESM(Es modules模块)的规范来执行代码,由于现代浏览器基本上都支持了ESM规范,所以在开发阶段并不需要将代码打包编译成es5模块即可在浏览器上运行。我们只需要从入口文件出发, 在遇到对应的 import 语句时,将对应的模块加载到浏览器中就可以了。因此,这种不需要打包的特性,也是vite的速度能够如此快速的原因。
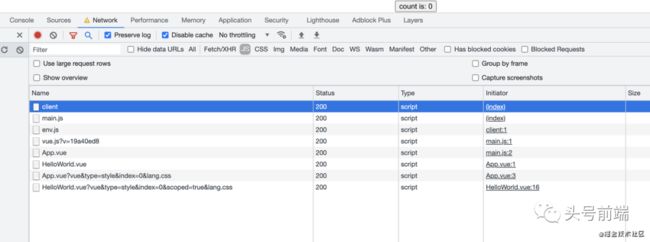
同时ts/jsx等文件的转译工作也会借助了esbuild来提升速度。Vite在内部实现上,会启动一个dev server, 并接受独立模块的HTTP请求,并让浏览器自身去解析和处理模块加载。下面以官方提供的demo为例,可以看到运行后,在访问对应页面的时候,不是加载一整个的bundle.js文件,而是按模块去加载。
从代码实现上,在允许 yarn dev 命令后,Vite就会启动一个dev server,然后加载各种中间件,进而监听对应的前端访问请求。 https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/cli.ts#L80
const { createServer } = await import('./server')
try {
const server = await createServer({
root,
base: options.base,
mode: options.mode,
configFile: options.config,
logLevel: options.logLevel,
clearScreen: options.clearScreen,
server: cleanOptions(options) as ServerOptions
})
await server.listen()
} catch (e) {
createLogger(options.logLevel).error(
chalk.red(`error when starting dev server:\n${e.stack}`)
)
process.exit(1)
}
同时,会在开发环境中注入Vite自身的client客户端代码,用于监听HMR等处理。 https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/server/middlewares/indexHtml.ts#L141
裸模块重写
由于目前ESM不支持类似 import vue from "vue" 这样的裸模块加载(import maps 提案 https://github.com/WICG/import-maps 可解决这个问题,但还未实现),所以需要对模块加载地址进行重写操作。将其转换成类似于 import vue from "/ @modules/vue" 这种形式。实现原理上主要通过 es-module-lexer 和 magic-string 两个包进行替换,比起AST语义解析和转换,在性能上更有优势。下面介绍一下这两个包:
Es-module-lexer
https://github.com/guybedford/es-module-lexer 虽然js代码的词法分析通常都使用babel, acorn等工具,但是针对ESM文件来说,使用es-module-lexer库在性能上能够有很大的提升,其压缩后的体积只有4kb,而且根据官方给出的例子720kb的Angular1库经过acorn解析要超过100ms,而使用es-module-lexer库只需要5ms, 在性能上提升了将近20倍。
Magic-string
https://github.com/rich-harris/magic-string#readme vite中使用了大量这个库做一些字符串的替换工作,从而避免操作AST。具体代码可以参考 https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/plugins/importAnalysis.ts#L155 整体思路大概类似于下面代码:
import { init, parse as parseImports, ImportSpecifier } from 'es-module-lexer'
// 借助es-module-lexer来分析import语句
imports = parseImports(source)[0]
// 接着在依赖分析及路径重写过程中利用magic-string来替换源码。
let s: MagicString | undefined
const str = () => s || (s = new MagicString(source))
// 省略部分代码
for (let index = 0; index < imports.length; index++) {
const {
s: start,
e: end,
ss: expStart,
se: expEnd,
d: dynamicIndex,
n: specifier
} = imports[index]
// 省略部分代码
// 解析代码
const { imports, importsString, exp, endIndex, base, pattern } =
await transformImportGlob(
source,
start,
importer,
index,
root,
normalizeUrl
)
str().prepend(importsString)
str().overwrite(expStart, endIndex, exp)
imports.forEach((url) => importedUrls.add(url.replace(base, '/')))
if (!(importerModule.file! in server._globImporters)) {
server._globImporters[importerModule.file!] = {
module: importerModule,
importGlobs: []
}
}
server._globImporters[importerModule.file!].importGlobs.push({
base,
pattern
})
}
// 最终返回处理过的代码
if (s) {
return s.toString()
} else {
return source
}
自定义区块处理
这个功能是通过在模块后面链接 ?type= 的参数来区分不同区块。然后针对每个区块单独进行处理。
根据不同的区块类型,在transform的时候会使用不同的插件进行编译。下面以json文件为例,在处理 xxx.json 为结尾的文件的时候,首先json插件会匹配模块的id名是否是json。接着再进行转译工作。
// Custom json filter for vite
const jsonExtRE = /\.json($|\?)(?!commonjs-proxy)/
export function jsonPlugin(
options: JsonOptions = {},
isBuild: boolean
): Plugin {
return {
name: 'vite:json',
transform(json, id) {
if (!jsonExtRE.test(id)) return null
if (SPECIAL_QUERY_RE.test(id)) return null
try {
if (options.stringify) {
if (isBuild) {
return {
code: `export default JSON.parse(${JSON.stringify(
JSON.stringify(JSON.parse(json))
)})`,
map: { mappings: '' }
}
} else {
return `export default JSON.parse(${JSON.stringify(json)})`
}
}
const parsed = JSON.parse(json)
return {
code: dataToEsm(parsed, {
preferConst: true,
namedExports: options.namedExports
}),
map: { mappings: '' }
}
} catch (e) {
const errorMessageList = /[\d]+/.exec(e.message)
const position = errorMessageList && parseInt(errorMessageList[0], 10)
const msg = position
? `, invalid JSON syntax found at line ${position}`
: `.`
this.error(`Failed to parse JSON file` + msg, e.idx)
}
}
}
}
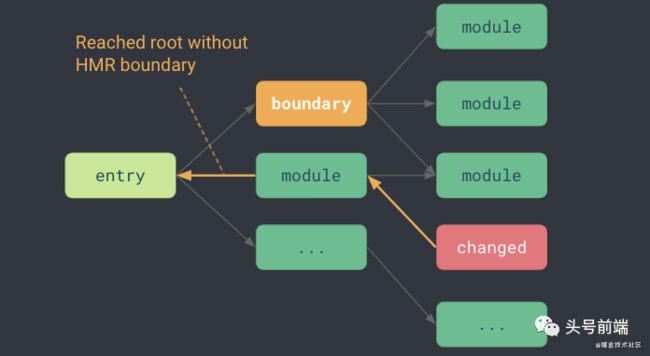
HMR
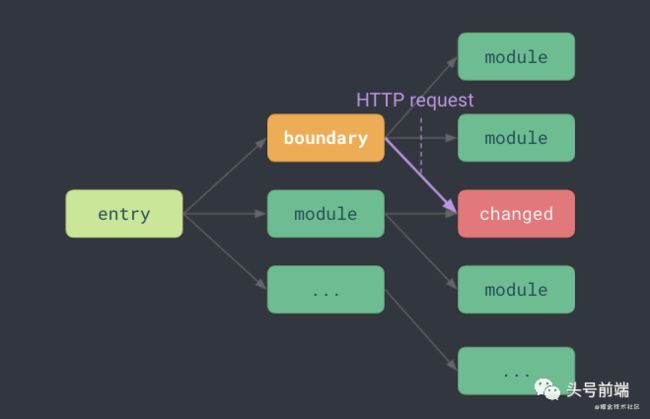
热更新是前端开发体验中很重要的一环,那么Vite中主要依赖以下几个步骤来实现HMR的功能:
-
在重写模块地址的时候,记录模块依赖链
importMaps。这样在后续更新的时候,可以知道哪些文件需要被热更新。
-
代码中可以使用
import.meta.hot接口来标记"HMR Boundary"。
-
接着,当文件更新的时候,会沿着之前记录下
imoprtMaps链式结构找到对应的"HMR Boundary", 再从此处重新加载对应更新的模块。
-
如果没有遇到对应的boundary, 则整个应用重新刷新。
使用方法如下:
import foo from './foo.js'
foo()
if (import.meta.hot) {
import.meta.hot.accept('./foo.js', (newFoo) => {
newFoo.foo()
})
}
下面将以具体代码进行介绍其原理。客户端逻辑: https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/plugins/importAnalysis.ts#L399
// record for HMR import chain analysis
// make sure to normalize away base
importedUrls.add(url.replace(base, '/'))
if (hasHMR && !ssr) {
debugHmr(
`${
isSelfAccepting
? `[self-accepts]`
: acceptedUrls.size
? `[accepts-deps]`
: `[detected api usage]`
} ${prettyImporter}`
)
// 在用户业务代码中注入Vite客户端代码
str().prepend(
`import { createHotContext as __vite__createHotContext } from "${clientPublicPath}";` +
`import.meta.hot = __vite__createHotContext(${JSON.stringify(
importerModule.url
)});`
)
}
https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/client/client.ts#L70
case 'update':
notifyListeners('vite:beforeUpdate', payload)
// 发生错误的时候,重新加载整个页面
if (isFirstUpdate && hasErrorOverlay()) {
window.location.reload()
return
} else {
clearErrorOverlay()
isFirstUpdate = false
}
payload.updates.forEach((update) => {
if (update.type === 'js-update') {
// js更新逻辑, 会进入一个缓存队列,批量更新,从而保证更新顺序
queueUpdate(fetchUpdate(update))
} else {
// css更新逻辑, 检测到更新的时候,直接替换对应模块的链接,重新发起请求
let { path, timestamp } = update
path = path.replace(/\?.*/, '')
const el = (
[].slice.call(
document.querySelectorAll(`link`)
) as HTMLLinkElement[]
).find((e) => e.href.includes(path))
if (el) {
const newPath = `${path}${
path.includes('?') ? '&' : '?'
}t=${timestamp}`
el.href = new URL(newPath, el.href).href
}
console.log(`[vite] css hot updated: ${path}`)
}
})
break
break
服务端处理HMR模块更新逻辑: https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/server/hmr.ts#L42
export async function handleHMRUpdate(
file: string,
server: ViteDevServer
): Promise {
const { ws, config, moduleGraph } = server
const shortFile = getShortName(file, config.root)
const isConfig = file === config.configFile
const isConfigDependency = config.configFileDependencies.some(
(name) => file === path.resolve(name)
)
const isEnv = config.inlineConfig.envFile !== false && file.endsWith('.env')
if (isConfig || isConfigDependency || isEnv) {
// 重启server
await restartServer(server)
return
}
// (dev only) the client itself cannot be hot updated.
if (file.startsWith(normalizedClientDir)) {
ws.send({
type: 'full-reload',
path: '*'
})
return
}
const mods = moduleGraph.getModulesByFile(file)
// check if any plugin wants to perform custom HMR handling
const timestamp = Date.now()
const hmrContext: HmrContext = {
file,
timestamp,
modules: mods ? [...mods] : [],
read: () => readModifiedFile(file),
server
}
for (const plugin of config.plugins) {
if (plugin.handleHotUpdate) {
const filteredModules = await plugin.handleHotUpdate(hmrContext)
if (filteredModules) {
hmrContext.modules = filteredModules
}
}
}
if (!hmrContext.modules.length) {
// html file cannot be hot updated
if (file.endsWith('.html')) {
[config.logger.info](http://config.logger.info/)(chalk.green(`page reload `) + chalk.dim(shortFile), {
clear: true,
timestamp: true
})
ws.send({
type: 'full-reload',
path: config.server.middlewareMode
? '*'
: '/' + normalizePath(path.relative(config.root, file))
})
} else {
// loaded but not in the module graph, probably not js
debugHmr(`[no modules matched] ${chalk.dim(shortFile)}`)
}
return
}
updateModules(shortFile, hmrContext.modules, timestamp, server)
}
function updateModules(
file: string,
modules: ModuleNode[],
timestamp: number,
{ config, ws }: ViteDevServer
) {
const updates: Update[] = []
const invalidatedModules = new Set()
let needFullReload = false
for (const mod of modules) {
invalidate(mod, timestamp, invalidatedModules)
if (needFullReload) {
continue
}
const boundaries = new Set<{
boundary: ModuleNode
acceptedVia: ModuleNode
}>()
// 向上传递更新,直到遇到边界
const hasDeadEnd = propagateUpdate(mod, timestamp, boundaries)
if (hasDeadEnd) {
needFullReload = true
continue
}
updates.push(
...[...boundaries].map(({ boundary, acceptedVia }) => ({
type: `${boundary.type}-update` as Update['type'],
timestamp,
path: boundary.url,
acceptedPath: acceptedVia.url
}))
)
}
if (needFullReload) {
// 重刷页面
} else {
// 相ws客户端发送更新事件, Websocket 监听模块更新, 并且做对应的处理。
ws.send({
type: 'update',
updates
})
}
}
优化策略
由于vite打包是让浏览器一个个模块去加载的,因此,就很容易存在http请求的瀑布流问题(浏览器并发一次最多6个请求)。此次,vite内部为了解决这个问题,主要采取了3个方案。
-
预打包,确保每个依赖只对应一个请求/文件。比如lodash。此处可以参考 https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/optimizer/esbuildDepPlugin.ts#L73
-
代码分割code split。可以借助rollup内置的
manualChunks来实现。 -
Etag 304状态码,让浏览器在重复加载的时候直接使用浏览器缓存。
https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/server/middlewares/transform.ts#L155
// check if we can return 304 early
const ifNoneMatch = req.headers['if-none-match']
if (
ifNoneMatch &&
(await moduleGraph.getModuleByUrl(url))?.transformResult?.etag ===
ifNoneMatch
) {
isDebug && debugCache(`[304] ${prettifyUrl(url, root)}`)
res.statusCode = 304
return res.end()
}
esbuild的使用
https://github.com/vitejs/vite/blob/main/packages/vite/src/node/plugins/esbuild.ts#L82 利用esbuild来转换ts/jsx文件,从而更快地提升编译速度。
export async function transformWithEsbuild(
code: string,
filename: string,
options?: TransformOptions,
inMap?: object
): Promise {
// if the id ends with a valid ext, use it (e.g. vue blocks)
// otherwise, cleanup the query before checking the ext
const ext = path.extname(
/\.\w+$/.test(filename) ? filename : cleanUrl(filename)
)
let loader = ext.slice(1)
if (loader === 'cjs' || loader === 'mjs') {
loader = 'js'
}
const resolvedOptions = {
loader: loader as Loader,
sourcemap: true,
// ensure source file name contains full query
sourcefile: filename,
...options
} as ESBuildOptions
delete resolvedOptions.include
delete resolvedOptions.exclude
delete resolvedOptions.jsxInject
try {
const result = await transform(code, resolvedOptions)
if (inMap) {
const nextMap = JSON.parse(result.map)
nextMap.sourcesContent = []
return {
...result,
map: combineSourcemaps(filename, [
nextMap as RawSourceMap,
inMap as RawSourceMap
]) as SourceMap
}
} else {
return {
...result,
map: JSON.parse(result.map)
}
}
} catch (e) {
debug(`esbuild error with options used: `, resolvedOptions)
// patch error information
if (e.errors) {
e.frame = ''
e.errors.forEach((m: Message) => {
e.frame += `\n` + prettifyMessage(m, code)
})
e.loc = e.errors[0].location
}
throw e
}
}
总结
总体来说,Vite在前端构建工具领域上开辟了一条和webpack完全不同的道路,很好地解决了前端开发阶段构建速度慢的问题。预计将会使前端开发体验上更上一层楼。同时,vite.js的源码也在不停迭代过程中,如果有想要更加了解其具体的实现细节,还是希望能够亲自去阅读其源码。本文主要希望能够起到抛砖引玉的作用。
参考文档
https://cn.vitejs.dev/guide/#overview
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xXrhg26VCSc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fgwSJ-xXUTY