滴水逆向总纪录
滴水逆向从指针开始
- 前言
- 一.滴水逆向指针2
-
- 1 列出每一行的反汇编代码:
- 2、列出每一行的反汇编代码:
- 3、完成代码,实现数组值的互换
- 二,指针三练习题
-
- 4,模拟实现CE的数据搜索功能:
- 四,指针五
-
- 模拟实现CE的数据搜索功能:
- 上面写错了就很尴尬
- 考完试回家了,接着看滴水
-
- 指针六
- 指针8
- 位运算
- 内存分配文件读写
- pe头解析手动
- pe02
- pe03节表
- 昨天的没有写好只能输出一个节表,所以又改了一下
前言
今天才用到这种模版,以后就用这种方法记录了。也好看也好写也连贯。
一.滴水逆向指针2
1 列出每一行的反汇编代码:
char a = 10; mov byte ptr[a], 0Ah
short b = 20; mov eax, 14h mov word ptr[b], ax
int c = 30; mov dword ptr[c], 1Eh
char* pa = &a; lea rax, [a] mov qword ptr[pa], rax
short* pb = &b; lea rax,[b] mov qword ptr[pb], rax
int* pc = &c; lea rax, [c] mov qword ptr[pc], rax
char** ppa = &pa; lea rax, [pa] mov qword ptr[ppa], rax
short** ppb = &pb; lea rax, [pb] mov qword ptr[ppb], rax
int** ppc = &pc; lea rax, [pc] mov qword ptr[ppc], rax
2、列出每一行的反汇编代码:
int p = 10;
int******* p7;
int****** p6;
int***** p5;
int**** p4;
int*** p3;
int** p2;
int* p1;
p1 = &p; lea rax, [p] mov qword ptr[p1], rax
p2 = &p1; lea rax, [p1] mov qword ptr[p2], rax
p3 = &p2; lea rax, [p2] mov qword ptr[p3], rax
p4 = &p3; lea rax, [p3] mov qword ptr[p4], rax
p5 = &p4; lea rax, [p4] mov qword ptr[p5], rax
p6 = &p5; lea rax, [p5] mov qword ptr[p6], rax
p7 = &p6; lea rax, [p6] mov qword ptr[p7], rax
3、完成代码,实现数组值的互换
void Function()
{
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
//..此处添加代码,使用指针,将数组的值倒置
int* p=arr;
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
temp = *(p + i);
*(p + i) = *(p + 4-i);
*(p + 4-i) = temp;
}
//打印数组值的代码已经写完,不需要修改
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
{
printf("%d\n", *(p + k));
}
}
二,指针三练习题
4,模拟实现CE的数据搜索功能:
这一堆数据中存储了角色的血值信息,假设血值的类型为int类型,值为100(10进制)
请列出所有可能的值以及该值对应的地址.
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x07, 0x09,
0x00, 0x20, 0x10, 0x03, 0x03, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x00, 0x44, 0x00,
0x00, 0x33, 0x00, 0x47, 0x0C, 0x0E, 0x00, 0x0D, 0x00, 0x11,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x64, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xAA, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x10, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x74, 0x0F, 0x41, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0A, 0x00,
0x00, 0x02, 0x74, 0x0F, 0x41, 0x00, 0x06, 0x08, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00, 0x0F, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0D, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x23, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00
思路就是先用一个char指针一个个的往后移,在移到下一个char之前强转成int 型的指针然后再用int 型的指针去判断是不是0x64,如果是就输出,不是就检查下一个char。
#include 四,指针五
模拟实现CE的数据搜索功能:
这一堆数据中存储了角色的名字信息(WOW),请列出角色名的内存地址.
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x07, 0x09,
0x00, 0x20, 0x10, 0x03, 0x03, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x00, 0x44, 0x00,
0x00, 0x33, 0x00, 0x47, 0x0C, 0x0E, 0x00, 0x0D, 0x00, 0x11,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x64, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xAA, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x10, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x74, 0x0F, 0x41, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0A, 0x00,
0x00, 0x02, 0x57, 0x4F, 0x57, 0x00, 0x06, 0x08, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00, 0x0F, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0D, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x23, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00
1、编写函数,返回角色名字信息的地址,如果没有返回0
char* FindRoleNameAddr(char* pData, char* pRoleName)
2、编写函数,遍历上面数据中所有角色名字.
FindName()
4、int strcmp(char* s1, char* s2);
一样返回0 不一样返回1
写了半天
#include 感觉还是不是得心应手还得接着学,发现返回的指针呢(也就是FindRoleNameAddr是返回来的指针)。
如果直接输出呢,是返回了内存的值也就是wow,如果是想看到这个wow名字的位置呢是需要&的。本来是想用自己写的strcmp函数但是strncmp直接可以用而且更方便一点所以就没有用。~
上面写错了就很尴尬
if (result == NULL)
printf("not found\n");
else
cout << &result<<endl<<result;
return 0;
最后不该用cout直接输出这个char的地址的,导致输出来的就是内存里的值(就像是printf(‘%s’,reslut)了一样),然后&result是result的内存地址跟wow的地址没有关系。
下面是正确的写法
if (result == NULL)
printf("not found\n");
else
printf(" %p \n %c \n %c \n %c", result,*result, *(result+1), *(result+2));
这样就可以正确的输出wow的地址,并且正确的输出wow。
还有一点,%p是专门用来输出指针的,之前我上网查的用%llx麻烦了。
cout与printf的区别
根据师傅的描述,cout应该是将我的char指针当成字符串输出了。
考完试回家了,接着看滴水
指针六
* () 与[]是可以互换的,也就是说:
* (*(p + 1) + 2) 相当与 p[1][2]
那 * (p + 1)[2] 是否一定等于p[1][2]呢? 通过反汇编进行论证。
2、使用数组指针遍历一个一维数组.
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
printf("%d \n",*(px+0)[1]);
00007FF655BC1948 B8 14 00 00 00 mov eax,14h
00007FF655BC194D 48 6B C0 01 imul rax,rax,1
00007FF655BC1951 48 8B 4D 38 mov rcx,qword ptr [px]
00007FF655BC1955 48 03 C8 add rcx,rax
00007FF655BC1958 48 8B C1 mov rax,rcx
00007FF655BC195B B9 04 00 00 00 mov ecx,4
00007FF655BC1960 48 6B C9 00 imul rcx,rcx,0
00007FF655BC1964 8B 14 08 mov edx,dword ptr [rax+rcx]
00007FF655BC1967 48 8D 0D 36 83 00 00 lea rcx,[string "%d \n" (07FF655BC9CA4h)]
00007FF655BC196E E8 1D F8 FF FF call printf (07FF655BC1190h)
printf("%d ", px[0][1]);
00007FF612991938 B8 14 00 00 00 mov eax, 14h
00007FF61299193D 48 6B C0 00 imul rax, rax, 0
00007FF612991941 48 8B 4D 38 mov rcx, qword ptr[px]
00007FF612991945 48 03 C8 add rcx, rax
00007FF612991948 48 8B C1 mov rax, rcx
00007FF61299194B B9 04 00 00 00 mov ecx, 4
00007FF612991950 48 6B C9 01 imul rcx, rcx, 1
00007FF612991954 8B 14 08 mov edx, dword ptr[rax + rcx]
00007FF612991957 48 8D 0D 92 83 00 00 lea rcx, [string "%d " (07FF612999CF0h)]
00007FF61299195E E8 2D F8 FF FF call printf(07FF612991190h)
综上一模一样。
第二题
int arr[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int(*px)[5]; //这是个啥?指向数组的指针。。
px = &arr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d \n",px[0][1]);
}
这个很简单一个for
指针8
1、将一个函数存储到数据区,通过指针进行访问.
2、char数组内容如下:
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x07, 0x09,
0x00, 0x20, 0x10, 0x03, 0x03, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x00, 0x44, 0x00,
0x00, 0x33, 0x00, 0x47, 0x0C, 0x0E, 0x00, 0x0D, 0x00, 0x11,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x64, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xAA, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x10, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x74, 0x0F, 0x41, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x05, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0A, 0x00,
0x00, 0x02, 0x74, 0x0F, 0x41, 0x00, 0x06, 0x08, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00, 0x0F, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0D, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x23, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00, 0x00, 0x64, 0x00
不运行说出下面的结果: 指针定义如下:
*(*(px + 0) + 0) int(*px)[2];
0
* (*(px + 1) + 0) int(*py)[2][3];
8
* (*(px + 2) + 3) char(*pz)[2];
16 + 12
* (*(*(py + 1) + 2) + 3) char(*pk)[2][3];
24 + 24 + 12
* (*(pz + 2) + 3)
4 + 3
* (*(*(pk + 2) + 3) + 4)
12 + 9 + 4
直接答案也出来了
第一个可能是我的机器是64位的所以一直没有成功。
附上别人写的代码。
#include位运算
1、定义一个unsiged char 类型,通过程序为第3、5、7位赋值, 赋值时不能
影响到其它位原来的值.
(使用位操作指令、比如:& | !^ << >>等)
2、判断某个位的值是否为1
(使用位操作指令、比如: & | !^ << >>等)
3、读取第7、6、5位的值,以十进制显示(unsigned).
(使用位操作指令、比如: & | !^ << >>等)
4、用十六进制文本编辑器分别打开一个.exe、.dll、.sys、.txt、.doc
.jpg、.pdf等将前四个字节写在下了.
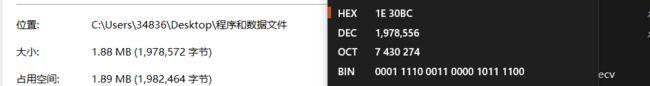
5、将一个在十六进制编辑器中打开的.exe文件,拖拽到最后,观察文件中的大小和硬盘上的大小.
(下载一个WinHex)
1,假设是这么个数 0010 1010 & 1101 0101 (.赋值为0) | 0010 1010(赋值为1)
2,第二题和第三题写了个函数,先右移后判断是奇数还是偶数来判读是不是1;
#include 4,exe 4D 5A90 00
dll 4D 5A90 00
sys 4D 5A90 00
doc D0 CF 11 E0
txt 534c 41 43
jpg FF D8 FF E0
pdf 25 50 44 46
5,算了一下
内存分配文件读写
作业有点难搞,对于我这从来没用过c库函数的。
一,前面没什么不一样从winhew看的是一样的,最后的有些不一样。
二,
先是用fopen,返回file指针指向的记事本程序;
然后再用fseek指向文件的结尾,然后就可以用fteel获得文件的大小了。
接下来是个,容易犯错的点再fseek再返回到文件头
malloc开辟内存,再用fread读进内存里就成了。
void neicun()
{
FILE* fp;
int a = 0, b = 0;
fp = fopen("C:\\WINDOWS\\system32\\notepad.exe", "rb");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("打开文件错误");
exit(1);
}
else
{
perror("打开文件成功");
}
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
a = ftell(fp);
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
//rewind(fp);
char* ptr;
ptr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(int) * a);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
cout << "地址分配不成功"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "地址分配成功"<<endl;
}
memset(ptr, 0, sizeof(int) * a);
int result = fread(ptr, 1, a, fp);
if (result != a)
{
cout << "读入内存失败" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "读入内存成功" << endl;
}
printf(" %p\n", ptr);
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
fclose(fp);
}
三,
neicun();
FILE* fp;
int a = 0, b = 0;
fp = fopen("C:\\WINDOWS\\system32\\notepad.exe", "rb");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("打开文件错误");
exit(1);
}
else
{
perror("打开文件成功");
}
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
a = ftell(fp);
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
//rewind(fp);
char* ptr;
ptr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(int) * a);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
cout << "地址分配不成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "地址分配成功" << endl;
}
memset(ptr, 0, sizeof(int) * a);
printf(" %p\n", ptr);
FILE* fp2 = fopen("F://test.exe", "wb");
fread(ptr, 1, a, fp);
int c=fwrite(ptr, 1, a, fp2);
if (c==a)
{
perror("成功");
}
else
{
perror("失败");
}
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
fclose(fp);
fclose(fp2);
其实就是在后面加上了fwrite,读到内存里再写回来。

虽然是有了,但是怎么双击也打不开。
pe头解析手动
我是用的010editor打开的红警战网。还是蛮方便的。
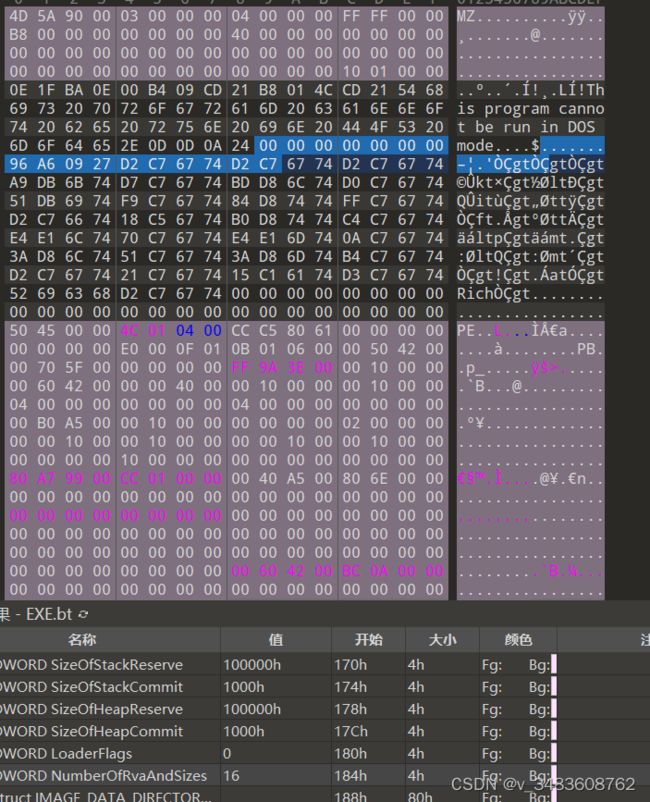
下面可以显示节表的名称
DOC头
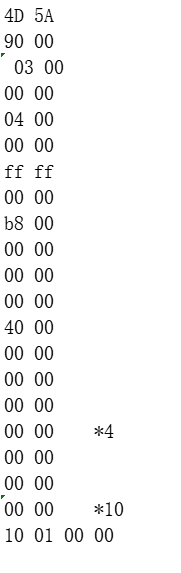
pe头相对于整个文件的开头为110 也就是272
范围是0到3f 大小是40h
标准pe头

可选pe头
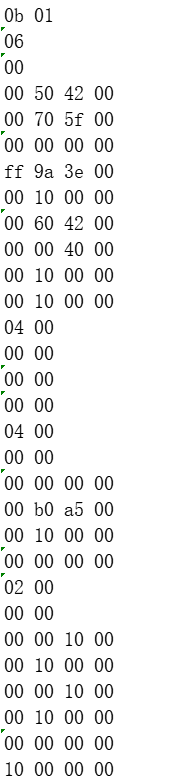
pe02
1、编写程序读取一个.exe文件,输出所有的PE头信息.
2、使用第三方的PE工具,对比如下信息,看是否一致:
#include 感觉写的不是很好,只是自己找的位置然后填进去,这还写了俩天。。。
在010editor里比着写的肯定没问题了。
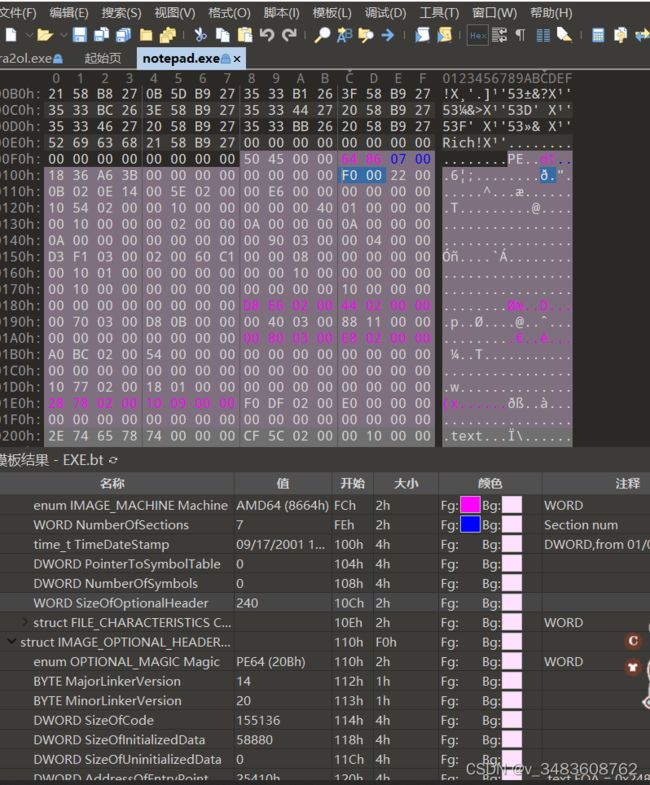
pe03节表
-
编写程序打印节表中的信息.
-
根据节表中的信息,到文件中找到所有的节,观察节的开始位置与大小是否
与节表中的描述一致(使用notepad.exe来练习).
感觉写的还是慢。。。
#include 昨天的没有写好只能输出一个节表,所以又改了一下
可以输出所有节表的内容。
#include