string的简单实现
创造一个string的对象,含有char*str和一下基本成员函数
class String
{ //友原重载<<和>>
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const String& s);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, String& s);
public:
String() {
str = new char[100];
str[0] = '\0';
}//string的默认构造
String(const char* other)
{
str = new char[strlen(other) + 1];
strcpy(str, other);
}//有参构造
~String()
{
delete[]str;
}//析构
String(const String& other);//复制构造
int Length();//字符串的长度
String& operator=(const String& other);
String& operator=(const char* ch);//重载=
String operator+(const String& other);//重载+
String& operator+=(const String& other);//重载+=
char& operator[](int x);//重载[]
bool operator==(const String& other);//重载==
bool operator<(const String& other);//重载<
private:
char* str;
};
下面逐步写出每个成员函数
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const String& s);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, String& s);
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const String& s)
{
out << s.str;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, String& s)
{
char ch[1000];//临时创造一个数组储存输入值
in >> ch;
delete[]s.str;//释放s的空间
s.str = new char[strlen(ch) + 1];//为s重新分配新的空间
strcpy(s.str, ch);//赋值给s
return in;
}
String(const String& other);
String::String(const String& other)
{
str = new char[strlen(other.str) + 1];
strcpy(str, other.str);
}
int Length();
int String::Length()
{
return strlen(str);//返回str的长度
}
String& operator=(const String& other);
String& operator=(const char* ch);
String& operator=(const String& other)
{
if (this != &other)//判断是否和原来一样,一样直接返回原值
{
delete[]str;
str = new char[strlen(other.str) + 1];
strcpy(str, other.str);
}
return *this;
}//重载与string的=
String& operator=(const char* ch)
{
delete[]str;
str = new char[strlen(ch) + 1];
strcpy(str, ch);
return *this;
}//重载与字符串的=
String operator+(const String& other);
String operator+(const String& other)
{
int len = strlen(str) + strlen(other.str) + 1;
//求出需要开辟空间的大小
char* newstr = new char[len];//用一个新指针去接收
strcpy(newstr, str);
strcat(newstr, other.str);
return String(newstr);
}//重载+
String& operator+=(const String& other);
String& operator+=(const String& other)
{
*this = *this + other;
return *this;
}//使用重载后的=和+完成+=的重载
char& operator[](int x);
bool operator==(const String& other);
bool operator<(const String& other);
char& operator[](int x)
{
assert(x >= 0 && x <= strlen(str));
//使用断言判断是否在范围内
return str[x];
}//重载[]
bool operator==(const String& other)
{
return !strcmp(str, other.str);
}//重载==
bool operator<(const String& other)
{
return strcmp(str, other.str) < 0;
}//重载<
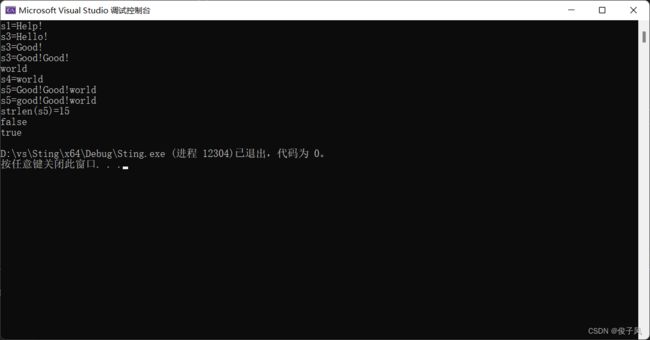
完整代码及样例的使用
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include