python rtsp 硬件解码 二
上次使用了python的opencv模块
述说了使用PyNvCodec 模块,这个模块本身并没有rtsp的读写,那么读写rtsp是可以使用很多方法的,我们为了输出到pytorch直接使用AI程序,简化rtsp 输入,可以直接使用ffmpeg的子进程
方法一
使用pyav,这个下次再讲
方法二
使用pipe方式,也就是我们使用任何一种方式都可以,如果我们有ffmpeg,那么直接使用ffmpeg来读取流也是可行的,使用live555 去读取流也是可行的,只要把流取过来pipe给python程序就行,把ffmpeg的可执行放到py文件的同一文件夹,如下图所示
我们为了使用硬件解码,安装了nvidia本身的PyNvCodec模块
首先我们要判决本身系统是否安装有cuda,
if os.name == "nt":
# Add CUDA_PATH env variable
cuda_path = os.environ["CUDA_PATH"]
if cuda_path:
os.add_dll_directory(cuda_path)
else:
print("CUDA_PATH environment variable is not set.", file=sys.stderr)
print("Can't set CUDA DLLs search path.", file=sys.stderr)
exit(1)
# Add PATH as well for minor CUDA releases
sys_path = os.environ["PATH"]
if sys_path:
paths = sys_path.split(";")
for path in paths:
if os.path.isdir(path):
os.add_dll_directory(path)
else:
print("PATH environment variable is not set.", file=sys.stderr)
exit(1)
使用ffmpeg来探测
我们可以使用ffprobe来探测我们的rtsp流,用来知道流的格式,是h264,还是h265,ok,我们使用process来启动子进程来探测
def get_stream_params(url: str) -> Dict:
cmd = [
"ffprobe",
"-v",
"quiet",
"-print_format",
"json",
"-show_format",
"-show_streams",
url,
]
proc = subprocess.Popen(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
stdout = proc.communicate()[0]
bio = BytesIO(stdout)
json_out = json.load(bio)
params = {}
if not "streams" in json_out:
return {}
for stream in json_out["streams"]:
if stream["codec_type"] == "video":
params["width"] = stream["width"]
params["height"] = stream["height"]
params["framerate"] = float(eval(stream["avg_frame_rate"]))
codec_name = stream["codec_name"]
is_h264 = True if codec_name == "h264" else False
is_hevc = True if codec_name == "hevc" else False
if not is_h264 and not is_hevc:
raise ValueError(
"Unsupported codec: "
+ codec_name
+ ". Only H.264 and HEVC are supported in this sample."
)
else:
params["codec"] = (
nvc.CudaVideoCodec.H264 if is_h264 else nvc.CudaVideoCodec.HEVC
)
pix_fmt = stream["pix_fmt"]
is_yuv420 = pix_fmt == "yuv420p"
is_yuv444 = pix_fmt == "yuv444p"
# YUVJ420P and YUVJ444P are deprecated but still wide spread, so handle
# them as well. They also indicate JPEG color range.
is_yuvj420 = pix_fmt == "yuvj420p"
is_yuvj444 = pix_fmt == "yuvj444p"
if is_yuvj420:
is_yuv420 = True
params["color_range"] = nvc.ColorRange.JPEG
if is_yuvj444:
is_yuv444 = True
params["color_range"] = nvc.ColorRange.JPEG
if not is_yuv420 and not is_yuv444:
raise ValueError(
"Unsupported pixel format: "
+ pix_fmt
+ ". Only YUV420 and YUV444 are supported in this sample."
)
else:
params["format"] = (
nvc.PixelFormat.NV12 if is_yuv420 else nvc.PixelFormat.YUV444
)
# Color range default option. We may have set when parsing
# pixel format, so check first.
if "color_range" not in params:
params["color_range"] = nvc.ColorRange.MPEG
# Check actual value.
if "color_range" in stream:
color_range = stream["color_range"]
if color_range == "pc" or color_range == "jpeg":
params["color_range"] = nvc.ColorRange.JPEG
# Color space default option:
params["color_space"] = nvc.ColorSpace.BT_601
# Check actual value.
if "color_space" in stream:
color_space = stream["color_space"]
if color_space == "bt709":
params["color_space"] = nvc.ColorSpace.BT_709
return params
return {}
rtsp client
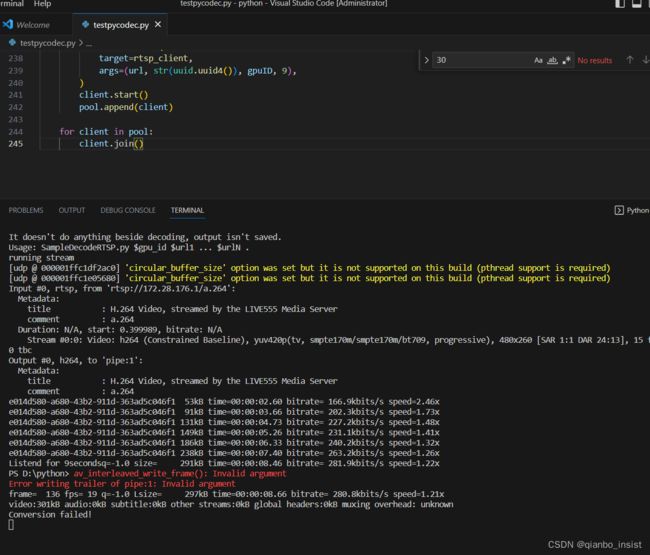
写一个rtsp client,实际上使用了ffmpeg的子进程,并且使用管道来获取数据,然后使用PyCodec来解码
def rtsp_client(url: str, name: str, gpu_id: int, length_seconds: int) -> None:
# Get stream parameters
params = get_stream_params(url)
if not len(params):
raise ValueError("Can not get " + url + " streams params")
w = params["width"]
h = params["height"]
f = params["format"]
c = params["codec"]
g = gpu_id
# Prepare ffmpeg arguments
if nvc.CudaVideoCodec.H264 == c:
codec_name = "h264"
elif nvc.CudaVideoCodec.HEVC == c:
codec_name = "hevc"
bsf_name = codec_name + "_mp4toannexb,dump_extra=all"
cmd = [
"ffmpeg",
"-hide_banner",
"-i",
url,
"-c:v",
"copy",
"-bsf:v",
bsf_name,
"-f",
codec_name,
"pipe:1",
]
# Run ffmpeg in subprocess and redirect it's output to pipe
proc = subprocess.Popen(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
# Create HW decoder class
nvdec = nvc.PyNvDecoder(w, h, f, c, g)
# Amount of bytes we read from pipe first time.
read_size = 4096
# Total bytes read and total frames decded to get average data rate
rt = 0
fd = 0
# Main decoding loop, will not flush intentionally because don't know the
# amount of frames available via RTSP.
t0 = time.time()
print("running stream")
while True:
if (time.time() - t0) > length_seconds:
print(f"Listend for {length_seconds}seconds")
break
# Pipe read underflow protection
if not read_size:
read_size = int(rt / fd)
# Counter overflow protection
rt = read_size
fd = 1
# Read data.
# Amount doesn't really matter, will be updated later on during decode.
bits = proc.stdout.read(read_size)
if not len(bits):
print("Can't read data from pipe")
break
else:
rt += len(bits)
# Decode
enc_packet = np.frombuffer(buffer=bits, dtype=np.uint8)
pkt_data = nvc.PacketData()
try:
surf = nvdec.DecodeSurfaceFromPacket(enc_packet, pkt_data)
if not surf.Empty():
fd += 1
# Shifts towards underflow to avoid increasing vRAM consumption.
if pkt_data.bsl < read_size:
read_size = pkt_data.bsl
# Print process ID every second or so.
fps = int(params["framerate"])
if not fd % fps:
print(name)
# Handle HW exceptions in simplest possible way by decoder respawn
except nvc.HwResetException:
nvdec = nvc.PyNvDecoder(w, h, f, c, g)
continue
主流程
if __name__ == "__main__":
gpuID = 0
urls = []
urls.append('rtsp://172.28.176.1/a.264')
pool = []
for url in urls:
client = Process(
target=rtsp_client,
args=(url, str(uuid.uuid4()), gpuID, 9),
)
client.start()
pool.append(client)
for client in pool:
client.join()