arduino使用FreeRTOS实时操作系统
How to use FreeRTOS with Arduino – Real time operating system
如何让Arduino运行FreeRTOS实时操作系统
在本文中,您将学习如何使用带Arduino的Freertos操作系统来执行特定的任务。实时操作系统又称RTOS,是一种旨在满足实时应用要求的操作系统。它能够处理输入的数据,通常不需要缓冲延迟。RTOS是调用预定义函数的组合。实时操作系统中的关键因素是最小的中断延迟和最小的线程切换延迟。实时操作系统的价值更多地体现在它对给定时间段内完成任务的响应速度和可预测性。
有三种 RTOS 实时操作系统:
- Hard RTOS; 必须在规定的期限内完成任务;
- Firm RTOS; 任务有时间限制,不过如果错过也能接受;
- Soft RTOS; 任务无时间限制
Examples of RTOS:
- LynxOS
- RTLinux
- VxWorks
- FreeRTOS
- OSE
- QNX
- Windows CE
Why RTOS are required:
当我们编写好的嵌入式软件时,我们不需要RTOS,但是当它的复杂性和大小增加时,RTOS总是有益的,原因如下:
- 摘要时间信息
- 可维护性/可扩展性
- 模块化
- 清洁界面
- 更容易测试(在某些情况下)
- 代码重用
- 提高效率
- 空闲时间
- 灵活的中断处理
- 混合加工要求
- 更轻松地控制外围设备
这些是RTOS的优点,但也有一些缺点,如下所示;
- 低优先级任务
- 代码精度
- 有限的任务
- 复杂算法
- 设备驱动程序和中断信号
- 线程优先级
- 贵
- 不容易编程
该项目中使用的操作系统是FreeRTOS。 FreeRTOS由Real Time Engineers Ltd.开发.FreeRTOS是一种流行的实时操作系统内核。 FreeRTOS是开源的。 它用于嵌入在所述35微控制器中的嵌入式设备。 它主要用C语言编写,但有些函数是用汇编语言编写的。 还有在线提供的SafeRTOS和OpenRTOS,与FreeRTOS类似。
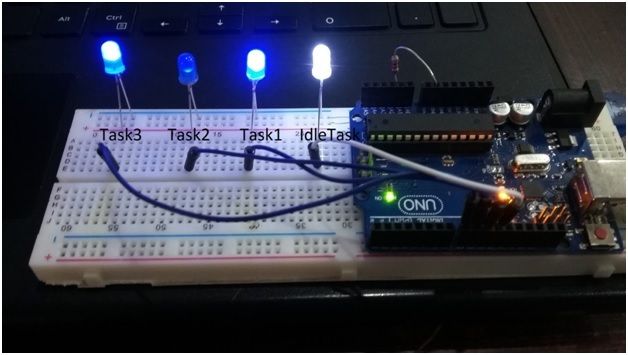
使用Arduino进行任务切换:
在这个项目中,3 Led表示三个任务,一个Led表示空闲状态。 三个任务分别是Task1,Task2和Task3。
安装FreeRTOS库:
https://github.com/feilipu/Arduino_FreeRTOS_Library
代码:
#include 每个任务有不同的优先级以及延时时间
Implementation:
link: http://microcontrollerslab.com/use-freertos-arduino/
// 实验中包含五个实时任务:
#include