TypeScript学习笔记
目录
一、简介
1、TypeScript与JavaScript
2、为什么要有TypeScript
二、基础认识
1、基础类型
2、函数类型
3、接口interface
4、类
三、高级类型
1、类型【不涉及泛型的】
2、泛型
四、实战
1、声明文件
2、泛型约束后端接口类型
一、简介
1、TypeScript与JavaScript
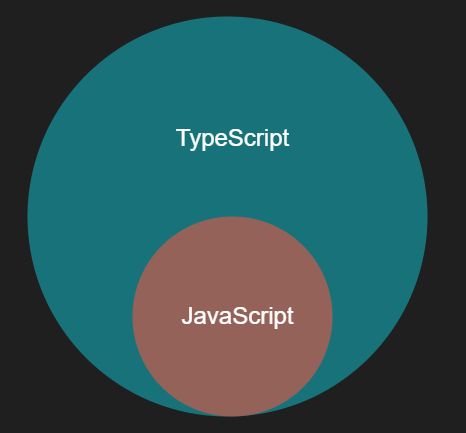
(1)TypeScript其实是JavaScript的一个超集
(2)TypeScript是在JavaScript的基础上,进行类型检测和语法补充,TypeScript是强类型语言,能支持静态和动态类型
(3)TypeScript可以在编译期间发现并纠正错误,而JavaScript只能在运行是发现错误
(4)TypeScript不允许改变变量的数据类型,更加严谨
2、为什么要有TypeScript
(1)类型安全
(2)具备下一代JS特性
(3)有完善的工具链
二、基础认识
1、基础类型
(1)boolean、number、string
number:包含了整数、浮点数、复数,既保留了JS原始类型,又对其进行扩展
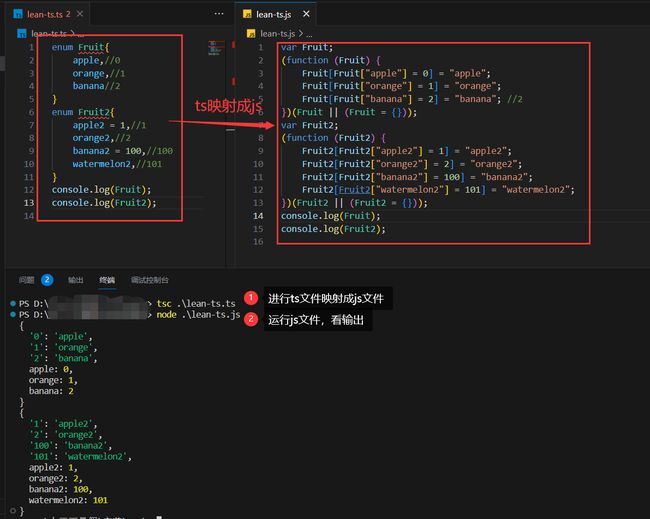
(2)枚举enum
通过枚举对枚举值进行类型定义,包括对常量,异构的枚举,这些值不仅仅是映射到js中,并且进行了反映射【不仅仅是成员名=》成员值,也从成员值=》成员名】
enum Fruit{
apple,//0
orange,//1
banana//2
}
enum Fruit2{
apple2 = 1,//1
orange2,//2
banana2 = 100,//100
watermelon2,//101
}
console.log(Fruit);
console.log(Fruit2);
(3)any、unknown、void
①unknown是any的替代类型
②any赋值或者反向赋值都可以,不会有报错检测,unknown只允许被赋值
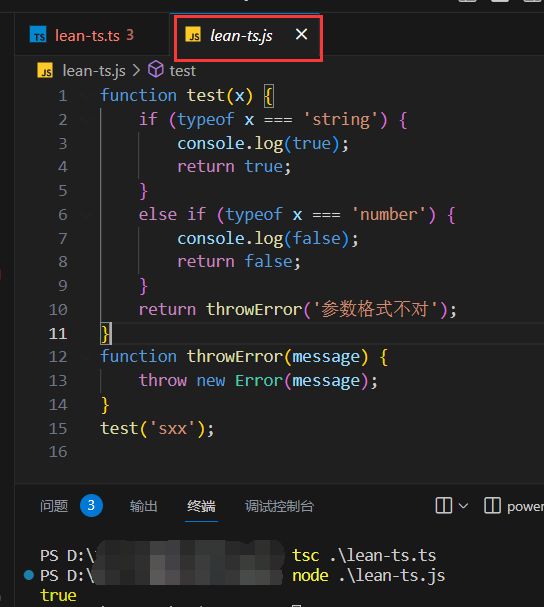
(4)never
①永远不存在值的类型
②使用场景:防御性编程
function test(x: string | number):boolean {
if (typeof x === 'string') {
console.log(true);
return true
} else if (typeof x === 'number') {
console.log(false);
return false
}
return throwError('参数格式不对')
}
function throwError(message: string): never {
throw new Error(message)
}
test('sxx')
(5)数组类型[]
(6)元组类型tuple
元组是数据的一种特殊形式,需要显示的去标注每一个数组跟元素的类型
2、函数类型
(1)定义∶TS定义函数类型时要定义输入参数类型和输出类型
输入参数:参数支持可选参数和默认参数
输出参数:输出可以自动推断,没有返回值时,默认为void类型
函数重载:名称相同但参数不同,可以通过重载支持多种类型
(2)代码例子
function add(x: number[]):number
function add(x: string[]): string
function add(x: any[]):any{
if(typeof x[0]==='string'){
return x.join()
}
if(typeof x[0] === 'number'){
return x.reduce((acc,cur)=>acc+cur)
}
}
定义一个add()函数类型,代码对参数类型进行多次定义,会进行函数重载,对类型进行拼接,前几次都是函数定义,最后一个是函数的实现
3、接口interface
(1)定义:接口是为了定义对象类型
(2)特点:
①可选属性:?
②只读属性:readonly
③可以描述函数类型
④可以描述自定义属性
总结︰接口非常灵活duck typing
4、类
(1)定义:写法和JS差不多,增加了一些定义
(2)特点:
①增加了public、private、protected修饰符
②抽象类:
-只能被继承,不能被实例化
-作为基类,抽象方法必须被子类实现
③interface约束类,使用implements关键字
abstract class Animal {
constructor(name:string) {
this.name = name
}
public name:string
public abstract sayHi():void
}
class Dog extends Animal{
constructor(name:string){
super(name)
}
}
三、高级类型
1、类型【不涉及泛型的】
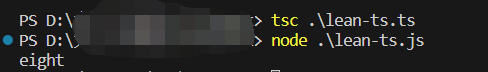
(1)联合类型 |
当在一个类型定义上,可能存在多个基础类型,那么就需要用联合类型进行取值
let num: number | string
num = 8
num = 'eight'
console.log(num);
(2)交叉类型 &
例子:定义一个Person对象类型,当需要对这个对象进行属性扩展
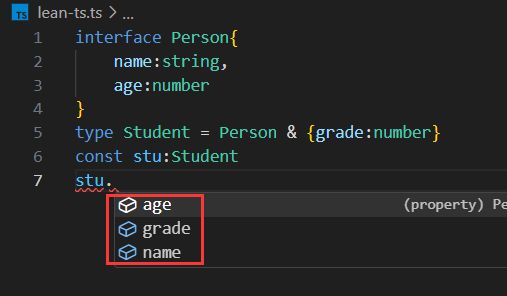
interface Person{
name:string,
age:number
}
type Student = Person & {grade:number}
const stu:Student
stu.
(3)类型断言as操作符
ts在编译时,会检测代码当前变量实际类型的定义情况,那么当使用as断言时,设置当前类型一定有断言所指定的类型,来省去编译时检测及错误的报出
①两种用法:
- 通过标识符,去进行属性前置的断言定义
- 通过as(推荐使用)
②更多分类:
- 非空断言
- 确定赋值的断言
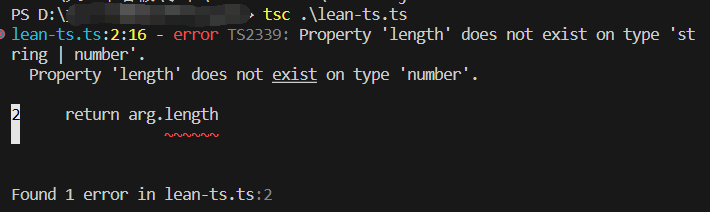
function getLength(arg:number | string):number{
return arg.length
}
function getLength(arg:number | string):number {
const str=arg as string
if(str.length){
return str.length
}else{
const number = arg as number
return number.toString().length
}
}
(4)类型别名
①定义:给类型起个别名
②相同点
- 都可以定义对象或函数
- 都允许继承
③差异点
- interface是ts用来定义对象,type是用来定义别名方便使用
- type可以定义基本类型,interface不行
- interface可以合并重复声明,type不行
④总结
- interface是一个接口概念,去描述对象;type是一个类型别名概念,对各个类型进行别名定义,能更清晰
- 使用组合或交叉类型时,使用type;涉及到类(implements、extends去定义类)时,使用interface;其他情况如定义一个对象或函数时,按习惯进行定义即可
2、泛型
(1)官方定义
软件工程中,我们不仅要创建一致的定义良好的 API,同时也要考虑可重用性
组件不仅能够支持当前的数据类型、同时也能支持未来的数据类型
(2)代码例子
①应用场景:定义一个print函数,这个函数的功能是把传入的参数打印出来,再返回这个参数,传入参数的类型是string,函数返回类型为string。
function print(arg:string):string{
console.log(arg);
return arg
}
print('df')
②想支持打印number类型
function print(arg:string | number):string|number{
console.log(arg);
return arg
}
print(123)
③想支持任意类型
function print(arg:any):any{
console.log(arg);
return arg
}
print([123])
④需要有一个类型解决输入输出可关联【泛型】 在入参里标识一个泛型定义,然后对入参进行泛型举止,然后出参进行泛型定义
function printA(arg:T):T{
console.log(arg);
return arg
}
printA(23)
(3)基本定义
①泛型的语法是<>里面写类型参数,一般用T表示
②使用时有两种方法指定类型
- 定义要使用的类型
- 通过TS类型推断,自动推导类型
③泛型的作用是临时占位,之后通过传来的类型进行推导【核心】
function print(arg:T):T{
console.log(arg);
return arg
}
print('hello')//定义T为string
print('hello')//TS类型推断,自动推导类型为string
(4)基础操作符
①typeof:获取类型
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
}
const sem: Person = { name: 'semlinker', age: 30 }
type Sem = typeof sem;
②keyof:获取所有键
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
}
type K1 = keyof Person;//"name" | "age"
type K2 = keyof Person[];// "length" | "toString" | "pop" | "push" | "concat" | "join"
③in:遍历枚举类型 在Keys里面定义联合类型,通过in来对里面所有的数据进行类型定义
type Keys = "a" | "b" | "c"
type Obj={
[p in Keys]:any
}// =>{a: any,b: any,c: any}
④T[K]:索引访问 定义一个IPerson接口,T[K]可以在每个接口的key单独进行取值和类型定义
interface IPerson {
name: string;
age: number;
}
let type1: IPerson['name'] //string
let type2: IPerson['age']//number
⑤extends:泛型约束 定义一个泛型loggingIdentity,继承Lengthwise接口,则会对Lengthwise里面的length属性进行类型扩充
interface Lengthwise {
length: number;
}
function loggingIdentity(arg: T): T {
console.log(arg.length);
return arg;
}
loggingIdentity({value: 3})
loggingIdentity({length: 5})
(5)常用工具类型
①Partial:将类型属性变为可选 举例:把泛型中的所有的key进行枚举,在遍历过程中把对应的key进行可选符的操作,使得类型属性变为可选
type Partial = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P];
}
②Required:将类型属性变为必选
type Required = {
[P in keyof T]-?:T[P]
}
③Readonly:将类型属性变为只读
type Readonly = {
readonly [P in keyof T]: T[P]
}
四、实战
1、声明文件
(1)declare:三方库需要类型声明文件
类型环境,是存放在类型声明里的一些环境上下文
(2).d.ts:声明文件定义
(3)@types:三方库TS类型包
(4)tsconfig.json:定义TS的配置
2、泛型约束后端接口类型
例子:对接口的使用场景
import axios from 'axios'
interface API{
'/book/detail':{
id:number,
},
'/book/comment':{
id:number,
comment:string
}
}
function request(url: T,obj: API[T]){
return axios.post(url,obj)
}
request('/book/comment',{
id:1,
comment:'非常棒!'
})