HDLBits-Verilog学习记录 | Verilog Language-Vectors
文章目录
- 11.vectors | vector0
- 12.vectors in more detail | vector1
- 13.Vector part select | Vector2
- 14.Bitwise operators | Vectorgates
- 15.Four-input gates | Gates4
- 16.Vector concatenation operator | Vector3
- 17.Vector reversal 1 | Vectorr
- 18. Replication operator | Vector4
- 19.More replication | Vector5
11.vectors | vector0
practice:Build a circuit that has one 3-bit input, then outputs the same vector, and also splits it into three separate 1-bit outputs. Connect output o0 to the input vector’s position 0, o1 to position 1, etc.
In a diagram, a tick mark with a number next to it indicates the width of the vector (or “bus”), rather than drawing a separate line for each bit in the vector.

module top_module (
input wire [2:0] vec,
output wire [2:0] outv,
output wire o2,
output wire o1,
output wire o0 ); // Module body starts after module declaration
assign o0 = vec[0];
assign o1 = vec[1];
assign o2 = vec[2];
assign outv = vec;
endmodule
其实可以发现,只要有C语或者其他计算机语言的基础的话,刷vetilog题不算很难上手,写代码的时候还真并不确定语法正不正确,单凭借着对c语言的理解,试着运行,还成功了。
12.vectors in more detail | vector1
practice:Build a combinational circuit that splits an input half-word (16 bits, [15:0] ) into lower [7:0] and upper [15:8] bytes.
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi[7:0] = in[15:8];
assign out_lo[7:0] = in[7:0];
endmodule
13.Vector part select | Vector2
practice;A 32-bit vector can be viewed as containing 4 bytes (bits [31:24], [23:16], etc.). Build a circuit that will reverse the byte ordering of the 4-byte word.
AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd => DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaa
module top_module(
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
// assign out[31:24] = ...;
assign out[31:24] = in[7:0];
assign out[23:16] = in[15:8];
assign out[15:8] = in[23:16];
assign out[7:0] = in[31:24];
endmodule
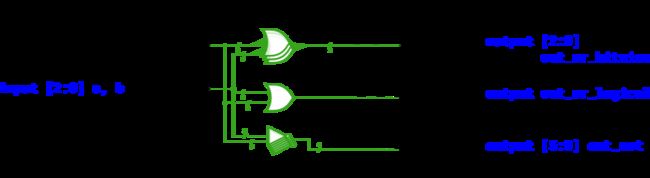
14.Bitwise operators | Vectorgates
Build a circuit that has two 3-bit inputs that computes the bitwise-OR of the two vectors, the logical-OR of the two vectors, and the inverse (NOT) of both vectors. Place the inverse of b in the upper half of out_not (i.e., bits [5:3]), and the inverse of a in the lower half.
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise = a | b;
assign out_or_logical = a || b;
assign out_not[5:3] = ~b;
assign out_not[2:0] = ~a;
endmodule
15.Four-input gates | Gates4
practice:
Build a combinational circuit with four inputs, in[3:0].
There are 3 outputs:
out_and: output of a 4-input AND gate.
out_or: output of a 4-input OR gate.
out_xor: output of a 4-input XOR gate.
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = in[3] & in[2] & in[1] & in[0];
assign out_or = in[3] | in[2] | in[1] | in[0];
assign out_xor = in[3] ^ in[2] ^ in[1] ^ in[0];
endmodule
注:其中代码可以简化为
assign out_and = & in;
assign out_or = | in;
assign out_xor = ^ in;
16.Vector concatenation operator | Vector3
practice:
Given several input vectors, concatenate them together then split them up into several output vectors. There are six 5-bit input vectors: a, b, c, d, e, and f, for a total of 30 bits of input. There are four 8-bit output vectors: w, x, y, and z, for 32 bits of output. The output should be a concatenation of the input vectors followed by two 1 bits:
module top_module (
input [4:0] a, b, c, d, e, f,
output [7:0] w, x, y, z );
assign {w,x,y,z} = {a,b,c,d,e,f,2'b11};
endmodule
17.Vector reversal 1 | Vectorr
practice:Given an 8-bit input vector [7:0], reverse its bit ordering.
module top_module(
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] out
);
assign out = {in[0],in[1],in[2],in[3],in[4],in[5],in[6],in[7]};
endmodule
18. Replication operator | Vector4
practice:Build a circuit that sign-extends an 8-bit number to 32 bits. This requires a concatenation of 24 copies of the sign bit (i.e., replicate bit[7] 24 times) followed by the 8-bit number itself.
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output [31:0] out );
assign out = {{24{in[7]}},in};
endmodule
注:1这里要非常注意大括号的使用,倍数和后面要成为一个整体,一开始少加一个括号,找了半天错误,后来看错误有提示,才知道。
19.More replication | Vector5
practice:

As the diagram shows, this can be done more easily using the replication and concatenation operators.
The top vector is a concatenation of 5 repeats of each input
The bottom vector is 5 repeats of a concatenation of the 5 inputs
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out );
assign out = ~{{5{a}},{5{b}},{5{c}},{5{d}},{5{e}}} ^ {5{a,b,c,d,e}};
endmodule
注:1、同样需要大括号