es 嵌套对象查询
文章目录
-
-
-
- 基础环境
- 嵌套查询的问题
- 使用 nested 类型
- join
- nested vs join
-
-
基础环境
- 使用docker来搭建环境(es+kibana)
- docker-compose.yaml 可以使用 https://github.com/xieruixiang/study_config/blob/master/docker/es_kibana/docker-compose.yaml 中的
- 后续的操作都在kibana中进行
嵌套查询的问题
下面的例子通过 PUT order 创建表结构,POST order/_doc/10001 填充表数据,goods 使用 es的自动类型推断,且是由多个对象组成
GET order/_search是想要获取 goods中 包含 {"name":"当归","num":5}的数据,正常应该是没有的,但是结果却查出来了
PUT order
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"type":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
POST order/_doc/10001
{
"id":10001,
"type":"changfan",
"goods":[
{
"id":1,
"name":"当归",
"price":102,
"num":1
},
{
"id":1,
"name":"人参",
"price":102,
"num":5
}
]
}
GET order/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"goods.num": {
"value": 5
}
}
},{
"match_phrase": {
"goods.name": "当归"
}
}
]
}
}
}
这种嵌套数据在es中是下面的存储格式
{
"goods.name":["当归","人参"],
"goods.num":[1,5]
}
使用 nested 类型
nested 类型用于处理嵌套的文档结构,其中一个文档中包含了另一个文档的数组。
将需要嵌套查询的字段设置为nested
PUT order2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"type":{
"type": "text"
},
"goods":{
"type": "nested"
}
}
}
}
POST order2/_doc/10001
{
"id":10001,
"type":"changfan",
"goods":[
{
"id":1,
"name":"当归",
"price":102,
"num":1
},
{
"id":1,
"name":"人参",
"price":102,
"num":5
}
]
}
使用 nested 进行查询
在普通的查询中 增加了 nested属性,其中path 指对那个属性进行嵌套查询,这个就解决了嵌套查询的问题
GET order2/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"nested": {
"path": "goods",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"goods.num": {
"value": 1
}
}
},
{
"match_phrase": {
"goods.name": "当归"
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
join
- join 在 mapping 中指定了父子文档的关系
- 有了关系就可以使用 has 查询,类似于 ORM框架 的 whereHas 过滤
- join 获取嵌套数据不像 nested 能够一次性取出
指定了goods的类型为 join, 关联关系为父子
PUT order3
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"type":{
"type": "text"
},
"goods":{
"type": "join",
"relations":{
"parent":"child"
}
}
}
}
}
创建父文档
POST order3/_doc/10001
{
"id":10001,
"type":"changfan",
"goods":{
"name":"parent"
}
}
创建子文档
POST order3/_doc/10001-1?routing=10001
{
"goods":{
"name":"child",
"parent":10001
},
"id": 1,
"name": "当归",
"price": 102,
"num": 1
}
POST order3/_doc/10001-2?routing=10001
{
"goods": {
"name": "child",
"parent": 10001
},
"id": 2,
"name": "人参",
"price": 102,
"num": 5
}
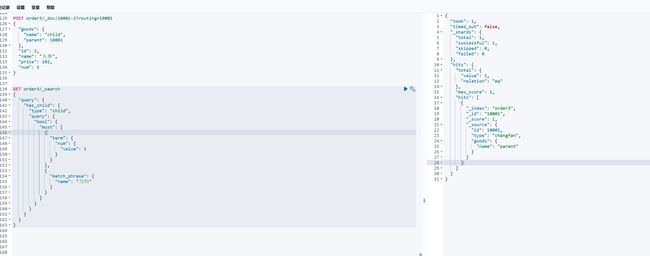
使用 has_child 查出符合条件的父文档
GET order3/_search
{
"query": {
"has_child": {
"type": "child",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"num": {
"value": 1
}
}
},
{
"match_phrase": {
"name": "当归"
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
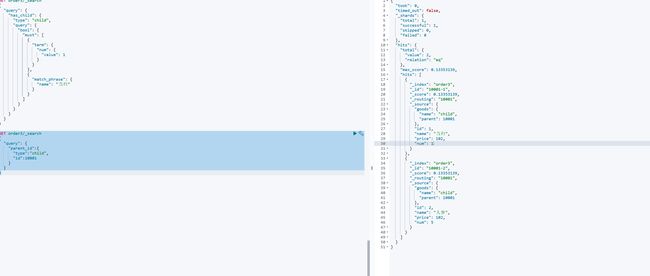
GET order3/_search
{
"query": {
"parent_id":{
"type":"child",
"id":10001
}
}
}
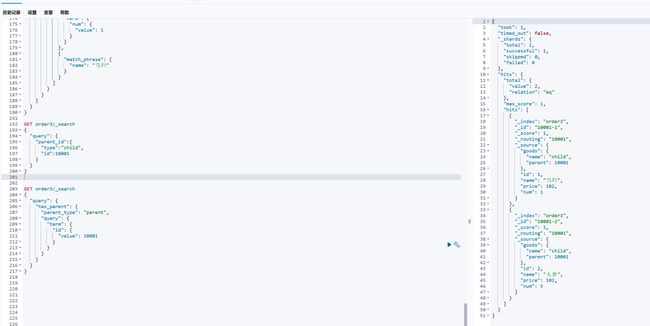
GET order3/_search
{
"query": {
"has_parent": {
"parent_type": "parent",
"query": {
"term": {
"id": {
"value": 10001
}
}
}
}
}
}
nested vs join
| nested | join | |
|---|---|---|
| 优点 | 读取更快 | 父子可以单独更新,不相互影响 |
| 缺点 | 不像join可以父子单独更新,只要更新,就全部受影响 | 由于父子分开,读取性能比 nested 差 |
| 常用场景 | 查多写少,需要获取全部子文档 | 子文档数量多,且更新频繁 |