Vuex(六)--Vue核心概念Module
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
/**
* 1) 包含多个 module
* 2) 一个 module 是一个 store 的配置对象
* 3) 与一个组件(包含有共享数据)对应
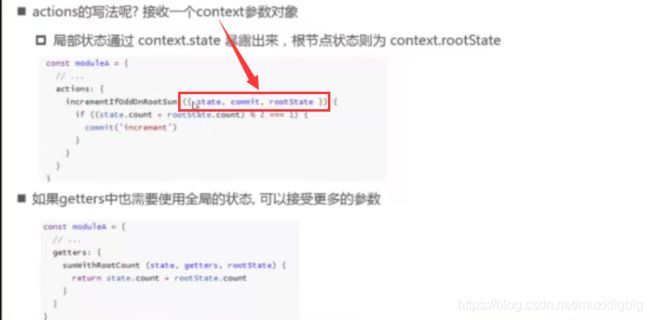
* 4) 谁来取值:组件:$store.state.module 名称.xxx
*/const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
实例
1.store.js
const moduleA = {
state: {
moduleAList: [{
name: 'A赣州橙子',
price: '8.8'
}, {
name: 'A新疆哈密瓜',
price: '2.0'
}, {
name: 'A山东大枣',
price: '3.2'
}, {
name: 'A阳澄湖大闸蟹',
price: '10.0'
}]
}, // 每个模块里面都可以自己的 state, getters,mutations,actions
// getters: { ... },
// mutations: { ... },
// actions: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: {
moduleBList: [{
name: 'B赣州橙子',
price: '8.8'
}, {
name: 'B新疆哈密瓜',
price: '2.0'
}, {
name: 'B山东大枣',
price: '3.2'
}, {
name: 'B阳澄湖大闸蟹',
price: '10.0'
}]
},
getters: { // 商品价格减半 // rootState:根节点的状态
moduleBgoodsPriceDiscount: (state, rootState)=> {
var moduleBgoodsPriceDiscount = state.moduleBList.map(function (item) {
return {
price: item.price / 2,
name: item.name
}
})
return moduleBgoodsPriceDiscount;
}
}
}
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
},
state: {
goodsList: [...],
},
getters: {...},
mutations: {...},
actions: {...},
})
page9.vue
Module
-
商品:{{item.name}}
价格:¥{{item.price}}
-
商品:{{item.name}}
价格:¥{{item.price}}
模块内部的mutations和actions这里就不再写了,自己动手补充。
有一个rootState属性(根节点的状态)
注意:
在取每个module中state的值的时候需要加上在vuex实例modules属性中的module名称
this.$store.state.a.moduleAListmodule的更多应用查看官方api链接
命名空间 namespaced: true
1.moduleA.js
export default {
// 为当前模块开启命名空间,每个模块里面都可以自己的 state, getters,mutations,actions
namespaced: true,
// 模块的 state 数据
state: () => ({
moduleAList: [{
name: 'A赣州橙子',
price: '8.8'
}, {
name: 'A新疆哈密瓜',
price: '2.0'
}, {
name: 'A山东大枣',
price: '3.2'
}, {
name: 'A阳澄湖大闸蟹',
price: '10.0'
}]
}),
// 模块的 mutations 方法
mutations: {
// mutations 中的函数,调用 mutations 中的函数,m_moduleA/函数
},
// 模块的 getters 属性
getters: {},
}2.store.js
import moduleA from './moduleA .js'
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
// TODO:挂载 store 模块
modules: {
// 2. 挂载购物车的 vuex 模块,模块内成员的访问路径被调整为 m_moduleA,例如:
// 购物车模块中 moduleAList 数组的访问路径是 m_moduleA/moduleAList
m_moduleA: moduleA,
},
})page9.vue
Module
-
商品:{{item.name}}
价格:¥{{item.price}}
项目结构
Vuex 并不限制你的代码结构。但是,它规定了一些需要遵守的规则:
-
应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中。
-
提交 mutation 是更改状态的唯一方法,并且这个过程是同步的。
-
异步逻辑都应该封装到 action 里面。
只要你遵守以上规则,如何组织代码随你便。如果你的 store 文件太大,只需将 action、mutation 和 getter 分割到单独的文件。
对于大型应用,我们会希望把 Vuex 相关代码分割到模块中。下面是项目结构示例: