日志系统——日志落地模块设计
一,大致框架
首先我们需要明确模块的功能,将格式化后的日志信息字符串,输出到对应的位置。同时由于用户输出信息的方式是多样的,因此我们日志落地模块也支持拓展的功能,也就是用户自定义落地方式。
日志信息落地的方式大概可以分为下面三种
1.标准输出,指的是将信息直接进行cout打印,程序相当简单,但是不方便分析
2.指定文件, 将日志信息打印到目标文件中,方便后续查看进程运行状况,但也有问题例如单个文件过大,多天的信息堆积一处不方便查询观看。
3.滚动文件,滚动文件分为两种:①按照文件大小进行切换,例如一个文件存储1G的内容,内容超出1G,重新创建文件存储。②按照时间进行切换,例如以天为单位,每一天都开一个新文件存储信息(该方式我们会以用户自定义输出方法的方法实现)。
实现思路:
1.抽象出一个日志落地模块基类
2.不同的落地方式从基类创建派生类实现
3.使用简单工厂模式,将对落地方式进行一层封装,也就是将创建和实现分开。
二,代码实现
2.1 sink.hpp
#ifndef _M_SINK_H_
#define _M_SINK_H_
#include "util.hpp"
#include "format.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
namespace mjwlog
{
// 基类
class Sink
{
public:
using ptr = std::shared_ptr;
Sink(){};
virtual ~Sink(){};
virtual void log(const char *msg, const size_t len) = 0;
};
// 标准输出落地方向
class StdoutSink : public Sink
{
public:
void log(const char *msg, const size_t len) override
{
std::cout.write(msg, len);
}
};
// 文件输出落地方向
class FileSink : public Sink
{
public:
// 先获得存储位置
FileSink(const std::string& filepath)
: _filepath(filepath)
{
// 在构造的时候就将文件打开
// 1.先判断目录是否存在,不存在创建
util::FileDirectory::createDirectory(util::FileDirectory::getDirectory(_filepath));
_ofs.open(_filepath, std::ios_base::binary | std::ios_base::app);
assert(_ofs.is_open()); // 打开失败,直接退出报错
}
// 写入内容
void log(const char *msg, const size_t len) override
{
_ofs.write(msg, len);
if (!_ofs.good())
{
std::cout << "日志写入文件失败" << std::endl;
}
}
private:
std::string _filepath;
std::ofstream _ofs;
};
// 滚动文件输出落地方向(按照大小)
class RollFileSink : public Sink
{
public:
// 先获得存储位置
// basepath:"/a/b/log"(自行添加后缀方便辨认) ->"/a/b/log200208051123.log-_filecount"
RollFileSink(const std::string& basepath,const size_t& max_size)
: _basepath(basepath),
_max_size(max_size),
_cur_size(0),
_filecount(1)
{
// 在构造的时候就将文件打开
//检查目录"/a/b/log"是否存在
util::FileDirectory::createDirectory(util::FileDirectory::getDirectory(_basepath));
//打开文件
creatfile();
}
// 写入内容
void log(const char *msg, const size_t len) override
{
//判断文件是否已满,满了就重新开文件
if(_cur_size>=_max_size)
{
creatfile();
//注意创建新文件后,_cur_size需要置为0
_cur_size=0;
}
_ofs.write(msg,len);
if (!_ofs.good())
{
std::cout << "日志写入文件失败" << std::endl;
}
_cur_size+=len;
}
private:
//辅助接口
//1.添加后缀
std::string AddSuffix()
{
std::string suffix = _basepath;
// basepath:"/a/b/log"(自行添加后缀方便辨认) ->"/a/b/log200208051123.log-_filecount"
time_t time = util::gettime::nowtime();
// localtime_r 函数获取时间详细属性
struct tm attr;
localtime_r(&time, &attr);
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_year+1900); // 年,默认从1900开始算,因此需要+1900
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_mon+1); // 月,0-11
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_mday); // 日
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_hour); // 时
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_min); // 分
suffix += ".log";
suffix+="-"+std::to_string(_filecount++);
return suffix;
}
//2.重新开文件
void creatfile()
{
//打开前需要将原文件关闭
_ofs.close();
// 1.先判断目录是否存在,不存在创建
std::string filepath=AddSuffix();
_ofs.open(filepath, std::ios_base::binary | std::ios_base::app);
assert(_ofs.is_open()); // 打开失败,直接退出报错
}
private:
std::string _basepath;
std::ofstream _ofs;
size_t _max_size; // 文件空间上限
size_t _cur_size; // 文件当前空间大小
int _filecount;
};
//简单工厂模式,将创建和实现方法分开
class SinkFactory
{
public:
template
static Sink::ptr LogSink(Args &&...args)
{
return std::make_shared(std::forward(args)...);
}
};
}
#endif 测试
#include "util.hpp"
#include "level.hpp"
#include "format.hpp"
#include "sink.hpp"
int main()
{
mjwlog::message msg(53,mjwlog::LogLevel::level::DEBUG,"test","root","日志格式化输出调试");
mjwlog::Formatter ft;
std::cout<();
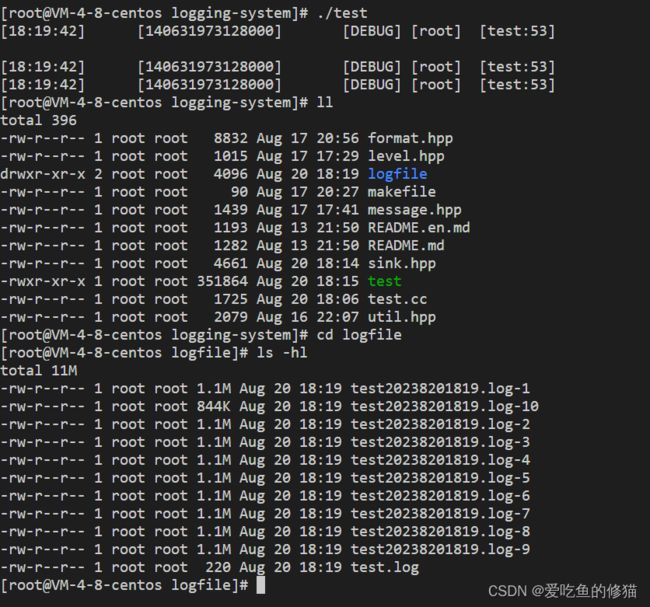
mjwlog::Sink::ptr file_ptr=mjwlog::SinkFactory::LogSink("./logfile/test.log");
//以1m为分界线,进行滚动文件输出
mjwlog::Sink::ptr rollfile_ptr=mjwlog::SinkFactory::LogSink("./logfile/test",1024*1024);
stdout_ptr->log(ft.format(msg).c_str(),ft.format(msg).size());
file_ptr->log(ft.format(msg).c_str(),ft.format(msg).size());
size_t testsize=0;
//我们写入10m的内容
while(testsize<1024*1024*10)
{
rollfile_ptr->log(ft.format(msg).c_str(),ft.format(msg).size());
testsize+=ft.format(msg).size();
}
//std::cout<<"abc\taaa"< 结果
2.2 自定义日志落地方式
这里我们以写入滚动文件(按照时间)为例
#include "util.hpp"
#include "level.hpp"
#include "format.hpp"
#include "sink.hpp"
// 滚动文件输出落地方向(按照时间)
enum class time_seg
{
SECOND = 0,
MINUTE,
HOUR,
DAY
};
//注意:当_seg以秒为单位时,getTimeSecond(_seg)返回1的话,任何数%1都为0
//这样就导致_create_time和_cur_time永远为0,这样就永远没办法创新文件
//因此当_seg以秒为单位时,_create_time和_cur_time不%上任何值
class TimeFileSink : public mjwlog::Sink
{
public:
// 先获得存储位置
// basepath:"/a/b/log"(自行添加后缀方便辨认) ->"/a/b/log200208051123.log-_filecount"
TimeFileSink(const std::string &basepath, const time_seg &seg)
: _basepath(basepath),
_seg(seg),
_create_time(0),
_cur_time(0),
_filecount(1)
{
// 在构造的时候就将文件打开
// 检查目录"/a/b/log"是否存在
mjwlog::util::FileDirectory::createDirectory(mjwlog::util::FileDirectory::getDirectory(_basepath));
// 打开文件
creatfile();
//确定创建时的时间段,注意每次重新创建文件都要重置_create_time
_create_time=_seg==time_seg::SECOND?mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime():mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime()%getTimeSecond(_seg);
}
// 写入内容
void log(const char *msg, const size_t len) override
{
// 判断文件是否已满,满了就重新开文件
_cur_time=_seg==time_seg::SECOND?mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime():mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime()%getTimeSecond(_seg);
if (_cur_time != _create_time)
{
creatfile();
// 注意创建新文件后,_cur_size需要置为0
_create_time=_seg==time_seg::SECOND?mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime():mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime()%getTimeSecond(_seg);
}
_ofs.write(msg, len);
if (!_ofs.good())
{
std::cout << "日志写入文件失败" << std::endl;
}
}
private:
// 辅助接口
// 1.添加后缀
std::string AddSuffix()
{
std::string suffix = _basepath;
// basepath:"/a/b/log"(自行添加后缀方便辨认) ->"/a/b/log200208051123.log-_filecount"
time_t time = mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime();
// localtime_r 函数获取时间详细属性
struct tm attr;
localtime_r(&time, &attr);
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_year + 1900); // 年,默认从1900开始算,因此需要+1900
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_mon + 1); // 月,0-11
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_mday); // 日
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_hour); // 时
suffix += std::to_string(attr.tm_min); // 分
suffix += ".log";
suffix += "-" + std::to_string(_filecount++);
return suffix;
}
// 2.重新开文件
void creatfile()
{
// 打开前需要将原文件关闭
_ofs.close();
// 1.先判断目录是否存在,不存在创建
std::string filepath = AddSuffix();
_ofs.open(filepath, std::ios_base::binary | std::ios_base::app);
assert(_ofs.is_open()); // 打开失败,直接退出报错
}
// 3.获取时间对应的秒数,SECOND——1
int getTimeSecond(time_seg seg)
{
switch (seg)
{
case time_seg::SECOND:
return 1;
case time_seg::HOUR:
return 60;
case time_seg::MINUTE:
return 2400;
case time_seg::DAY:
return 2400 * 24;
default:
std::cout << "暂时不支持当前间隔时间" << std::endl;
abort();
}
}
private:
std::string _basepath;
std::ofstream _ofs;
// 时间间隔,由用户确定
time_seg _seg;
// 例如我们以1秒为间隔分文件存储
// 创建文件时为第31秒,32秒存入内容时检测,发现两个时间段对不上
// 此时就需要重新创建文件写入日志
size_t _create_time; // 文件创建时的时间段
size_t _cur_time; // 现在的时间段
int _filecount;
};
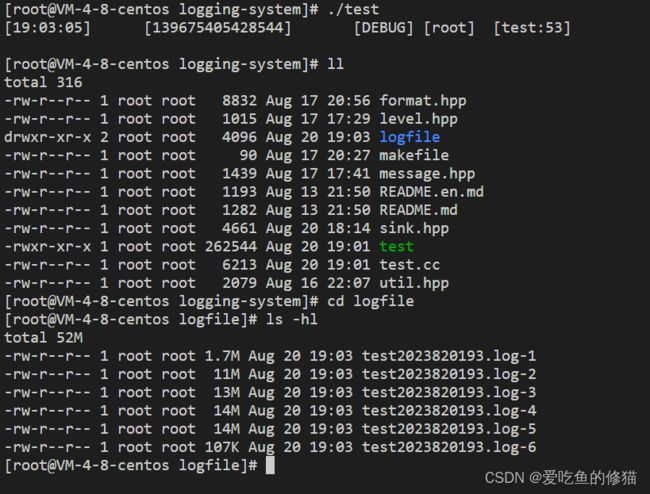
int main()
{
mjwlog::message msg(53, mjwlog::LogLevel::level::DEBUG, "test", "root", "日志格式化输出调试");
mjwlog::Formatter ft;
std::cout << ft.format(msg) << std::endl;
mjwlog::Sink::ptr timefile_ptr=mjwlog::SinkFactory::LogSink("./logfile/test",time_seg::SECOND);
time_t old=mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime();
while(mjwlog::util::gettime::nowtime()log(ft.format(msg).c_str(), ft.format(msg).size());
usleep(1000);
}
return 0;
} 结果
写入滚动文件(按照时间)落地方向,主要用来证明用户可以根据自己需要自定义日志落地,完成证明后,我们将其并入到sink.hpp中。