【C#】委托、匿名方法、Lambda表达式和事件
【C#】委托、匿名方法、Lambda表达式和事件
委托
什么是委托?
委托和类一样,是用户自定义类型,是方法(函数)的抽象。通俗讲,委托就是 自定义类型的方法(函数)的代表。
声明委托
//<访问修饰符> delegate <函数返回类型> <自定义委托名> (函数返回参数);
//定义 返回值为null 只有1个参数 且参数为int类型 的委托
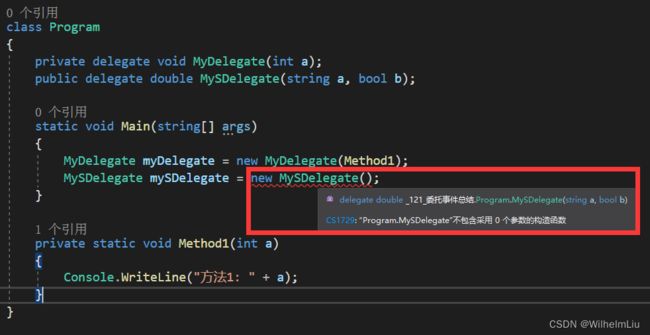
private delegate void MyDelegate(int a);
//定义 返回值为double 有2个参数 且参数为string 和 bool 类型 的委托
public delegate double MySDelegate(string a, bool b);
注意:委托可以在类里面和类外面声明。委托可以有参数,也可以无参数。返回类型可以为null,也可以为其他。
委托的实例化
委托对象必须使用new关键字来创建,且必须传入声明委托时 定义类型的方法(函数)作为注册方法。
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(Method1);//委托实例化
委托的使用
下列代码中,声明 返回一个带有string参数 返回值null 的委托,并且将Student实例对象stu1的Perform方法(函数)作为注册方法,进行实例化委托对象。
class Student
{
public void Perform(string content)
{
Console.WriteLine("学生表演关于" + content + "的内容");
}
}
class Program
{
private delegate void PerformDelegate(string content);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
PerformDelegate performDelegate = new PerformDelegate(stu1.Perform);
performDelegate("编写程序");//输出:学生表演关于编写程序的内容
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
委托的单播与多播
委托可以代表多个方法(函数),委托对象使用“=”进行赋值,此时的委托只有一个方法,称为单播。
委托对象可以使用“+=”添加相同类型方法(函数),或者使用“-=”移除委托对象中的方法(函数),这些操作会使得委托包含多个方法(函数),称为多播,又称组播。
private delegate string MethodDelegate(int a, int b);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MethodDelegate methodDelegate = Method1;//单播
methodDelegate += Method2;
methodDelegate += Method1;
methodDelegate -= Method1;
methodDelegate += Method2;
methodDelegate(1, 2);
//输出:
//Method1 : 3
//Method2 : 2
//Method2 : 2
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static string Method1(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 : " + (a + b));
return "" + (a + b);
}
private static string Method2(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2 : " + (a * b));
return "" + (a * b);
}
注意:对于有返回值的委托,将返回最后方法执行后的返回值。
Action委托和Func委托
两个委托都是系统内置的委托类型。
Action委托:返回值为空,有0-16个参数为任何类型的方法(函数)的委托类型。
Func委托:返回一个任何类型的值,有0-16个参数为任何类型的方法(函数)的委托类型。
class Program
{
private static void Method1(bool a, string b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Action<bool, string> actionDelegate = Method1;
actionDelegate(true, "a");//输出:Method1
Func<int, double, Program, object, string> funcDelegate = Method2;
funcDelegate(1, 2.2f, new Program(), (object)1);//输出:Method2
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static string Method2(int a, double b, Program c, object d)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2");
return "";
}
}
Action是 第一个参数为bool类型,第二个参数为string类型,返回null 的委托。
Func是 第一个参数为int类型,第二个参数为double类型,第三个为Program类型,第四个为object类型,返回string类型 的委托。
匿名方法与Lambda表达式
对于不需重复编写的代码内容,通过使用匿名方法或者Lambda表达式,可以不必创建单独的方法,从而能够精简代码的编写量。
1. 匿名方法
匿名方法的语法
delegate(<函数参数>){函数体};
匿名方法的使用
Action<bool, string> actionDelegate = delegate(bool a, string b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1");
};
actionDelegate(true, "a");//输出:Method1
2. Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式的语法
多个参数多条语句:(<函数参数>) => {函数体};
多个参数一条返回语句:(<函数参数>) => <返回语句>;
一个参数多条语句:<函数参数> => {函数体}
一个参数一条返回语句:<函数参数> => <返回语句>;
Lambda表达式的使用
//多个参数多条语句:(<函数参数>) => {函数体};
Func<double, bool, int> funcDelegate1 =
(a, b) =>{
if(b)
{
return (int)(a * a);
}
return (int)a;
};
Console.WriteLine("funcDelegate1 : " + funcDelegate1(2, true));//输出:funcDelegate1 : 4
//多个参数一条返回语句:(<函数参数>) => <返回语句>;
Func<int, bool, bool> funcDelegate2 = (a, b) => b;
Console.WriteLine("funcDelegate2 : " + funcDelegate2(2, false));//输出:funcDelegate2 : False
//一个参数多条语句:<函数参数> => {函数体}
Action<string> actionDelegate1 = a =>
{
string tmp = "actionDelegate1" + a;
Console.WriteLine(tmp);
};
actionDelegate1("函数体");//输出:actionDelegate1函数体
//一个参数一条返回语句:<函数参数> => <返回语句>;
Func<float, float> funcDelegate3 = x => x * x;
Console.WriteLine("funcDelegate3 : " + funcDelegate3(8));//输出:funcDelegate3 : 64
Console.ReadLine();
事件
事件是被“限制”的委托。
声明事件
public delegate void WriteDelegate();
//<访问修饰符> event 委托名 事件名
public event WriteDelegate WriteEvent;
事件的使用
class Student
{
private string Name { get; set; }
public Student(string Name)
{
this.Name = Name;
}
public void StartWriting()
{
Console.WriteLine(Name + "开始作答");
}
}
class Teacher
{
public delegate void WriteDelegate();
//<访问修饰符> event 委托名 事件名
public event WriteDelegate WriteEvent;
public void Begin()
{
WriteEvent();//引发事件
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
Student stu1 = new Student("张三");
Student stu2 = new Student("李四");
Student stu3 = new Student("王五");
Student stu4 = new Student("刘六");
teacher.WriteEvent += stu1.StartWriting;
teacher.WriteEvent += stu2.StartWriting;
teacher.WriteEvent += stu3.StartWriting;
teacher.WriteEvent += stu4.StartWriting;
teacher.Begin();
//输出:
//张三开始作答
//李四开始作答
//王五开始作答
//刘六开始作答
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
委托和事件的区别
- 事件不能再外部调用,而委托可以。
- 事件不能再外部使用“=”进行赋值,而委托可以。
因为作者精力有限,文章中难免出现一些错漏,敬请广大专家和网友批评、指正。