LInux之chrony服务器
目录
场景
重要性
LInux的两个时钟
硬件时钟
系统时钟
NTP协议
Chrony介绍
定义
组成 --- chronyd和chronyc
安装与配置
安装
Chrony配置文件分析
同步时间服务器
chronyc命令
chronyc sources输出分析
其它命令
查看时间服务器的状态
查看时间服务器是否在线
同步系统时钟
常见时区
案例
定位server端
编辑配置文件
重启服务并测试
设置node1端可以访问本机进行时间同步
定位node1端
重启服务进行测试
场景
重要性
由于IT系统中,准确的计时非常重要,有很多种原因需要准确计时
-
在网络传输中,数据包和日志需要准确的时间戳
-
各种应用程序中,如订单信息,交易信息等 都需要准确的时间戳
LInux的两个时钟
硬件时钟
BIOS时钟 --- 也就是我们主板中用电池供电的时钟,是将时间写入到BIOS中,系统断电后时间不会丢失,可以在开机时通过主板程序中进行设置
[root@localhost ~]# hwclock # 查看计算机的硬件时间系统时钟
Linux系统内的时钟 --- 是由Linux内核来提供的,系统时钟是基于内存,如果系统断电时间就会丢失
[root@localhost ~]# date # 查看软件时间
[root@localhost ~]# date -s 22:00 # 设置错误时间
[root@localhost ~]# date # 查看软件时间
[root@localhost ~]# hwclock -s # 向硬件时间同步
[root@localhost ~]# dateNTP协议
NTP(Network Time Protocol,网络时间协议)--- 是由RFC 1305定义的时间同步协议,用来在分布式时间服务器和客户端之间进行时间同步
NTP基于UDP报文进行传输,使用的UDP端口号为123
NTP可以对网络内所有具有时钟的设备进行时钟同步,使网络内所有设备的时钟保持一致,从而使设备能够提供基于统一时间的多种应用,对于运行NTP的本地系统,既可以接受来自其他时钟源的同步,又可以作为时钟源同步其他的时钟,并且可以和其他设备互相同步
NTP的其精度在局域网内可达0.1ms,在互联网上绝大多数的地方其精度可以达到1-50ms
Chrony介绍
定义
chrony --- 一个开源的自由软件,它能帮助你保持系统时钟与时钟服务器(NTP)同步,因此让你的时间保持精确
组成 --- chronyd和chronyc
chronyd --- 是一个后台运行的守护进程,用于调整内核中运行的系统时钟和时钟服务器同步。它确定计算机增减时间的比率,并对此进行补偿
chronyc --- 提供了一个用户界面,用于监控性能并进行多样化的配置。它可以在chronyd实例控制的计算机上工作,也可以在一台不同的远程计算机上工作
注意:
Chrony与NTP都是时间同步软件,两个软件不能够同时开启,会出现时间冲突
安装与配置
安装
[root@localhost ~]# yum install chrony -y # 安装
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start chronyd # 启动服务
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status chronyd # 查看状态Chrony配置文件分析
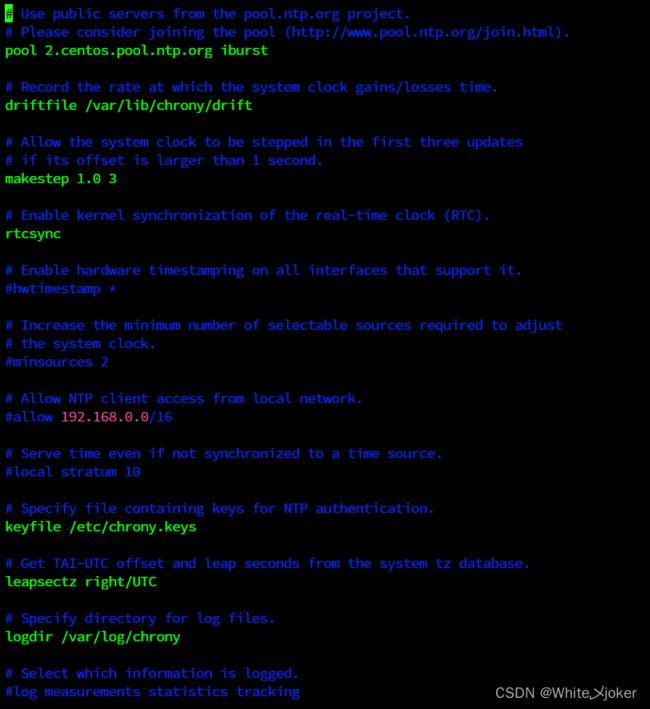
主配置文件 --- /etc/chrony.conf
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
# 使用 pool.ntp.org 项目中的公共服务器
# 或者使用server开头的服务器,理论上想添加多少时间服务器都可以
# iburst表示的是首次同步的时候快速同步
pool 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Record the rate at which the system clock gains/losses time.
# 根据实际时间计算出服务器增减时间的比率,然后记录到一个文件中,在系统重启后为系统做出最佳时间 补偿调整
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift
# Allow the system clock to be stepped in the first three updates
# if its offset is larger than 1 second.
# 如果系统时钟的偏移量大于1秒,则允许系统时钟在前三次更新中步进
makestep 1.0 3
# Enable kernel synchronization of the real-time clock (RTC).
# 启用实时时钟(RTC)的内核同步
rtcsync
# Enable hardware timestamping on all interfaces that support it.
# 通过使用 hwtimestamp 指令启用硬件时间戳
#hwtimestamp *
# Increase the minimum number of selectable sources required to adjust
# the system clock.
#minsources 2
# Allow NTP client access from local network.
# 指定 NTP 客户端地址,以允许或拒绝连接到扮演时钟服务器的机器
#allow 192.168.0.0/16
# Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source.
#local stratum 10
# Specify file containing keys for NTP authentication.
# 指定包含 NTP 身份验证密钥的文件
keyfile /etc/chrony.keys
# Get TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system tz database.
leapsectz right/UTC
# Specify directory for log files.
# 指定日志文件的目录
logdir /var/log/chrony
# Select which information is logged.
# 选择日志文件要记录的信息
#log measurements statistics tracking同步时间服务器
完成时间同步,修改默认的时间服务器地址
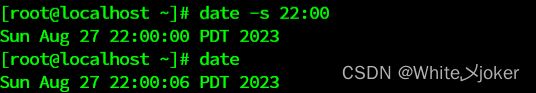
[root@localhost ~]# date -s 22:00 # 修改为错误时间
[root@localhost ~]# date # 查看修改后的错误时间[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf
# 删除所有内容,复制粘贴阿里官方的配置
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst
stratumweight 0
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift
rtcsync
makestep 10 3
bindcmdaddress 127.0.0.1
bindcmdaddress ::1
keyfile /etc/chrony.keys
commandkey 1
generatecommandkey
logchange 0.5
logdir /var/log/chrony内容[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart chronyd # 重要:必须重启服务,才会生效
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc source -v # 时间同步
[root@localhost ~]# timedatectl status chronyc命令
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc sources -v # -v参数表示显示内容是否有解释chronyc sources输出分析
M --- 这表示信号源的模式。^表示服务器,=表示对等方,#表示本地连接的参考时钟
![]()
S --- 此列指示源的状态
| 符号 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| * | chronyd当前同步到的源 |
| + | 表示可接受的信号源,与选定的信号源组合在一起 |
| - | 表示被合并算法排除的可接受源 |
| ? | 表示已失去连接的源 |
| x | 表示chronyd认为是虚假行情的时钟(即,其时间与大多数其他来源不一致) |
| ~ | 表示时间似乎具有太多可变性的来源 |
Name/IP address --- 显示服务器源的名称或IP地址
Stratum --- 表示源的层级,层级1表示本地连接的参考时钟,第2层表示通过第1层级计算机的时钟实现同步,依此类推
Poll --- 表示源轮询频率,以秒为单位,值是基数2的对数,例如值6表示每64秒进行一次测量,chronyd会根据当时的情况自动改变轮询频率
Reach --- 表示源的可达性的锁存值(八进制数值),该锁存值有8位,并在当接收或丢失一次时进行一次更新,值377表示最后八次传输都收到了有效的回复
LastRx --- 表示从源收到最近的一次的时间,通常是几秒钟,字母m,h,d或y分别表示分钟,小时,天或年
Last sample --- 表示本地时钟与上次测量时源的偏移量,方括号左侧的数字表示原始测量值,方括号右侧表示偏差值,+/-指示器后面的数字表示测量中的误差范围。正偏移表示本地时钟位于源时钟之前
其它命令
查看时间服务器的状态
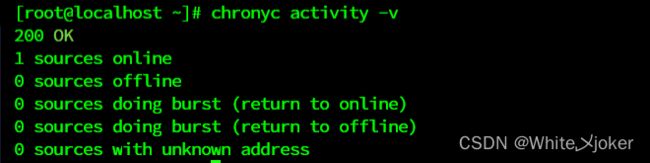
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc sourcestats -v查看时间服务器是否在线
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc activity -v同步系统时钟
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc -a makestep 常见时区
UTC --- 整个地球分为二十四时区,每个时区都有自己的本地时间。在国际无线电通信场合,为了统一起见,使用一个统一的时间,称为通用协调时(UTC, Universal Time Coordinated)。
GMT --- 格林威治标准时间 (Greenwich Mean Time)指位于英国伦敦郊区的格林尼治天文台的标准时间,因为本初子午线被定义在通过那里的经线。(UTC与GMT时间基本相同)
CST --- 中国标准时间 (China Standard Time)GMT + 8 = UTC + 8 = CST
DST --- 夏令时(Daylight Saving Time) 指在夏天太阳升起的比较早时,将时间拨快一小时,以提早日光的使用。(中国不使用)
案例
使用server主机向阿里时间同步服务器进行时间同步,并向node1主机提供时间同步服务,node1主机向server主机提出时间同步申请
定位server端
编辑配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf
# 编辑配置文件,定位定3行,修改为阿里的时间同步服务器地址
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst重启服务并测试
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart chronyd
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc sources -v
[root@localhost ~]# timedatectl status 设置node1端可以访问本机进行时间同步
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf
#编辑配置文件,定位定26行,设置谁可以访问本机进行时间同步
allow 192.168.149.137 # IP地址改为node1主机的地址定位node1端
[root@localhost ~]# yum install chrony -y
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf重启服务进行测试
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart chronyd
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc sources -v #查看时间服务器的IP是否为server端的IP地址[root@localhost ~]# timedatectl status注意:出现错误如何拍错
检查网络连通性,需要能ping通
检查server端的allow查看设置是否正确
需要重启服务