【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_DECIDER
文章目录
- 前言
- PATH_DECIDER功能简介
- PATH_DECIDER相关配置
- PATH_DECIDER总体流程
-
- 路径决策代码流程及框架
- MakeStaticObstacleDecision
- PATH_DECIDER相关子函数
- 参考
前言
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {
stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGE
enabled: true
task_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
task_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_DECIDER
task_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
task_type: SPEED_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第7个TASK——PATH_DECIDER
PATH_DECIDER功能简介
根据选出的路径给出对障碍物的决策
 若是绕行的路径,则产生绕行的决策;若前方有障碍物阻塞,则产生停止的决策。
若是绕行的路径,则产生绕行的决策;若前方有障碍物阻塞,则产生停止的决策。
PATH_DECIDER相关配置
modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
default_task_config: {
task_type: PATH_DECIDER
path_decider_config{
static_obstacle_buffer: 0.3
}
}
modules/planning/proto/task_config.proto
//
// PathDeciderConfig
message PathDeciderConfig {
// buffer for static obstacles (meter)
optional double static_obstacle_buffer = 1 [default = 0.3];
}
PATH_DECIDER总体流程
输入:
Status PathDecider::Process(const ReferenceLineInfo *reference_line_info,
const PathData &path_data,
PathDecision *const path_decision) {
输出:
路径决策的信息都保存到了path_decision中。
路径决策代码流程及框架

在Process函数主要功能是调用了MakeObjectDecision函数。而在MakeObjectDecision函数中调用了MakeStaticObstacleDecision函数。
路径决策的主要功能都在MakeStaticObstacleDecision中。这部分代码还是比较清晰的。
Status PathDecider::Process(const ReferenceLineInfo *reference_line_info,
const PathData &path_data,
PathDecision *const path_decision) {
// skip path_decider if reused path
if (FLAGS_enable_skip_path_tasks && reference_line_info->path_reusable()) {
return Status::OK();
}
std::string blocking_obstacle_id;
if (reference_line_info->GetBlockingObstacle() != nullptr) {
blocking_obstacle_id = reference_line_info->GetBlockingObstacle()->Id();
}
// 调用MakeObjectDecision函数
if (!MakeObjectDecision(path_data, blocking_obstacle_id, path_decision)) {
const std::string msg = "Failed to make decision based on tunnel";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
return Status::OK();
}
bool PathDecider::MakeObjectDecision(const PathData &path_data,
const std::string &blocking_obstacle_id,
PathDecision *const path_decision) {
// path decider的主要功能在MakeStaticObstacleDecision中
if (!MakeStaticObstacleDecision(path_data, blocking_obstacle_id,
path_decision)) {
AERROR << "Failed to make decisions for static obstacles";
return false;
}
return true;
}
MakeStaticObstacleDecision
获取frenet坐标系下的坐标
... ...
// 1.获取frenet坐标下的path路径
const auto &frenet_path = path_data.frenet_frame_path();
if (frenet_path.empty()) {
AERROR << "Path is empty.";
return false;
}
... ...
根据障碍物做决策
... ...
// 2.遍历每个障碍物,做决策
for (const auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
const std::string &obstacle_id = obstacle->Id();
const std::string obstacle_type_name =
PerceptionObstacle_Type_Name(obstacle->Perception().type());
ADEBUG << "obstacle_id[<< " << obstacle_id << "] type["
<< obstacle_type_name << "]";
... ...
如果障碍物不是静态或virtual,则跳过
// 2.1 如果障碍物不是静态的或者是virtual的,就跳过
if (!obstacle->IsStatic() || obstacle->IsVirtual()) { // (stop fence,各种fence)
continue;
}
如果障碍物有了ignore/stop决策,则跳过
// 2.2 如果障碍物已经有 ignore/stop 决策,就跳过
if (obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision() &&
obstacle->LongitudinalDecision().has_ignore() &&
obstacle->HasLateralDecision() &&
obstacle->LateralDecision().has_ignore()) {
continue;
}
if (obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision() &&
obstacle->LongitudinalDecision().has_stop()) {
// STOP decision
continue;
}
如果障碍物挡住了路径,加stop决策
// 2.3 如果障碍物挡住了路径,加stop决策
if (obstacle->Id() == blocking_obstacle_id &&
!injector_->planning_context()
->planning_status()
.path_decider()
.is_in_path_lane_borrow_scenario()) {
// Add stop decision
ADEBUG << "Blocking obstacle = " << blocking_obstacle_id;
ObjectDecisionType object_decision;
*object_decision.mutable_stop() = GenerateObjectStopDecision(*obstacle);
path_decision->AddLongitudinalDecision("PathDecider/blocking_obstacle",
obstacle->Id(), object_decision);
continue;
}
如果是clear-zone,跳过
// 2.4 如果是clear-zone,跳过
if (obstacle->reference_line_st_boundary().boundary_type() ==
STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
continue;
}
如果障碍物不在路径上,跳过
// 2.5 如果障碍物不在路径上,跳过
ObjectDecisionType object_decision;
object_decision.mutable_ignore();
const auto &sl_boundary = obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary();
if (sl_boundary.end_s() < frenet_path.front().s() ||
sl_boundary.start_s() > frenet_path.back().s()) {
path_decision->AddLongitudinalDecision("PathDecider/not-in-s",
obstacle->Id(), object_decision);
path_decision->AddLateralDecision("PathDecider/not-in-s", obstacle->Id(),
object_decision);
continue;
}
nudge判断
- 如果距离静态障碍物距离太远,则忽略。
- 如果静态障碍物距离车道中心太近,则停止。
- 如果横向方向很近,则避开。
// 2.6 nudge判断,如果距离静态障碍物距离太远,则忽略。
// 如果静态障碍物距离车道中心太近,则停止。
// 如果横向方向很近,则避开。
if (curr_l - lateral_radius > sl_boundary.end_l() ||
curr_l + lateral_radius < sl_boundary.start_l()) {
// 1. IGNORE if laterally too far away.
path_decision->AddLateralDecision("PathDecider/not-in-l", obstacle->Id(),
object_decision);
} else if (sl_boundary.end_l() >= curr_l - min_nudge_l &&
sl_boundary.start_l() <= curr_l + min_nudge_l) {
// 2. STOP if laterally too overlapping.
*object_decision.mutable_stop() = GenerateObjectStopDecision(*obstacle);
if (path_decision->MergeWithMainStop(
object_decision.stop(), obstacle->Id(),
reference_line_info_->reference_line(),
reference_line_info_->AdcSlBoundary())) {
path_decision->AddLongitudinalDecision("PathDecider/nearest-stop",
obstacle->Id(), object_decision);
} else {
ObjectDecisionType object_decision;
object_decision.mutable_ignore();
path_decision->AddLongitudinalDecision("PathDecider/not-nearest-stop",
obstacle->Id(), object_decision);
}
} else {
// 3. NUDGE if laterally very close.
if (sl_boundary.end_l() < curr_l - min_nudge_l) { // &&
// sl_boundary.end_l() > curr_l - min_nudge_l - 0.3) {
// LEFT_NUDGE
ObjectNudge *object_nudge_ptr = object_decision.mutable_nudge();
object_nudge_ptr->set_type(ObjectNudge::LEFT_NUDGE);
object_nudge_ptr->set_distance_l(
config_.path_decider_config().static_obstacle_buffer());
path_decision->AddLateralDecision("PathDecider/left-nudge",
obstacle->Id(), object_decision);
} else if (sl_boundary.start_l() > curr_l + min_nudge_l) { // &&
// sl_boundary.start_l() < curr_l + min_nudge_l + 0.3) {
// RIGHT_NUDGE
ObjectNudge *object_nudge_ptr = object_decision.mutable_nudge();
object_nudge_ptr->set_type(ObjectNudge::RIGHT_NUDGE);
object_nudge_ptr->set_distance_l(
-config_.path_decider_config().static_obstacle_buffer());
path_decision->AddLateralDecision("PathDecider/right-nudge",
obstacle->Id(), object_decision);
}
}
PATH_DECIDER相关子函数
GenerateObjectStopDecision主要用以生成停止决策。
ObjectStop PathDecider::GenerateObjectStopDecision(
const Obstacle &obstacle) const {
ObjectStop object_stop;
// Calculate stop distance with the obstacle using the ADC's minimum turning radius
double stop_distance = obstacle.MinRadiusStopDistance(
VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param());
object_stop.set_reason_code(StopReasonCode::STOP_REASON_OBSTACLE);
object_stop.set_distance_s(-stop_distance);
// 停止时的参考位置
const double stop_ref_s =
obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().start_s() - stop_distance;
const auto stop_ref_point =
reference_line_info_->reference_line().GetReferencePoint(stop_ref_s);
object_stop.mutable_stop_point()->set_x(stop_ref_point.x());
object_stop.mutable_stop_point()->set_y(stop_ref_point.y());
object_stop.set_stop_heading(stop_ref_point.heading());
return object_stop;
}
对于停止距离的计算,会调用MinRadiusStopDistance函数,
modules/planning/common/obstacle.cc
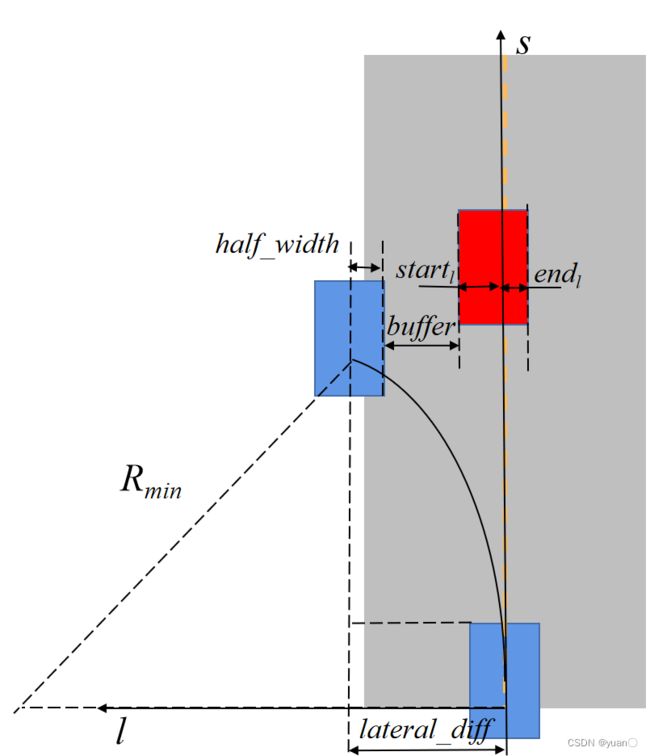
double Obstacle::MinRadiusStopDistance(
const common::VehicleParam& vehicle_param) const {
if (min_radius_stop_distance_ > 0) {
return min_radius_stop_distance_;
}
// 定义一个停止距离的缓冲区0.5m
static constexpr double stop_distance_buffer = 0.5;
// 获取最小安全转弯半径
const double min_turn_radius = VehicleConfigHelper::MinSafeTurnRadius();
// 计算横向距离
double lateral_diff =
vehicle_param.width() / 2.0 + std::max(std::fabs(sl_boundary_.start_l()),
std::fabs(sl_boundary_.end_l()));
const double kEpison = 1e-5;
lateral_diff = std::min(lateral_diff, min_turn_radius - kEpison);
// 勾股定理求得停止距离
double stop_distance =
std::sqrt(std::fabs(min_turn_radius * min_turn_radius -
(min_turn_radius - lateral_diff) *
(min_turn_radius - lateral_diff))) +
stop_distance_buffer;
// 减掉车辆前端到后轴中心的距离
stop_distance -= vehicle_param.front_edge_to_center();
// 限幅
stop_distance = std::min(stop_distance, FLAGS_max_stop_distance_obstacle); // 10.0
stop_distance = std::max(stop_distance, FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle); // 6.0
return stop_distance;
}
modules/common/configs/vehicle_config_helper.cc
double VehicleConfigHelper::MinSafeTurnRadius() {
const auto ¶m = vehicle_config_.vehicle_param();
double lat_edge_to_center =
std::max(param.left_edge_to_center(), param.right_edge_to_center());
double lon_edge_to_center =
std::max(param.front_edge_to_center(), param.back_edge_to_center());
return std::sqrt((lat_edge_to_center + param.min_turn_radius()) *
(lat_edge_to_center + param.min_turn_radius()) +
lon_edge_to_center * lon_edge_to_center);
}
MinSafeTurnRadius这段函数是获取当车辆以最大转向角转弯时的最大安全转弯半径。具体计算参考下图:

A , B , C , D A,B,C,D A,B,C,D分别是车辆的四个角, X O XO XO是车辆的最小转弯半径VehicleParam.min_turn_radius(), X X X与 A D AD AD之间的距离是左边缘到中心的距离left_edge_to_center, X X X与 A B AB AB之间的距离是前边缘到中心的距离front_edge_to_center。最大安全转弯半径则是 A O AO AO,定义中心到横向边缘最长的距离为 l l a t l_{lat} llat,到纵向边缘最长的距离为 l l o n l_{lon} llon, A O AO AO计算公式如下:
A O = ( X O + l l a t ) 2 + l l o n 2 AO=\sqrt{(XO+l_{lat})^2+{l_{lon}}^2} AO=(XO+llat)2+llon2
个人感觉这么做是为了获得足够的安全冗余量。
参考
[1] 路径决策