Android 蓝牙开发(一)
蓝牙简介
蓝牙(Bluetooth)是一种无线技术标准,能够在短距离内实现设备之间的数据交换和通信。蓝牙技术最初由瑞典爱立信公司于1994年开发,其名称源自丹麦国王哈拉尔·布吕特的译名“Harald Bluetooth”,他曾统一了斯堪的纳维亚半岛。
蓝牙技术是基于无线射频技术的,工作频率为2.4GHz,可支持多达8个设备同时连接。蓝牙技术应用广泛,包括手机、电脑、音频设备、手环、智能家居等领域,可以实现数据传输、音频传输、遥控和定位等功能。蓝牙技术的优点包括低功耗、低成本、易于使用和可靠性高等,成为了现代通信领域不可或缺的一部分。
前言
蓝牙是一种短距离无线通信技术,我们相对熟悉的移动端设备短距离通信技术有NFC,红外,蓝牙 ;
NFC:主要应用于操作简单,即时相应的刷卡
红外:主要应用于需要按键控制,例如家电遥控
蓝牙:主要用于两部设备之间复杂且大量的数据传输(这里又分为低功耗蓝牙和经典蓝牙)今天小编给大家分享的是经典蓝牙
Android蓝牙开发步骤
1.检查设备是否支持蓝牙
在应用程序中,你需要首先检查设备是否支持蓝牙。你可以在AndroidManifest.xml文件中声明必需的蓝牙权限,并使用BluetoothAdapter类来查询设备是否支持蓝牙
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if (bluetoothAdapter == null) {
// 该设备不支持蓝牙
} else {
// 该设备支持蓝牙
}
2.打开蓝牙
在你的应用程序中,你需要引导用户打开他们的蓝牙功能。你可以使用ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE活动提供一个请求
if (!bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
//如果该设备蓝牙未开启
Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);
}
3.扫描可用蓝牙设备
一旦蓝牙已启用,你就可以开始扫描设备了。你可以使用BluetoothAdapter类和BluetoothDevice类执行扫描操作
bluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();
可以使用BroadcastReceiver类来接收扫描结果:
private final BroadcastReceiver broadcastReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
//该设备成功搜索到蓝牙设备
}
}
};4.选择蓝牙并与其配对成功
通过BluetoothAdapter对象,你可以来进行蓝牙配对。你需要将BluetoothDevice类实例化并使用其connect()方法来建立连接
BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
BluetoothDevice device = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(address);
device.createBond();
5.选择蓝牙并与其建立连接
通过BluetoothDevice对象,你可以使用BluetoothSocket类来建立蓝牙连接。你需要将BluetoothSocket类实例化并使用其connect()方法来建立连接
BluetoothSocket socket = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
socket.connect();
6.数据传输
一旦蓝牙连接已建立,你可以使用BluetoothSocket的getInputStream()和getOutputStream()方法来发送和接收数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
以上就是Android蓝牙开发的基本流程,需要注意的是在实际开发中,还需要处理蓝牙连接的断开、多设备连接等复杂情况
7.断开蓝牙连接并关闭蓝牙
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
bluetoothAdapter.disable(); //关闭蓝牙
注意:Android提供了蓝牙模块的管理工具BluetoothAdapter(蓝牙适配器)
BluetoothAdapter类的一些常用方法说明:
1. enable() - 开启蓝牙
2. disable() - 关闭蓝牙
3. startDiscovery() - 开始搜索设备
4. cancelDiscovery() - 取消搜索设备
5. getBondedDevices() - 获取已配对的设备列表
6. getRemoteDevice(String address) - 获取远程设备对象
7. setState(int state) - 设置蓝牙状态
8. setScanMode(int mode) - 设置扫描模式
9. getScanMode() - 获取扫描模式
10. getName() - 获取本地蓝牙设备名称
11. setName(String name) - 设置本地蓝牙设备名称
12. getAddress() - 获取本地蓝牙设备地址
13. isDiscovering:判断是否正在搜索周围的蓝牙设备
14. getBluetoothLeScanner() - 获取BluetoothLeScanner对象
15. getProfileProxy(Context context, BluetoothProfile.ServiceListener listener, int profile) - 获取BluetoothProfile对象
16. closeProfileProxy(int profile, BluetoothProfile proxy) - 关闭BluetoothProfile对象的连接
Android蓝牙开发效果演示
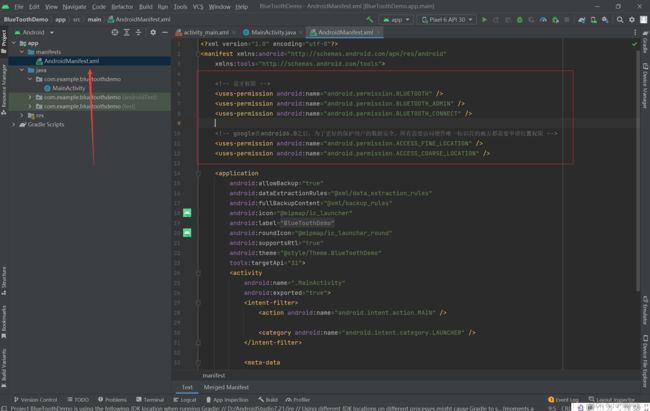
1. 声明蓝牙权限
新建一个Android项目,然后在AndroidManifest清单文件里声明相关的权限
2. 动态获取定位权限
package com.example.bluetoothdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.Manifest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//判断是否有访问位置的权限,没有权限,直接申请位置权限
isPermission();
}
//动态获取位置权限
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private void isPermission(){
if ((checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
|| (checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
requestPermissions(new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION}, 200);
}
}
}运行效果:
3. 判断该设备是否支持蓝牙功能
package com.example.bluetoothdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.Manifest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if (isBluetoothSupport()){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "该设备支持蓝牙功能", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "该设备不支持蓝牙功能", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
//判断该设备是否支持蓝牙功能
private Boolean isBluetoothSupport(){
if(mBluetoothAdapter == null){
return false;
}else {
return true;
}
}
}运行效果:
4. 判断本机是否开启蓝牙
package com.example.bluetoothdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.Manifest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
//判断蓝牙是否打开
if(!isBluetoothEnabled()){
//如果蓝牙未开启,则申请打开蓝牙
Intent enableBluetoothIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableBluetoothIntent, RESULT_CANCELED);
}else {
}
}
/**
* 检查该设备蓝牙是否开启
*/
private boolean isBluetoothEnabled(){
if(mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode == RESULT_CANCELED) {
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
// 蓝牙已成功开启
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "用户已开启蓝牙", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
// 用户取消了蓝牙开启请求
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "用户已拒绝开启蓝牙", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
}运行效果:
5. 获取设备已配对过的蓝牙设备
package com.example.bluetoothdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.Manifest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.Set;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
@SuppressLint({"MissingPermission", "MissingInflatedId"})
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
//判断是否有访问位置的权限,没有权限,直接申请位置权限
isPermission();
getPairedDevices();
}
//动态获取位置权限
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private void isPermission(){
if ((checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
|| (checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
requestPermissions(new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION}, 200);
}
}
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
private void getPairedDevices() {
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
Set pairedDevices = bluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices();
if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) {
for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) {
String deviceName = device.getName();
String deviceHardwareAddress = device.getAddress();
Log.d("MainActivity","设备名:"+deviceName+'\n'+"地址:"+deviceHardwareAddress);
}
}
}
} 运行效果:
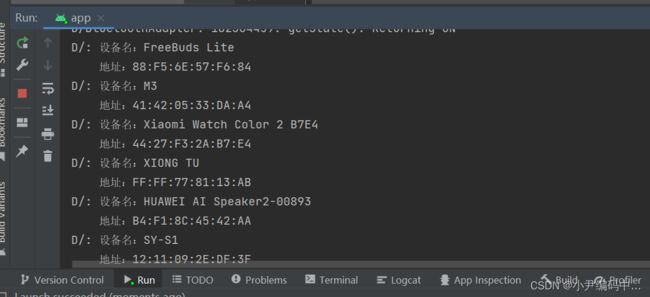
6. 搜索蓝牙设备
package com.example.bluetoothdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.Manifest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.Set;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
@SuppressLint({"MissingPermission", "MissingInflatedId"})
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
//判断是否有访问位置的权限,没有权限,直接申请位置权限
isPermission();
mBluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();
registerBluetoothReceiver();
}
//动态获取位置权限
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private void isPermission(){
if ((checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
|| (checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
requestPermissions(new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION}, 200);
}
}
private void registerBluetoothReceiver(){
//filter注册广播接收器
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
//蓝牙当前状态
filter.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_STATE_CHANGED);
//开始扫描蓝牙设备广播
filter.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_STARTED);
//找到蓝牙设备广播
filter.addAction(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND);
//扫描蓝牙设备结束广播
filter.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED);
//蓝牙设备配对状态改变广播
filter.addAction(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED);
//设备扫描模式改变广播
filter.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_SCAN_MODE_CHANGED);
registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
}
//处理找到蓝牙设备和搜索完成的广播消息
BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
//开始查找设备
if(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_STARTED.equals(action)){
Log.d("","开始查找");
}
//找到蓝牙设备
else if(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)){
//搜到蓝牙设备
BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
//把搜索到的设备添加到已找到列表中,显示它的信息
Log.d("","设备名:"+device.getName()+'\n'+"地址:"+device.getAddress());
}
//查找设备结束
else if(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED.equals(action)){
//搜索完毕
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "选择要配对的蓝牙设备", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.d("","查找结束");
}
}
};
}运行效果:
7. 配对蓝牙设备
package com.example.bluetoothdemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.Manifest;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.Set;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
@SuppressLint({"MissingPermission", "MissingInflatedId"})
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
//判断是否有访问位置的权限,没有权限,直接申请位置权限
isPermission();
getPairedDevices();
}
//动态获取位置权限
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private void isPermission(){
if ((checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
|| (checkSelfPermission(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
requestPermissions(new String[]{Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION}, 200);
}
}
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
private void getPairedDevices() {
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
Set pairedDevices = bluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices();
if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) {
int i=0;
for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) {
i++;
if(i==pairedDevices.size()){
device.createBond();
Log.d("","本机与另一个蓝牙设备"+device.getName()+"成功配对");
}
String deviceName = device.getName();
String deviceHardwareAddress = device.getAddress();
Log.d("","设备名:"+deviceName+'\n'+"地址:"+deviceHardwareAddress);
}
}
}
} 运行效果:
这一篇文章就先分享到这里,大家可以把代码复制一下去运行;下一篇再给大家分享一下蓝牙项目实战用法
Android蓝牙开发注意事项:
-
确保设备支持蓝牙:在开发之前,请确保您的设备支持蓝牙。大多数现代智能手机和平板电脑都支持蓝牙。
-
获取必要的权限:在开发蓝牙应用之前,您需要获取适当的权限。例如,您需要请求“android.permission.BLUETOOTH”权限,以便您的应用程序可以使用蓝牙。
-
确定您需要的蓝牙配置类型:Android提供了两种不同的蓝牙配置类型:经典蓝牙和低功耗蓝牙。使用低功耗蓝牙可以延长设备电池寿命,但需要Android 4.3(API level 18)或更高版本。
-
确保您的应用程序与其他应用程序兼容:在您的应用程序中使用蓝牙之前,请确保它与其他应用程序兼容。如果您的应用程序和其他应用程序同时使用蓝牙,可能会导致冲突和不稳定的行为。
-
使用正确的蓝牙协议:在开发蓝牙应用程序时,您需要确保使用正确的蓝牙协议。不同的设备和应用程序可能使用不同的蓝牙协议,因此您需要确定您的应用程序需要使用哪些协议。
-
处理错误和异常:在使用蓝牙时,可能会出现错误和异常。要确保您的应用程序具有适当的错误处理和异常处理代码,以确保它可以在出现问题时正确地处理蓝牙连接。
-
调试您的应用程序:在开发蓝牙应用程序时,请确保使用适当的调试工具。Android Studio提供了一些内置的调试工具,用于诊断和修复蓝牙连接问题。
-
避免使用已知的蓝牙错误:在使用蓝牙时,可能会出现许多已知的错误。要避免这些错误,请编写适当的代码,以确保您的应用程序可以正确处理这些错误。
需要注意的是,蓝牙开发需要特别注意电量和性能问题,对于频繁的蓝牙搜索、连接和数据传输等操作,应尽量减少或优化,避免对设备电量和性能造成过大的影响。