Codeforces Round 892 (Div. 2) 题解
A. United We Stand
Given an array a of length n, containing integers. And there are two initially empty arrays b and c. You need to add each element of array a to exactly one of the arrays b or c, in order to satisfy the following conditions:
- Both arrays b and c are non-empty. More formally, let lb be the length of array b, and lc be the length of array c. Then lb,lc≥1
- For any two indices i and j (1≤i≤lb,1≤j≤lc), cj is not a divisor of bi
Output the arrays b and c that can be obtained, or output −1−1 if they do not exist.
Input
Each test consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤500) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (2≤n≤100) — the length of array a.
The second line of each test case contains n integers a1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤109) — the elements of array a.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer −1−1 if a solution does not exist.
Otherwise, in the first line, output two integers lb and lc — the lengths of arrays b and c respectively.
In the second line, output lb integers b1,b2,…,bl — the elements of array b
In the third line, output lc integers c1,c2,…,cl — the elements of array c.
If there are multiple solutions, output any of them. You can output the elements of the arrays in any order.
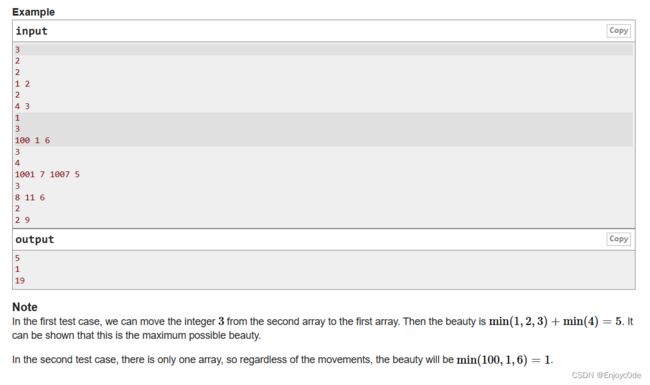
Example
input
Copy
5
3
2 2 2
5
1 2 3 4 5
3
1 3 5
7
1 7 7 2 9 1 4
5
4 8 12 12 4
output
Copy
-1 3 2 1 3 5 2 4 1 2 1 3 5 2 5 1 1 2 4 7 7 9 3 2 4 8 4 12 12
Note
In the first test case, a solution does not exist.
In the second test case, we can obtain b=[1,3,5]] and c=[2,4 Then elements 22 and 44 do not divide elements 1,31,3 and 55.
In the fifth test case, we can obtain b=[4,8,4]and c=[12,12]
题目分析:
给你一个数组是否能分成两个数组b 和 c, 其中c中的任一数都不是b中任一数的除数
解决方案就是让c当中的每一个数都比b中的每一个数大就行
代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N =10000;
const int INF =1e9+7;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int t;cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n;cin>>n;
int cnt=1;
int mins=INF;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
mins=min(mins,a[i]);
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
if(mins==a[n])
{
cout<<"-1"<=1;i--)
{
if(a[i]==a[n])
{
cnt++;
}
else break;
}
cout< B. Olya and Game with Arrays
 题目分析:
题目分析:
题目大意为给你几个数组,数组可以无限的接受外来的整数,但是只能送出1次整数,最终按照公式求出尽可能大的值。
既然每个数组只能送出一个整数,那么这个数组最大的值就是倒数第二小的数。
按照每个数组倒数第二小的数进行排序,找到倒数第二个数最小的那个数组用来接受其他数组的最小值,这样可以保证获得最大值。
代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N =50005;
long long a[N];
long long mins[N],mas[N];
int main()
{
int t;cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int m;cin>>m;
int o=1;
long long sum=0;
long long tmp=m;
while(tmp--)
{
int n;cin>>n;
for(long long i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
mins[o]=a[1];
mas[o]=a[2];
sum+=mas[o];
o++;
}
sort(mins+1,mins+1+m);
sort(mas+1,mas+1+m);
sum+=mins[1];
sum-=mas[1];
cout< C. Another Permutation Problem
 题目分析:
题目分析:
n大小的数组当中就是1~n的所有数组,可以交换数字的位置以来尽可能的求出公式的最大值
可以从后往前,数字依次倒序,取最大值即可
代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=300;
typedef long long ll;
ll mul[N];
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);
for(int i=1;i<=255;i++)mul[i]=mul[i-1]+i*i;
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;cin>>n;
ll pre=mul[n-1];
ll ans=0;
for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--){
ll mas=0;
ans=mul[i-1];
ll tmp=n;
for(int j=i;j<=n;j++){
ll a=j*tmp;
mas=max(mas,a);
ans+=a;
tmp--;
}
ans-=mas;
pre=max(ans,pre);
}
cout<