vue3学习源码笔记(小白入门系列)------ 组件是如何渲染成dom挂载到指定位置的?
文章目录
-
- os
- 准备
-
- 组件如何被挂载到页面上
-
- 第一步 createApp 做了哪些工作?
-
- ensureRenderer
- baseCreateRenderer
- createAppAPI
- mount
- render
- patch
- processComponent
- processElement
- 总结
os
学习一下vue3 源码,顺便记录分享下
使用vitest 插件调试源码 辅助阅读
准备
去 github 下载 vue3源码 最新仓库名 为 core-main 使用 版本 为3.3.4
安装好依赖
npm i pnpm -g
pnpm install
1 跳到下一个方法体
2 逐步执行
3 回退到上一步
4 重新执行
最后一个按钮就是 结束执行
组件如何被挂载到页面上
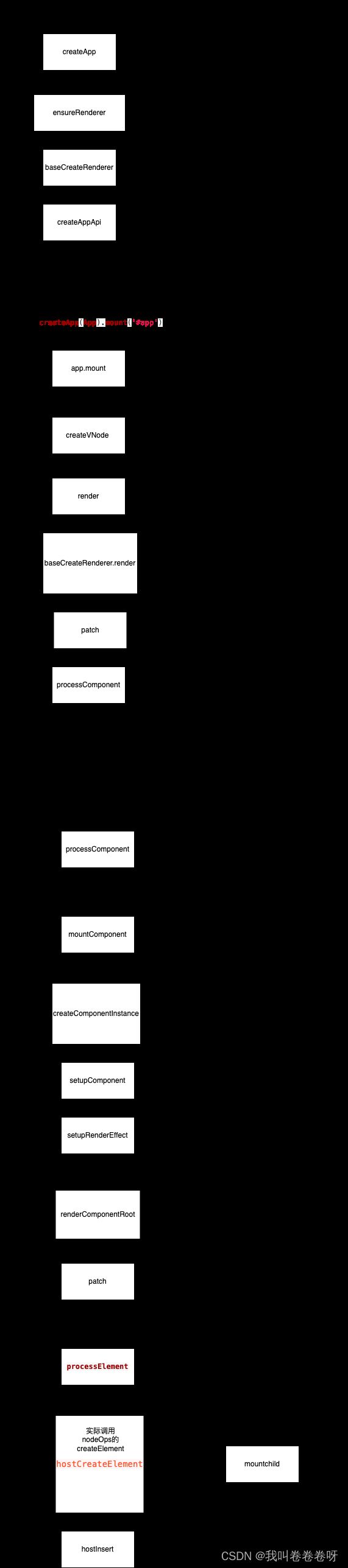
createApp(App).mount('#app')
第一步 createApp 做了哪些工作?
先看下入参和出参
export type CreateAppFunction<HostElement> = (
rootComponent: Component,
rootProps?: Data | null
) => App<HostElement>
入参: rootComponent 需要渲染的组件 App 也就是我们编写的 App.vue 文件
rootProps 传入根实例 的 props 最后会被 挂在 app _props 上
出参 : 返回app 实例对象
// packages/runtime-dom/src/index.ts
export const createApp = ((...args) => {
// 调用 ensureRender 生成render 对象
const render = ensureRenderer()
// 再调用 render中 createApp 方法 来生成 app实例
const app = render.createApp(...args)
···· 下面先省略
return app
})
ensureRenderer
// packages/runtime-dom/src/renderer.ts
// 实际调用的是 createRenderer
function ensureRenderer() {
/*
大致意思是 判断renderer实例是否存在,有就直接返回
没有执行 createRender 方法并 赋值 renderer 再返回
这里返回的 renderer 对象,可以认为是一个跨平台的渲染器对象,
针对不同的平台,会创建出不同的 renderer 对象,
上述是创建浏览器环境的 renderer 对象,对于服务端渲染的场景,
则会创建 server render 的 renderer
*/
return (
renderer ||
(renderer = createRenderer<Node, Element | ShadowRoot>(rendererOptions))
)
}
// 实际调用 baseCreateRenderer
function createRenderer<
HostNode = RendererNode,
HostElement = RendererElement
>(options: RendererOptions<HostNode, HostElement>) {
return baseCreateRenderer<HostNode, HostElement>(options)
}
baseCreateRenderer
有两种模式 hydration 模式是 服务端渲染的 我们只考虑 no-hydration 浏览器渲染
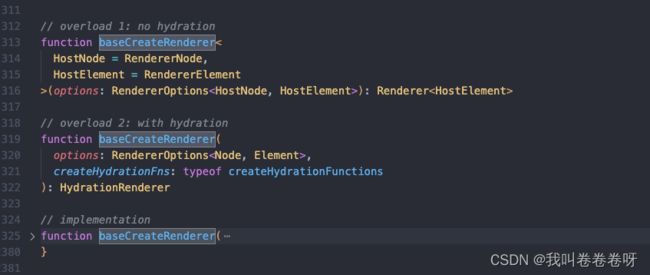
no-hydration 下
入参: options 初始化 渲染的参数 options 上挂载了 大量的操作dom 的操作 给 render 内部闭包使用
出参 :render
export interface Renderer<HostElement = RendererElement> {
render: RootRenderFunction<HostElement>
createApp: CreateAppFunction<HostElement>
}
具体伪代码 实现
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
export function createRenderer(options) {
// ...
// 这里不介绍 hydrate 模式
return {
render,
hydrate, // no-hydration 为空
createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate),
}
}
createAppAPI
// packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts
function createAppAPI(render, hydrate) {
// createApp createApp 方法接收的两个参数:根组件的对象和 prop
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
// 。。。 省略
const app = {
// ... 省略很多不需要在这里介绍的属性
_component: rootComponent,
_props: rootProps,
mount(rootContainer, isHydrate, isSVG) {
// ...
}
}
return app
}
}
Vue 3 初始化根组件的核心方法,也就是入口文件 createApp 真正执行的内容就是这里的 createAppAPI 函数中的 createApp 函数,该函数接收了 组件作为根组件 rootComponent,返回了一个包含 mount 方法的 app 对象,再看看 mount 具体实现
mount
// packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts
mount(rootContainer, isHydrate, isSVG) {
if (!isMounted) {
// ... 省略部分不重要的代码
// 1. 创建根组件的 vnode
const vnode = createVNode(
rootComponent,
rootProps
)
// 2. 渲染根组件 这里render方法 其实是baseCreateRenderer
// 返回的render对象带的 render方法
// 作用就是 将 vnode 渲染成真实dom
render(vnode, rootContainer, isSVG)
isMounted = true
}
}
render
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const render: RootRenderFunction = (vnode, container, isSVG) => {
// console.log('render-----');
//第一个 入参 没传 代表 需要卸载
if (vnode == null) {
if (container._vnode) {
unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true)
}
} else {
// 否则走 挂载 或更新 操作
patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container, null, null, null, isSVG)
}
flushPreFlushCbs()
flushPostFlushCbs()
container._vnode = vnode
}
// patch 所有vnode diff 比对 更新 转化新dom 操作全在里面
patch
const patch: PatchFn = (
n1, // 需要 对比的 旧 vnode
n2, // 新生成的 vnode
container, // 最后生成的元素 需要挂载到的 目标组件元素
anchor = null, // 挂载的参考元素;
parentComponent = null, // 父组件
parentSuspense = null,
isSVG = false,
slotScopeIds = null,
optimized = __DEV__ && isHmrUpdating ? false : !!n2.dynamicChildren
) => {
//n1 n2 完全一致 就 直接返回 不做更新 或 挂载
if (n1 === n2) {
return
}
// patching & not same type, unmount old tree 新旧 vnode 类型 不一样 直接 卸载 n1
if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
anchor = getNextHostNode(n1)
unmount(n1, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
n1 = null
}
if (n2.patchFlag === PatchFlags.BAIL) {
optimized = false
n2.dynamicChildren = null
}
// shapeFlag 判断vnode 实例是什么类型 有的是元素类型 函数类型 组件类型等
const { type, ref, shapeFlag } = n2
switch (type) {
//文本节点
case Text:
processText(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
// 注释节点
case Comment:
processCommentNode(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Static:
if (n1 == null) {
mountStaticNode(n2, container, anchor, isSVG)
} else if (__DEV__) {
patchStaticNode(n1, n2, container, isSVG)
}
break
case Fragment:
// 处理 template 的虚拟标签
processFragment(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
break
default:
// 其它类型
//ShapeFlags 是一个二进制左移操作符生成的对象
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
// 这里走的是 组件内部元素普通dom的比对更新挂载逻辑
processElement(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
// 这里是 组件对比 component 逻辑
processComponent(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} 。。。 // 其它省略
// set ref
if (ref != null && parentComponent) {
/*
通过 ref 参数获取组件的引用对象。
通过 n1 参数获取前一个 VNode 的引用对象(如果存在)。
通过 n2 参数获取当前 VNode 的引用对象(如果存在)。
如果前一个 VNode 的引用对象存在(即 n1.ref 存在),则将其置为 null,解除对前 一个组件引用的绑定。
如果当前 VNode 的引用对象存在(即 n2.ref 存在),则将其绑定到组件的引用上。
如果当前 VNode 不存在(即 !n2),则将组件的引用对象置为 null
*/
setRef(ref, n1 && n1.ref, parentSuspense, n2 || n1, !n2)
}
}
初始化挂载 会进入到 processComponent方法
processComponent
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
function processComponent(n1, n2, container, parentComponent) {
// 如果 n1 没有值的话,那么就是 mount
if (!n1) {
// 初始化 component
mountComponent(n2, container, parentComponent);
} else {
updateComponent(n1, n2, container);
}
}
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
function mountComponent(initialVNode, container, parentComponent) {
// 1. 先创建一个 component instance
const instance = (initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent
));
// 2. 初始化 instance 上的 props, slots, 执行组件的 setup 函数...
setupComponent(instance);
// 3. 设置并运行带副作用的渲染函数
setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container);
}
// packages/runtime-core/src/component.ts
function createComponentInstance(
vnode: VNode,
parent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
suspense: SuspenseBoundary | null
) {
const type = vnode.type as ConcreteComponent
// inherit parent app context - or - if root, adopt from root vnode
const appContext =
(parent ? parent.appContext : vnode.appContext) || emptyAppContext
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance = {
uid: uid++,
vnode,
type,
parent,
appContext,
root: null!, // to be immediately set
next: null,
subTree: null!, // will be set synchronously right after creation
effect: null!,
update: null!, // will be set synchronously right after creation
scope: new EffectScope(true /* detached */),
render: null,
proxy: null,
//。。。 省略 属性
}
if (__DEV__) {
instance.ctx = createDevRenderContext(instance)
} else {
instance.ctx = { _: instance }
}
instance.root = parent ? parent.root : instance
instance.emit = emit.bind(null, instance)
// apply custom element special handling
if (vnode.ce) {
vnode.ce(instance)
}
return instance
}
// packages/runtime-core/src/component.ts
export function setupComponent(instance) {
// 1. 处理 props
// 取出存在 vnode 里面的 props
const { props, children } = instance.vnode;
initProps(instance, props);
// 2. 处理 slots
initSlots(instance, children);
// 3. 调用 setup 并处理 setupResult
setupStatefulComponent(instance);
}
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
/*
componentUpdateFn 这个函数,
核心是调用了 renderComponentRoot 来生成 subTree,
然后再把 subTree 挂载到 container 中
*/
const setupRenderEffect = (instance, initialVNode, container, anchor, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
function componentUpdateFn() {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
// 渲染子树的 vnode
const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))
// 挂载子树 vnode 到 container 中
// 会重新进入 patch 方法 会走到 processElement 方法中
patch(null, subTree, container, anchor, instance, parentSuspense, isSVG)
// 把渲染生成的子树根 DOM 节点存储到 el 属性上
initialVNode.el = subTree.el
instance.isMounted = true
}
else {
// 更新相关,后面介绍
}
}
// 创建副作用渲染函数
instance.update = effect(componentUpdateFn, prodEffectOptions)
}
/*
返回 vnode
*/
function renderComponentRoot(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance
): VNode {
const {
type: Component,
vnode,
proxy,
withProxy,
props,
propsOptions: [propsOptions],
slots,
attrs,
emit,
render,
renderCache,
data,
setupState,
ctx,
inheritAttrs
} = instance
const proxyToUse = withProxy || proxy
// 省略一部分逻辑判断 normalizeVNode
/*
render 方法 其实是调用instance.render 方法
就是在 初始化instance 方法 中 将 template 模版
编译成 render 方法 用于 生成 vnode
*/
result = normalizeVNode(
render!.call(
proxyToUse,
proxyToUse!,
renderCache,
props,
setupState,
data,
ctx
)
)
return result
}
processElement
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
function processElement(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent) {
if (!n1) {
// 挂载元素节点
mountElement(n2, container, anchor);
} else {
// 更新元素节点
updateElement(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent);
}
}
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const mountElement = (vnode, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
let el
const { type, props, shapeFlag, transition, patchFlag, dirs } = vnode
// ...
// 根据 vnode 创建 DOM 节点
el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(vnode.type, isSVG, props && props.is)
if (props) {
// 处理 props 属性
for (const key in props) {
if (!isReservedProp(key)) {
hostPatchProp(el, key, null, props[key], isSVG)
}
}
}
// 文本节点处理
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
hostSetElementText(el, vnode.children)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
// 如果节点是个数据类型,则递归子节点
mountChildren(vnode.children, el)
}
// 把创建好的 el 元素挂载到容器中
hostInsert(el, container, anchor)
}
总结
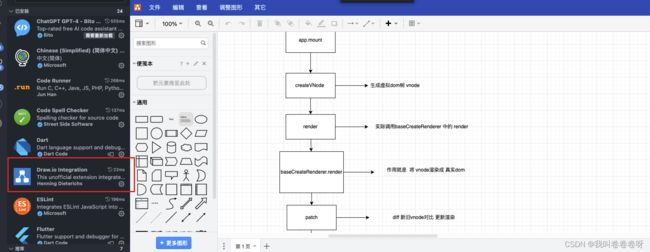
以上就完成了 组件初始化工作。下面画了 几个流程图来辅助理解 。最好阅读的时候自己 也可以画下
下一篇:准备写 数据代理这块