12_View的绘制流程
12_View的绘制流程
一.View是如何被添加到屏幕窗口上的
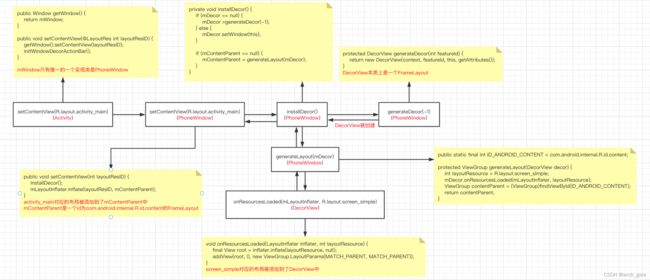
当在Activity的onCreate方法中调用setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)时,会调用Activity的setContentView方法,在Activity的setContentView方法中会调用PhoneWindow的setContentView方法,在PhoneWindow的setContentView方法中会调用installDecor方法,installDecor方法会创建一个DecorView,DecorView本质上是一个FrameLayout,并将screen_simple对应的布局加载到DecorView中,最后在PhoneWindow的setContentView方法中,会将activity_main对应的布局加载到id为com.android.internal.R.id.content的FrameLayout中。
二.View的绘制流程
View的绘制首先是从顶层容器DecorView开始的,绘制的入口为ActivityThread的handleResumeActivity方法。
在ActivityThread的handleResumeActivity方法中,会获取到一个WindowManagerImpl,然后调用WindowManagerImpl的addView方法。
而在WindowManagerImpl的addView方法中,会调用WindowManagerGlobal的addView,在WindowManagerGlobal的addView方法中,会创建一个ViewRootImpl对象,然后通过调用ViewRootImpl的setView方法,顶层容器DecorView与Window对象实现了关联,也就是说DecorView被添加到了Window中,在ViewRootImpl的setView方法中,紧接着会调用ViewRootImpl的requestLayout方法,然后调用ViewRootImpl的scheduleTraversals、doTraversal、performTraversals方法。
在ViewRootImpl的performTraversals方法中,会根据window的宽高以及window的LayoutParams确定DecorView的MeasureSpec,然后调用ViewRootImpl的performMeasure方法。
在ViewRootImpl的performMeasure方法中,会调用顶层容器DecorView的measure方法,此时DecorView的测量流程开始。
当ViewRootImpl的performLayout方法被调用时,会调用顶层容器DecorView的layout方法,此时DecorView的摆放流程开始。
当ViewRootImpl的performDraw方法被调用时,会调用顶层容器DecorView的draw方法,此时DecorView的绘制流程开始。
三.measure过程
-
DecorView的measure过程
因为measure方法是一个final类型的,并且在View中实现的,DecorView作为View的子类是不能重写measure方法的,所以调用DecorView的measure方法就是调用View的measure。
在View的measure方法中,会调用onMeasure方法,而DecorView重写了onMeasure,所以此时在View中调用onMeasure实际上调用的是DecorView的onMeasure方法。
在DecorView的onMeasure方法中,最终会通过super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)调用父类的onMeasure方法,而DecorView是继承自FrameLayout的,所以FrameLayout的onMeasure会被调用。
在FrameLayout的onMeasure方法中,会遍历每一个子View,通过调用measureChildWithMargins对子View进行测量。
在measureChildWithMargins方法中,会根据当前容器的MeasureSpec,以及当前容器的剩余空间,并结合子View的LayoutParams确定子View的MeasureSpec,最后通过调用子View的measure方法对子View进行测量。确定子View的MeasureSpec规则如下:
FrameLayout会根据子View的测量结果确定自身的宽高,并调用setMeasuredDimension方法保存自身的宽高。
最后FrameLayout会根据自身的测量结果判断,是否需要对子View重新测量,修正子View的测量结果。例如FrameLayout的widthMeasureSpec的mode不等于EXACTLY时,会重新测量LayoutParams的宽或高为match_parent的子View。
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
-
View的measure过程
从上面可以知道,DecorView或者其他容器组件在执行onMeasured的时候,会遍历所有子View,针对每一个子View去调用measureChildWithMargins,在measureChildWithMargins方法中,会根据当前容器的MeasureSpec,以及当前容器的剩余空间,并结合子View的LayoutParams确定子View的MeasureSpec,最后通过调用子View的measure方法,如果此时的子View是一个View,那么View的测量流程开始。
View的measure过程同样会执行onMeasure,与DecorView或者其他容器组件不同的是,在View的onMeasure方法中只需要根据父View传递下来的MeasureSpec参数以及自身的LayoutParams参数确定自身的宽高,并最终调用setMeasuredDimension方法保存自身的宽高即可。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
查看View的onMeasure源码,可以知道,如果我们在自定义View的时候,不重写onMeasure,那么,一般情况下,无论View的LayoutParams是wrap_content还是match_parent,View最终的测量结果都是父容器的可用空间的宽高。
四.layout过程
- DecorView的layout过程
在ViewRootImpl的performLayout方法中,当顶层容器DecorView的measur过程完成后,会根据DecorView的测量的宽高确定左、上、右、下的位置参数,然后调用DecorView的layout方法,而layout方法是一个final类型的,并且在View中实现的,DecorView作为View的子类是不能重写layout方法的,所以调用DecorView的layout方法就是调用View的layout。
在View的layout方法中,会将其左、上、右、下的值作为参数,调用它的onLayout方法,而DecorView重写了onLayout方法,所以DecorView的onLayout方法会被调用。
在DecorView的onLayout方法中,会通过super.onLayout调用父类的onLayout方法,而DecorView是继承自FrameLayout的,所以FrameLayout的onLayout方法会被调用。
在FrameLayout的onLayout方法中,会调用layoutChildren。
在FrameLayout的layoutChildren方法中,会遍历每一个子View,并根据自身的左、上、右、下的值以及子View的测量结果,确定子View的左、上、右、下的值,然后调用子View的layout方法
五.draw过程
ViewRootImpl的performLayout方法执行完之后,会调用performDraw,然后调用DecorView的draw方法,即调用View的draw方法。
在View的draw方法中,首先会依次调用drawBackground、onDraw、dispatchDraw、onDrawForeground方法,绘制背景、绘制自己、绘制子View、绘制前景。
六.总结
-
顶层容器DecorView的MeasureSpec,由window的LayoutParams以及window的宽高即屏幕可用空间的宽高共同决定
WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT: specSize为window的宽高,specMode为EXACTLY
WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT: specSize为window的宽高,specMode为AT_MOST
精确值(px/dp):specSize为开发者通过LayoutParams指定的值,specMode为EXACTLY
-
View的绘制流程的三大步measure、layout、draw会从顶层容器DecorView开始,根据View的嵌套层级一级一级的往下递归调用
-
我们在自定义View的时候,如果是自定义ViewGroup,需要重写onMeasure,在onMeasure中,需要遍历并测量子View,并根据子View的测量结果,计算自身的宽高,然后调用setMeasuredDimension保存自身的宽高,最后结合自身的测量结果、MeasureSpec以及子View的LayoutParams判断,是否需要对子View重新测量;如果是自定义View,则只需要在onMeasure方法中根据MeasureSpec以及自身的LayoutParams计算出自己的宽高,然后调用setMeasuredDimension保存测量结果即可
-
我们在自定义View的时候,如果是自定义ViewGroup,需要重写onLayout方法,在onLayout中,根据自身的左、上、右、下的值计算子View的左、上、右、下的值,然后调用子View的layout方法摆放子View。如果是自定义View,一般情况下,是不需要重写onLayout方法的。